
SINAD
Encyclopedia
SINAD stands for Signal-to-noise and distortion ratio. It is a measure of the quality of a signal from a communications device, often defined as: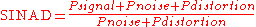
where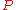 is the average power of the signal, noise
is the average power of the signal, noise
and distortion
components. SINAD is usually expressed in dB
and is quoted alongside the receiver RF sensitivity
, to give a quantitative evaluation of the receiver sensitivity. Note that with this definition, unlike SNR
, a SINAD reading can never be less than 1 (i.e. it is always positive when quoted in dB).
When calculating the distortion, it is common to exclude the DC
components.
Due to widespread use, SINAD has collected a few different definitions. SINAD is calculated as one of:
Regardless of the exact definition, it is always true that a lower SINAD value means worse performance of the system.
In a real world example as the received RF
signal becomes weaker it becomes progressively lost in the noise and distortion generated by receiver, demodulation and audio output drive circuits.
Convention is that in a narrow band FM
voice radio system a Signal, Noise and Distortion level of 12dB SINAD is the maximum acceptable level of noise that will not swamp intelligible speech.
A typical example quoted from a commercial hand held VHF or UHF radio;
The example above is stating that the receiver will produce intelligible speech with a signal at its input as low as 0.25μV. This value is typical for VHF commercial radio and 0.35μV is probably more typical for UHF. In the real world lower SINAD values (more noise) can still result in intelligible speech but it is tiresome work to listen to a voice in that much noise.
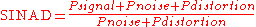
where
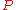 is the average power of the signal, noise
is the average power of the signal, noiseNoise
In common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
and distortion
Distortion
A distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
components. SINAD is usually expressed in dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
and is quoted alongside the receiver RF sensitivity
Sensitivity (electronics)
The sensitivity of an electronic device, such as a communications system receiver, or detection device, such as a PIN diode, is the minimum magnitude of input signal required to produce a specified output signal having a specified signal-to-noise ratio, or other specified criteria.Sensitivity is...
, to give a quantitative evaluation of the receiver sensitivity. Note that with this definition, unlike SNR
Signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
, a SINAD reading can never be less than 1 (i.e. it is always positive when quoted in dB).
When calculating the distortion, it is common to exclude the DC
DC bias
When describing a periodic function in the frequency domain, the DC bias, DC component, DC offset, or DC coefficient is the mean value of the waveform...
components.
Due to widespread use, SINAD has collected a few different definitions. SINAD is calculated as one of:
- The ratio of (a) total received powerPower (physics)In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
, i.e., the signal to (b) the noise-plus-distortion power. This is modeled by the equation above. - The ratio of (a) the power of original modulating audio signal, i.e., from a modulated radio frequencyRadio frequencyRadio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
carrierCarrier waveIn telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
to (b) the residual audio power, i.e., noise-plus-distortion powers remaining after the original modulating audio signal is removed. With this definition, it is now possible for SINAD to be less than 1. This definition is used when SINAD is used in the calculation of ENOBENOBEffective number of bits is a measure of the quality of a digitised signal. The resolution of a digital-to-analog or analog-to-digital converter is commonly specified by the number of bits used to represent the analog value, in principle giving 2N signal levels for an N-bit signal. However, all...
for an ADCAnalog-to-digital converterAn analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement...
.
Regardless of the exact definition, it is always true that a lower SINAD value means worse performance of the system.
In a real world example as the received RF
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
signal becomes weaker it becomes progressively lost in the noise and distortion generated by receiver, demodulation and audio output drive circuits.
Convention is that in a narrow band FM
Frequency modulation
In telecommunications and signal processing, frequency modulation conveys information over a carrier wave by varying its instantaneous frequency. This contrasts with amplitude modulation, in which the amplitude of the carrier is varied while its frequency remains constant...
voice radio system a Signal, Noise and Distortion level of 12dB SINAD is the maximum acceptable level of noise that will not swamp intelligible speech.
A typical example quoted from a commercial hand held VHF or UHF radio;
- Receiver sensitivity: 0.25μV at 12dB SINAD
The example above is stating that the receiver will produce intelligible speech with a signal at its input as low as 0.25μV. This value is typical for VHF commercial radio and 0.35μV is probably more typical for UHF. In the real world lower SINAD values (more noise) can still result in intelligible speech but it is tiresome work to listen to a voice in that much noise.

