
Rhomboid major muscle
Encyclopedia
The rhomboid major is a skeletal muscle
on the back that connects the scapula
with the vertebrae of the spinal column. In human anatomy, it acts together with the rhomboid minor
to keep the scapula pressed against thoracic wall and to retract the scapula toward the vertebral column.
T2 to T5 as well as the supraspinous ligament
. It inserts on the medial border of the scapula, from about the level of the scapular spine to the scapula's inferior angle.
The rhomboid major is considered a superficial back muscle. It is deep to the trapezius, and is located directly inferior to the rhomboid minor. As the word rhomboid suggests, the rhomboid major is diamond-shaped. The major in its name indicates that it is the larger of the two rhomboids.
The rhomboids also acts to retract the scapula, pulling it towards the vertebral column
.
The rhomboids work collectively with the levator scapulae muscle
s to elevate the medial border of the scapula, downwardly rotating the scapula with respect to the glenohumeral joint. Antagonists to this function (upward rotators of the scapulae) are the serratus anterior and upper and lower fibers of the trapezius. If the lower fibers are inactive, the serratus and upper traps work in tandem with rhomboids and levators to elevate the entire scapula.
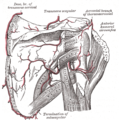 The rhomboid major, like the rhomboid minor, is innervated by the ventral primary ramus via the dorsal scapular nerve
The rhomboid major, like the rhomboid minor, is innervated by the ventral primary ramus via the dorsal scapular nerve
(C5).
Both rhomboid muscles also derive their arterial blood supply from the dorsal scapular artery
.
Treatment for scapular instability may include surgery followed by physical therapy
. Physical therapy may consist of stretching and endurance exercises of the shoulder. Pilates
and yoga
have been also suggested as potential treatment and prevention of scapular instability.
Skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle is a form of striated muscle tissue existing under control of the somatic nervous system- i.e. it is voluntarily controlled. It is one of three major muscle types, the others being cardiac and smooth muscle...
on the back that connects the scapula
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula , omo, or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle ....
with the vertebrae of the spinal column. In human anatomy, it acts together with the rhomboid minor
Rhomboid minor muscle
In human anatomy, the rhomboid minor is a small skeletal muscle on the back that connects the scapula with the vertebrae of the spinal column....
to keep the scapula pressed against thoracic wall and to retract the scapula toward the vertebral column.
Structure
The rhomboid major arises from the spinous processes of the thoracic vertebraeThoracic vertebrae
In human anatomy, twelve thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. They are intermediate in size between those of the cervical and lumbar regions; they increase in size as one proceeds down the spine, the upper...
T2 to T5 as well as the supraspinous ligament
Supraspinous ligament
The supraspinal ligament is a strong fibrous cord, which connects together the apices of the spinous processes from the seventh cervical vertebra to the sacrum; at the points of attachment to the tips of the spinous processes fibrocartilage is developed in the ligament.It is thicker and broader in...
. It inserts on the medial border of the scapula, from about the level of the scapular spine to the scapula's inferior angle.
The rhomboid major is considered a superficial back muscle. It is deep to the trapezius, and is located directly inferior to the rhomboid minor. As the word rhomboid suggests, the rhomboid major is diamond-shaped. The major in its name indicates that it is the larger of the two rhomboids.
Actions
The rhomboid major helps to hold the scapula (and thus the upper limb) onto the ribcage. Other muscles that perform this function include the serratus anterior and pectoralis minor.The rhomboids also acts to retract the scapula, pulling it towards the vertebral column
Vertebral column
In human anatomy, the vertebral column is a column usually consisting of 24 articulating vertebrae, and 9 fused vertebrae in the sacrum and the coccyx. It is situated in the dorsal aspect of the torso, separated by intervertebral discs...
.
The rhomboids work collectively with the levator scapulae muscle
Levator scapulae muscle
In human anatomy, the levator scapulae is a skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. As the name suggests, its main function is to lift the scapula.-Origin and insertion:...
s to elevate the medial border of the scapula, downwardly rotating the scapula with respect to the glenohumeral joint. Antagonists to this function (upward rotators of the scapulae) are the serratus anterior and upper and lower fibers of the trapezius. If the lower fibers are inactive, the serratus and upper traps work in tandem with rhomboids and levators to elevate the entire scapula.
Innervation and blood supply

Dorsal scapular nerve
The dorsal scapular nerve arises from the brachial plexus, usually from the plexus root of C5.It provides motor innervation to the rhomboid muscles, which pull the scapula towards the spine and levator scapulae muscle, which elevates the scapula....
(C5).
Both rhomboid muscles also derive their arterial blood supply from the dorsal scapular artery
Dorsal scapular artery
The dorsal scapular artery is a blood vessel which supplies thelevator scapulae, rhomboids, and trapezius.-Origin:...
.
Pathology
If the rhomboideus major is torn, wasted, or unable to contract, scapular instability may result. The implications of scapular instability caused by the rhomboideus major include scapular winging during scapular protraction, excessive lateral rotation and depression of the scapula, as the antagonistic action of the rhomboideus major is absent. With scapular instability, movement in the upper extremity is limited as the scapula cannot guide the desired movement of the arm and shoulders. Pain, discomfort, and limited range of motion of the shoulder are possible implications scapular instability.Treatment for scapular instability may include surgery followed by physical therapy
Physical therapy
Physical therapy , often abbreviated PT, is a health care profession. Physical therapy is concerned with identifying and maximizing quality of life and movement potential within the spheres of promotion, prevention, diagnosis, treatment/intervention,and rehabilitation...
. Physical therapy may consist of stretching and endurance exercises of the shoulder. Pilates
Pilates
Pilates is a physical fitness system developed in the early 20th century by Joseph Pilates in Germany, the UK and the USA. As of 2005, there were 11 million people practicing the discipline regularly and 14,000 instructors in the United States....
and yoga
Yoga
Yoga is a physical, mental, and spiritual discipline, originating in ancient India. The goal of yoga, or of the person practicing yoga, is the attainment of a state of perfect spiritual insight and tranquility while meditating on Supersoul...
have been also suggested as potential treatment and prevention of scapular instability.

