
Rodrigues equation
Encyclopedia
The Rodrigues equation is an equation used in chromatography
to describe the efficiency of a bed of permeable (large-pore) particles. It is thus an extension of Van Deemter's equation
. It was developed by Alirio E. Rodrigues et al..
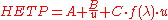
Where
Chromatography
Chromatography is the collective term for a set of laboratory techniques for the separation of mixtures....
to describe the efficiency of a bed of permeable (large-pore) particles. It is thus an extension of Van Deemter's equation
Van Deemter's equation
The Van Deemter equation in chromatography relates the variance per unit length of a separation column to the linear mobile phase velocity by considering physical, kinetic, and thermodynamic properties of a separation. These properties include pathways within the column, diffusion , and mass...
. It was developed by Alirio E. Rodrigues et al..
Equation
The equation is: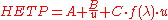
Where
- HETP is the height equivalent to a theoretical plateTheoretical plateA theoretical plate in many separation processes is a hypothetical zone or stage in which two phases, such as the liquid and vapor phases of a substance, establish an equilibrium with each other. Such equilibrium stages may also be referred to as an equilibrium stage, ideal stage or a theoretical...
- A = Eddy diffusionEddy diffusionEddy diffusion, eddy dispersion, or turbulent diffusion is any diffusion process by which substances are mixed in the atmosphere or in any fluid system due to eddy motion...
- B = Longitudinal diffusionDiffusionMolecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
- C = Resistance to mass transferMass transferMass transfer is the net movement of mass from one location, usually meaning a stream, phase, fraction or component, to another. Mass transfer occurs in many processes, such as absorption, evaporation, adsorption, drying, precipitation, membrane filtration, and distillation. Mass transfer is used...
- u = Flow rate
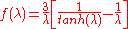
-
-
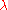 = Intraparticular Péclet numberPéclet numberThe Péclet number is a dimensionless number relevant in the study of transport phenomena in fluid flows. It is named after the French physicist Jean Claude Eugène Péclet. It is defined to be the ratio of the rate of advection of a physical quantity by the flow to the rate of diffusion of the same...
= Intraparticular Péclet numberPéclet numberThe Péclet number is a dimensionless number relevant in the study of transport phenomena in fluid flows. It is named after the French physicist Jean Claude Eugène Péclet. It is defined to be the ratio of the rate of advection of a physical quantity by the flow to the rate of diffusion of the same...

