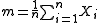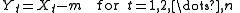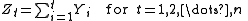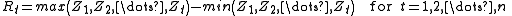Rescaled range
Encyclopedia
The rescaled range is a statistical measure of the variability of a time series introduced by the British hydrologist Harold Edwin Hurst
(1880-1978). Its purpose is to provide an assessment of how the apparent variability of a series changes with the length of the time-period being considered.
The rescaled range is calculated from dividing the range
of the values exhibited in a portion of the time series by the standard deviation
of the values over the same portion of the time series. For example, consider a time series
{2, 5, 3, 7, 8, 12, 4, 2} which has a range, R, of 12 - 2 = 10. Its standard deviation, s, is 3.69, so the rescaled range is R/s = 2.71. In this example, the number of observations, n, of the time series is 8.
If we consider the same time series, but increase the number of observations of it, the rescaled range will generally also increase. The increase of the rescaled range can be characterized by making a plot of the logarithm of R/s vs. the logarithm of n. The slope
of this line gives the Hurst exponent
, H. If the time series is generated by a random walk
(or a Brownian motion
process) it has the value of H =1/2. Many physical phenomena that have a long time series suitable for analysis exhibit a Hurst exponent greater than 1/2. For example, observations of the height of the Nile River measured annually over many years gives a value of H = 0.77.
Several researchers (including Peters, 1991) have found that the prices of many financial instruments
(such as currency exchange rates, stock values, etc.) also have H > 1/2. This means that they have a behavior that is distinct from a random walk, and therefore the time series is not generated by a stochastic process
that has the nth value independent of all of the values before this. This is referred to as long term memory. However this result is controversial and several studies using Lo's (Lo, 1991) modified rescaled range statistic have contradicted Peters' results.
Harold Edwin Hurst
Harold Edwin Hurst was a British hydrologist. Hurst's study on measuring the long-term storage capacity of reservoirs documented the presence of long-range dependence in hydrology. Much of Hurst's research was motivated by his empirical observations of the Nile. The Hurst exponent, which has been...
(1880-1978). Its purpose is to provide an assessment of how the apparent variability of a series changes with the length of the time-period being considered.
The rescaled range is calculated from dividing the range
Range (statistics)
In the descriptive statistics, the range is the length of the smallest interval which contains all the data. It is calculated by subtracting the smallest observation from the greatest and provides an indication of statistical dispersion.It is measured in the same units as the data...
of the values exhibited in a portion of the time series by the standard deviation
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
of the values over the same portion of the time series. For example, consider a time series
Time series
In statistics, signal processing, econometrics and mathematical finance, a time series is a sequence of data points, measured typically at successive times spaced at uniform time intervals. Examples of time series are the daily closing value of the Dow Jones index or the annual flow volume of the...
{2, 5, 3, 7, 8, 12, 4, 2} which has a range, R, of 12 - 2 = 10. Its standard deviation, s, is 3.69, so the rescaled range is R/s = 2.71. In this example, the number of observations, n, of the time series is 8.
If we consider the same time series, but increase the number of observations of it, the rescaled range will generally also increase. The increase of the rescaled range can be characterized by making a plot of the logarithm of R/s vs. the logarithm of n. The slope
Slope
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line describes its steepness, incline, or grade. A higher slope value indicates a steeper incline....
of this line gives the Hurst exponent
Hurst exponent
The Hurst exponent is used as a measure of the long term memory of time series. It relates to the autocorrelations of the time series and the rate at which these decrease as the lag between pairs of values increases....
, H. If the time series is generated by a random walk
Random walk
A random walk, sometimes denoted RW, is a mathematical formalisation of a trajectory that consists of taking successive random steps. For example, the path traced by a molecule as it travels in a liquid or a gas, the search path of a foraging animal, the price of a fluctuating stock and the...
(or a Brownian motion
Brownian motion
Brownian motion or pedesis is the presumably random drifting of particles suspended in a fluid or the mathematical model used to describe such random movements, which is often called a particle theory.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has several real-world applications...
process) it has the value of H =1/2. Many physical phenomena that have a long time series suitable for analysis exhibit a Hurst exponent greater than 1/2. For example, observations of the height of the Nile River measured annually over many years gives a value of H = 0.77.
Several researchers (including Peters, 1991) have found that the prices of many financial instruments
Financial instruments
A financial instrument is a tradable asset of any kind, either cash; evidence of an ownership interest in an entity; or a contractual right to receive, or deliver, cash or another financial instrument....
(such as currency exchange rates, stock values, etc.) also have H > 1/2. This means that they have a behavior that is distinct from a random walk, and therefore the time series is not generated by a stochastic process
Stochastic process
In probability theory, a stochastic process , or sometimes random process, is the counterpart to a deterministic process...
that has the nth value independent of all of the values before this. This is referred to as long term memory. However this result is controversial and several studies using Lo's (Lo, 1991) modified rescaled range statistic have contradicted Peters' results.
Calculation
- The Rescaled Range is calculated for a time series,
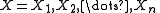 , as follows:
, as follows:
- Calculate the meanMeanIn statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
-
- Create a mean adjusted series
-
- Calculate the cumulative deviate series Z;
- Create a range series R;
- Create a standard deviationStandard deviationStandard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
series S;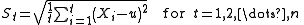
- Where u is the mean for the time series values
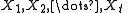
- Calculate the rescaled range series (R/S)
- Calculate the mean