Reverse semantic traceability
Encyclopedia
Reverse Semantic Traceability (RST) is a quality control
method for verification improvement that helps to insure high quality of artifact
s by backward translation at each stage of the software development process
.
team deals with customer’s requirements and expectations expressed in natural language. These customer requirements sometimes might be incomplete, vague or even contradictory to each other. The first step is specification and formalization of customer expectations, transition (“translation”) of them into a formal requirement document for the future system. Then requirements are translated into system architecture and step by step the project team generates megabyte
s of code written in a very formal programming language. There is always a threat of inserting mistakes, misinterpreting or losing something during the translation. Even a small defect in requirement or design
specifications can cause huge amounts of defects at the late stages of the project. Sometimes such misunderstandings can lead to project failure or complete customer dissatisfaction.
The highest usage scenarios of Reverse Semantic Traceability method can be:
and should be well justified (for example, for medical software where possible information loss is very critical).
It is a responsibility of company and Project manager
to decide what amount of project artifacts will be “reverse engineered
”. This amount depends on project specific details: trade-off
matrix, project and company quality assurance
policies
. Also it depends on importance of particular artifact for project success and level of quality control applied to this artifact.
Amount of RST sessions for project is defined at the project planning stage.
First of all project manager should create a list of all artifacts project team will have during the project. They could be presented as a tree with dependencies and relationships. Artifacts can be present in one occurrence (like Vision document
) or in several occurrences (like risks or bugs). This list can be changed later during the project but the idea behind the decisions about RST activities will be the same.
importance for project and level of quality control for each project artifact.
Importance of document is the degree of artifact impact to project success and quality of final product. It’s measured by the scale:
Level of quality control is a measure that defines amount of verification and validation activities applied to artifact, and probability of miscommunication during artifact creation.
Project manager defines what documents will be an input for RST session. For example, it can be not only an artifact to restore but some background project information. It is recommended to give to reverse engineers number of words in original text so that they have an idea about amount of text they should get as a result: it can be one sentence or several pages of text. Though, the restored text may not contain the same number of words as original text nevertheless the values should be comparable.
After that reverse engineers take the artifact and restore the original text from it. RST itself takes about 1 hour for one page text (750 words).
For assessment a group of experts is formed. Experts should be aware of project domain and be an experienced enough to assess quality level of compared artifacts. For example, business analysts will be experts for comparison of vision statement and restored vision statement from scenario.
RST assessment criteria:
Each of experts gives his assessment, and then the average value is calculated. Depending on this value Project Manager makes a decision should both artifacts be corrected or one of them or rework is not required.
If the average RST quality level is in range from 1 to 2 the quality of artifact is poor and it is recommended not only rework of validated artifact to eliminate defects but corrections of original artifact to clear misunderstandings. In this case one more RST session after rework of artifacts is required. For artifacts that have more than 2 but less than 3 corrections of validated artifact to fix defects and eliminate information loss is required, however review of original artifact to find out if there any vague piece of information that cause misunderstandings is recommended. No additional RST sessions is needed. If the average mark is more than 3 but less than 4 then corrections of validated artifact to remove defects and insignificant information loss is supposed. If the mark is greater than 4 it means that artifact is of good quality and no special corrections or rework is required.
Obviously the final decision about rework of artifacts is made by project manager and should be based on analysis of reasons of differences in texts.
Quality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
method for verification improvement that helps to insure high quality of artifact
Artifact (software development)
An artifact is one of many kinds of tangible by-product produced during the development of software. Some artifacts help describe the function, architecture, and design of software...
s by backward translation at each stage of the software development process
Software development process
A software development process, also known as a software development life cycle , is a structure imposed on the development of a software product. Similar terms include software life cycle and software process. It is often considered a subset of systems development life cycle...
.
Brief introduction
Each stage of development process can be treated as a series of “translations” from one language to another. At the very beginning a projectProject
A project in business and science is typically defined as a collaborative enterprise, frequently involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a particular aim. Projects can be further defined as temporary rather than permanent social systems that are constituted by teams...
team deals with customer’s requirements and expectations expressed in natural language. These customer requirements sometimes might be incomplete, vague or even contradictory to each other. The first step is specification and formalization of customer expectations, transition (“translation”) of them into a formal requirement document for the future system. Then requirements are translated into system architecture and step by step the project team generates megabyte
Megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage or transmission with two different values depending on context: bytes generally for computer memory; and one million bytes generally for computer storage. The IEEE Standards Board has decided that "Mega will mean 1 000...
s of code written in a very formal programming language. There is always a threat of inserting mistakes, misinterpreting or losing something during the translation. Even a small defect in requirement or design
Software design
Software design is a process of problem solving and planning for a software solution. After the purpose and specifications of software are determined, software developers will design or employ designers to develop a plan for a solution...
specifications can cause huge amounts of defects at the late stages of the project. Sometimes such misunderstandings can lead to project failure or complete customer dissatisfaction.
The highest usage scenarios of Reverse Semantic Traceability method can be:
- Validating UMLUnified Modeling LanguageUnified Modeling Language is a standardized general-purpose modeling language in the field of object-oriented software engineering. The standard is managed, and was created, by the Object Management Group...
models: quality engineerQuality controlQuality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
s restore a textual description of a domainProblem domainA problem domain is the area of expertise or application that needs to be examined to solve a problem. A problem domain is simply looking at only the topics you are interested in, and excluding everything else. For example, if you were developing a system trying to measure good practice in...
, original and restored descriptions are compared. - Validating model changes for a new requirement: given an original and changed versions of a model, quality engineers restore the textual description of the requirement, original and restored descriptions are compared.
- Validating a bug fix: given an original and modified Source codeSource codeIn computer science, source code is text written using the format and syntax of the programming language that it is being written in. Such a language is specially designed to facilitate the work of computer programmers, who specify the actions to be performed by a computer mostly by writing source...
, quality engineers restore a textual description of the bug that was fixed, original and restored descriptions are compared. - Integrating new software engineerSoftware engineerA software engineer is an engineer who applies the principles of software engineering to the design, development, testing, and evaluation of the software and systems that make computers or anything containing software, such as computer chips, work.- Overview :...
into a team: a new team member gets an assignment to do Reverse Semantic Traceability for the key artifacts from the current projects.
RST roles
Main roles involved in RST session are:- authors of project artifacts (both input and output),
- reverse engineers,
- expert group,
- project manager.
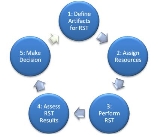
Define all project artifacts and their relationship
Reverse Semantic Traceability as a validation method can be applied to any project artifact, to any part of project artifact or even to a small piece of document or code. However, it is obvious that performing RST for all artifacts can create overheadOverhead (business)
In business, overhead or overhead expense refers to an ongoing expense of operating a business...
and should be well justified (for example, for medical software where possible information loss is very critical).
It is a responsibility of company and Project manager
Project manager
A project manager is a professional in the field of project management. Project managers can have the responsibility of the planning, execution, and closing of any project, typically relating to construction industry, architecture, computer networking, telecommunications or software...
to decide what amount of project artifacts will be “reverse engineered
Reverse engineering
Reverse engineering is the process of discovering the technological principles of a device, object, or system through analysis of its structure, function, and operation...
”. This amount depends on project specific details: trade-off
Trade-off
A trade-off is a situation that involves losing one quality or aspect of something in return for gaining another quality or aspect...
matrix, project and company quality assurance
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance, or QA for short, is the systematic monitoring and evaluation of the various aspects of a project, service or facility to maximize the probability that minimum standards of quality are being attained by the production process...
policies
Policy
A policy is typically described as a principle or rule to guide decisions and achieve rational outcome. The term is not normally used to denote what is actually done, this is normally referred to as either procedure or protocol...
. Also it depends on importance of particular artifact for project success and level of quality control applied to this artifact.
Amount of RST sessions for project is defined at the project planning stage.
First of all project manager should create a list of all artifacts project team will have during the project. They could be presented as a tree with dependencies and relationships. Artifacts can be present in one occurrence (like Vision document
Vision document
A Vision Document is a software process document that describes the overall 'vision', or plan, for a particular piece of software. It defines the stakeholders view of the product to be developed, specified in terms of the stakeholders key needs and features...
) or in several occurrences (like risks or bugs). This list can be changed later during the project but the idea behind the decisions about RST activities will be the same.
Prioritize
The second step is to analyze deliverableDeliverable
Deliverable is a term used in project management to describe a tangible or intangible object produced as a result of the project that is intended to be delivered to a customer . A deliverable could be a report, a document, a server upgrade or any other building block of an overall project.A...
importance for project and level of quality control for each project artifact.
Importance of document is the degree of artifact impact to project success and quality of final product. It’s measured by the scale:
- Crucial (1): the quality of deliverable is very important for overall quality of project and even for project success. Examples: Functional requirements, System architecture, critical bug fixes (show stoppers), risks with high probability and critical impact.
- High (2): the deliverable has an impact to quality of final product. Examples: Test caseTest caseA test case in software engineering is a set of conditions or variables under which a tester will determine whether an application or software system is working correctly or not. The mechanism for determining whether a software program or system has passed or failed such a test is known as a test...
s, User interfaceUser interfaceThe user interface, in the industrial design field of human–machine interaction, is the space where interaction between humans and machines occurs. The goal of interaction between a human and a machine at the user interface is effective operation and control of the machine, and feedback from the...
requirements, major severity bug fixes, risks with high expose. - Medium (3): the artifact has a medium or indirect impact to quality of final product. Examples: Project planProject planA project plan, according to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, isPRINCE2 defines:In some industries, particularly information technology, the term "project plan" can refer to a Gantt chart or other document that shows project activities along a timeline. While common, this use is inaccurate...
, medium severity bug fixes, risks with medium expose. - Low (4): the artifact has insignificant impact to the final product quality. Example: employees’ tasks, cosmetic bugs, risks with low probability.
Level of quality control is a measure that defines amount of verification and validation activities applied to artifact, and probability of miscommunication during artifact creation.
- Low (1): No review is supposed for the artifact, miscommunication and information loss are high probable, information channel is distributed, language barrier exists etc
- Medium (2): No review is supposed for the artifact, information channel is not distributed (e.g. creator of artifact and information provider are members of one team)
- Sufficient (3): Pair development or peer review is done, information channel is not distributed.
- Excellent (4): Pair development, peer review and/or testing are done, automation or unit testing is done, or there are some tools for artifact development and validation.
Define responsible people
Success of RST session strongly depends on correct assignment of responsible people.Perform Reverse Semantic Traceability of artifact
Reverse Semantic Traceability starts when decision that RST should be performed is made and resources for it are available.Project manager defines what documents will be an input for RST session. For example, it can be not only an artifact to restore but some background project information. It is recommended to give to reverse engineers number of words in original text so that they have an idea about amount of text they should get as a result: it can be one sentence or several pages of text. Though, the restored text may not contain the same number of words as original text nevertheless the values should be comparable.
After that reverse engineers take the artifact and restore the original text from it. RST itself takes about 1 hour for one page text (750 words).
Value the level of quality and make a decision
To complete RST session, restored and original texts of artifact should be compared and quality of artifact should be assessed. Decision about artifacts rework and its amount is made based on this assessment.For assessment a group of experts is formed. Experts should be aware of project domain and be an experienced enough to assess quality level of compared artifacts. For example, business analysts will be experts for comparison of vision statement and restored vision statement from scenario.
RST assessment criteria:
- Restored and original texts have quite big differences in meaning and crucial information loss
- Restored and original texts have some differences in meaning, important information loss
- Restored and original texts have some differences in meaning, some insignificant information loss
- Restored and original texts are very close, some insignificant information loss
- Restored and original texts are very close, none information is lost
Each of experts gives his assessment, and then the average value is calculated. Depending on this value Project Manager makes a decision should both artifacts be corrected or one of them or rework is not required.
If the average RST quality level is in range from 1 to 2 the quality of artifact is poor and it is recommended not only rework of validated artifact to eliminate defects but corrections of original artifact to clear misunderstandings. In this case one more RST session after rework of artifacts is required. For artifacts that have more than 2 but less than 3 corrections of validated artifact to fix defects and eliminate information loss is required, however review of original artifact to find out if there any vague piece of information that cause misunderstandings is recommended. No additional RST sessions is needed. If the average mark is more than 3 but less than 4 then corrections of validated artifact to remove defects and insignificant information loss is supposed. If the mark is greater than 4 it means that artifact is of good quality and no special corrections or rework is required.
Obviously the final decision about rework of artifacts is made by project manager and should be based on analysis of reasons of differences in texts.
External links
- Vladimir L. Pavlov website
- OMG UML website
- Wikipedia article on P-Modeling FrameworkP-Modeling FrameworkP-Modeling Framework is a package of guidelines, methods, tools and templates for the development process improvement. P-Modeling framework can be integrated into any other SDLC in use, e.g., MSF Agile, MSF CMMI, RUP, etc.- History :...
- P-Modeling Framework Whitepaper
- P-Modeling Framework

