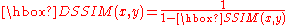SSIM
Encyclopedia
- SSIM redirects here. For the South Sudan Independence Movement, see South Sudan Liberation MovementSouth Sudan Liberation MovementThe South Sudan Liberation Movement is an armed group that operates in the Upper Nile Region in southern Sudan. The group's creation was announced in November 1999 by people of the Nuer ethnicity who were in both the rebel Sudan People's Liberation Army and the government-allied South Sudan...
.
The structural similarity (SSIM) index is a method for measuring the similarity between two images. The SSIM index is a full reference metric, in other words, the measuring of image quality based on an initial uncompressed or distortion-free image as reference. SSIM is designed to improve on traditional methods like peak signal-to-noise ratio
Peak signal-to-noise ratio
The phrase peak signal-to-noise ratio, often abbreviated PSNR, is an engineering term for the ratio between the maximum possible power of a signal and the power of corrupting noise that affects the fidelity of its representation...
(PSNR) and mean squared error
Mean squared error
In statistics, the mean squared error of an estimator is one of many ways to quantify the difference between values implied by a kernel density estimator and the true values of the quantity being estimated. MSE is a risk function, corresponding to the expected value of the squared error loss or...
(MSE), which have proved to be inconsistent with human eye perception.
The SSIM metric is calculated on various windows of an image. The measure between two windows
 and
and 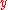 of common size N×N is:
of common size N×N is: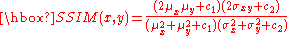
with
-
 the averageAverageIn mathematics, an average, or central tendency of a data set is a measure of the "middle" value of the data set. Average is one form of central tendency. Not all central tendencies should be considered definitions of average....
the averageAverageIn mathematics, an average, or central tendency of a data set is a measure of the "middle" value of the data set. Average is one form of central tendency. Not all central tendencies should be considered definitions of average....
of ;
; -
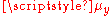 the averageAverageIn mathematics, an average, or central tendency of a data set is a measure of the "middle" value of the data set. Average is one form of central tendency. Not all central tendencies should be considered definitions of average....
the averageAverageIn mathematics, an average, or central tendency of a data set is a measure of the "middle" value of the data set. Average is one form of central tendency. Not all central tendencies should be considered definitions of average....
of ;
; -
 the varianceVarianceIn probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
the varianceVarianceIn probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
of ;
; -
 the varianceVarianceIn probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
the varianceVarianceIn probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
of ;
; -
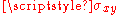 the covarianceCovarianceIn probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together. Variance is a special case of the covariance when the two variables are identical.- Definition :...
the covarianceCovarianceIn probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together. Variance is a special case of the covariance when the two variables are identical.- Definition :...
of and
and  ;
; -
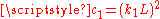 ,
, 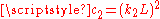 two variables to stabilize the division with weak denominator;
two variables to stabilize the division with weak denominator; -
 the dynamic rangeDynamic rangeDynamic range, abbreviated DR or DNR, is the ratio between the largest and smallest possible values of a changeable quantity, such as in sound and light. It is measured as a ratio, or as a base-10 or base-2 logarithmic value.-Dynamic range and human perception:The human senses of sight and...
the dynamic rangeDynamic rangeDynamic range, abbreviated DR or DNR, is the ratio between the largest and smallest possible values of a changeable quantity, such as in sound and light. It is measured as a ratio, or as a base-10 or base-2 logarithmic value.-Dynamic range and human perception:The human senses of sight and...
of the pixel-values (typically this is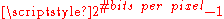 );
); -
 and
and  by default.
by default.
In order to evaluate the image quality this formula is applied only on luma
Luma (video)
In video, luma, sometimes called luminance, represents the brightness in an image . Luma is typically paired with chrominance. Luma represents the achromatic image without any color, while the chroma components represent the color information...
. The resultant SSIM index is a decimal value between -1 and 1, and value 1 is only reachable in the case of two identical sets of data. Typically it is calculated on window sizes of 8×8. The window can be displaced pixel-by-pixel on the image but the authors propose to use only a subgroup of the possible windows to reduce the complexity of the calculation.
Structural dissimilarity (DSSIM) is a distance metric derived from SSIM.