
Péclet number
Encyclopedia
The Péclet number is a dimensionless number relevant in the study of transport phenomena in fluid flows. It is named after the French physicist Jean Claude Eugène Péclet
. It is defined to be the ratio of the rate of advection
of a physical quantity by the flow to the rate of diffusion
of the same quantity driven by an appropriate gradient. In the context of the transport of heat, the Peclet number is equivalent to the product of the Reynolds number and the Prandtl number. In the context of species or mass dispersion, the Peclet number is the product of the Reynolds number and the Schmidt number
.
For diffusion of heat (thermal diffusion), the Péclet number is defined as:
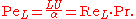
For diffusion of particles (mass diffusion), it is defined as:
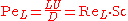
where L is the characteristic length, U the velocity
, D the mass diffusion coefficient, and α the thermal diffusivity
,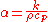
where k is the thermal conductivity
, ρ the density
, and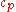 the heat capacity
the heat capacity
.
In engineering applications the Péclet number is often very large. In such situations, the dependency of the flow upon downstream locations is diminished, and variables in the flow tend to become 'one-way' properties. Thus, when modelling certain situations with high Péclet numbers, simpler computational models can be adopted.
A flow will often have different Péclet numbers for heat and mass. This can lead to the phenomenon of double diffusive convection
.
In the context of particulate motion the Péclet numbers have also been called Brenner numbers, with symbol Br, in honour of Howard Brenner.
Jean Claude Eugène Péclet
Jean Claude Eugène Péclet was a French physicist.He was born in Besançon, France.Péclet became, in 1812, one of the first students of the École Normale in Paris with Gay-Lussac and Dulong being his professors. In 1816, he was elected professor at the Collège de Marseille and taught physical...
. It is defined to be the ratio of the rate of advection
Advection
Advection, in chemistry, engineering and earth sciences, is a transport mechanism of a substance, or a conserved property, by a fluid, due to the fluid's bulk motion in a particular direction. An example of advection is the transport of pollutants or silt in a river. The motion of the water carries...
of a physical quantity by the flow to the rate of diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
of the same quantity driven by an appropriate gradient. In the context of the transport of heat, the Peclet number is equivalent to the product of the Reynolds number and the Prandtl number. In the context of species or mass dispersion, the Peclet number is the product of the Reynolds number and the Schmidt number
Schmidt number
Schmidt number is a dimensionless number defined as the ratio of momentum diffusivity and mass diffusivity, and is used to characterize fluid flows in which there are simultaneous momentum and mass diffusion convection processes...
.
For diffusion of heat (thermal diffusion), the Péclet number is defined as:
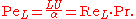
For diffusion of particles (mass diffusion), it is defined as:
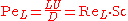
where L is the characteristic length, U the velocity
Velocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
, D the mass diffusion coefficient, and α the thermal diffusivity
Thermal diffusivity
In heat transfer analysis, thermal diffusivity is the thermal conductivity divided by density and specific heat capacity at constant pressure. It has the SI unit of m²/s...
,
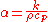
where k is the thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity
In physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
, ρ the density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
, and
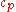 the heat capacity
the heat capacityHeat capacity
Heat capacity , or thermal capacity, is the measurable physical quantity that characterizes the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a given amount...
.
In engineering applications the Péclet number is often very large. In such situations, the dependency of the flow upon downstream locations is diminished, and variables in the flow tend to become 'one-way' properties. Thus, when modelling certain situations with high Péclet numbers, simpler computational models can be adopted.
A flow will often have different Péclet numbers for heat and mass. This can lead to the phenomenon of double diffusive convection
Double diffusive convection
Double-diffusive convection is an important fluid dynamics topic that describes a form of convection driven by two different density gradients which have different rates of diffusion.Convection in fluids is driven by density variation within them...
.
In the context of particulate motion the Péclet numbers have also been called Brenner numbers, with symbol Br, in honour of Howard Brenner.

