
Silicon nanotubes
Encyclopedia
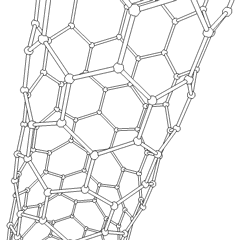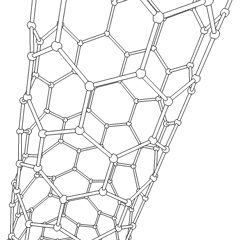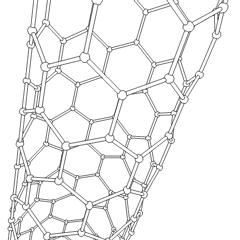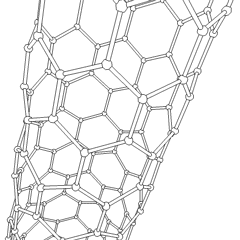
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
atoms. The nanotubes' discovery has many significant implications for electronics development, as silicon is already a vastly important material in the semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
industry. Only recently has it been possible to prepare these nanotubes which are similar to carbon nanotubes. Nano-materials are complex, and understanding how the behaviour of silicon materials differs from their carbon-based cousins is still under research.
Synthesis
The nanotubes are created using a reactor employing an electric arcElectric arc
An electric arc is an electrical breakdown of a gas which produces an ongoing plasma discharge, resulting from a current flowing through normally nonconductive media such as air. A synonym is arc discharge. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge, and relies on...
without the use of any catalyst. To ensure purity, the reactor was evacuated and filled with the nonreactive noble gas
Noble gas
The noble gases are a group of chemical elements with very similar properties: under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases, with very low chemical reactivity...
argon
Argon
Argon is a chemical element represented by the symbol Ar. Argon has atomic number 18 and is the third element in group 18 of the periodic table . Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.93%, making it more common than carbon dioxide...
. The actual formation of the nanotubes relies on the process of chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition is a chemical process used to produce high-purity, high-performance solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films. In a typical CVD process, the wafer is exposed to one or more volatile precursors, which react and/or...
.
Applications
While silicon nanotubes are still in the early stages of their development, scientists and engineers have already begun to consider the possible uses for the new material.Silicon nanotubes have been considered for use in electronics, because it appears that silicon nano-materials may behave like a metal fuel, since the structure can accommodate molecules of hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
so it might resemble coal without the CO2
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
. A silicon nanotube charged with hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
delivers energy and in the process leaves residual water, ethanol, silicon and sand. However, as hydrogen production
Hydrogen production
Hydrogen production is the family of industrial methods for generating hydrogen. Currently the dominant technology for direct production is steam reforming from hydrocarbons. Many other methods are known including electrolysis and thermolysis...
requires considerable energy, this is only a proposed method of storing energy, not producing it.
Lithium Ion Batteries
The most profound application of silicon nanotubes has been their possible use in lithium-ion batteries. Conventional Li-Ion batteries use graphitic carbon as the anode, but replacing this with silicon nanotubes experimentally increases the specific (by mass) anode capacity by a factor of 10 (but the battery capacity improvement is less due to far lower specific cathode capacities).Researchers from LG Chem (the makers of the battery in the Chevrolet Volt
Chevrolet Volt
The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle manufactured by General Motors. The Volt has been on sale in the U.S. market since mid-December 2010, and is the most fuel-efficient compact car sold in the United States, as rated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency...
), Stanford University
Stanford University
The Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University or Stanford, is a private research university on an campus located near Palo Alto, California. It is situated in the northwestern Santa Clara Valley on the San Francisco Peninsula, approximately northwest of San...
and Hanyang University have been researching ways in which this technology could improve electric car
Electric car
An electric car is an automobile which is propelled by electric motor, using electrical energy stored in batteries or another energy storage device. Electric cars were popular in the late-19th century and early 20th century, until advances in internal combustion engine technology and mass...
s by making the battery smaller. However, the costs currently associated with the nanotubes is high and therefore the research is currently theoretical - any employment of the silicon nanotubes will have to wait until the technology becomes cost effective.

