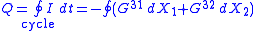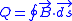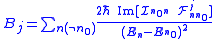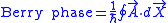
Quantum stirring, ratchets, and pumping
Encyclopedia
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
-driven device that generates a direct current
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
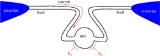
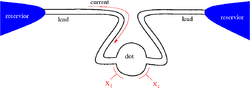
(DC). In the simplest configuration a pump has two leads connected to two reservoirs. In such open geometry the pump takes particles from one reservoir and emits them into the other. Accordingly a current is produced even if the reservoirs have the same temperature and chemical potential.
Main observations
Pumping and stirring effects in quantum physics have counterparts in purely classical stochastic and dissipative processes . The studies of quantum pumping and of quantum stirring emphasize the role of quantum interference in the analysis of the induced current. A major objective is to calculate the amount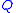 of transported particles per a driving cycle. There are circumstances in which
of transported particles per a driving cycle. There are circumstances in which  is an integer number due to the topology of parameter space. More generally
is an integer number due to the topology of parameter space. More generally  is affected by inter-particle interactions, disorder, chaos, noise and dissipation.
is affected by inter-particle interactions, disorder, chaos, noise and dissipation.Electric stirring explicitly breaks time-reversal symmetry. This property can be used to induce spin polarization in conventional semiconductors by purely electric means . Strictly speaking stirring is a non-linear effect, because in linear response theory (LRT) an AC driving induces an AC current with the same frequency. Still an adaptation of the LRT Kubo formalism allows the analysis of stirring. The quantum pumping problem (where we have an open geometry) can be regarded as a special limit of the quantum stirring problem (where we have a closed geometry). Optionally the latter can be analyzed within the framework of scattering theory. Pumping and Stirring devices are close relatives of ratchet systems. The latter are defined in this context as AC driven spatially periodic arrays, where DC current is induced.
It is possible to induce a DC current by applying a bias, or if the particles are charged then by applying an electro-motive-force. In contrast to that a quantum pumping mechanism produces a DC current in response to a cyclic deformation of the confining potential. In order to have a DC current from an AC driving, time reversal symmetry (TRS) should be broken. In the absence of magnetic field and dissipation it is the driving itself that can break TRS. Accordingly, an adiabatic pump operation is based on varying more than one parameter, while for non-adiabatic pumps
modulation of a single parameter may suffice for DC current generation. The best known example is the peristaltic mechanism that combines a cyclic squeezing operation with on/off switching of entrance/exit valves.
The Kubo approach to quantum stirring
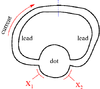
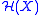 that depends on some control parameters
that depends on some control parameters 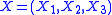 . If
. If 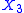 is an Aharonov Bohm magnetic flux through the ring, then by Faraday law
is an Aharonov Bohm magnetic flux through the ring, then by Faraday law 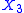 is the electro motive force. If linear response theory applies we have the proportionality
is the electro motive force. If linear response theory applies we have the proportionality 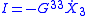 , where
, where 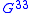 is the called the Ohmic conductance. In complete analogy if we change
is the called the Ohmic conductance. In complete analogy if we change 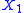 the current is
the current is 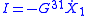 , and if we change
, and if we change 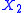 the current is
the current is 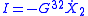 , where
, where 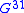 and
and 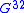 are elements of a conductance matrix. Accordingly for a full pumping cycle:
are elements of a conductance matrix. Accordingly for a full pumping cycle:The conductance can be calculated and analyzed using the Kubo formula approach to quantum pumping, which is based on the theory of adiabatic processes. Here we write the expression that applies in the case of low frequency "quasi static" driving process (the popular terms "DC driving" and "adiabatic driving" turn out to be misleading so we do not use them):
where
 is the current operator, and
is the current operator, and 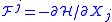 is the generalized force that is associated with the control parameter
is the generalized force that is associated with the control parameter 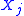 . Though this formula is written using quantum mechanical notations it holds also classically if the commutator is replaced by Poisson brackets. In general
. Though this formula is written using quantum mechanical notations it holds also classically if the commutator is replaced by Poisson brackets. In general  can be written as a sum of two terms: one has to do with dissipation, while the other, denoted as
can be written as a sum of two terms: one has to do with dissipation, while the other, denoted as  has to do with geometry. The dissipative part vanishes in the strict quantum adiabatic limit, while the geometrical part
has to do with geometry. The dissipative part vanishes in the strict quantum adiabatic limit, while the geometrical part  might be non-zero. It turns out that in the strict adiabatic limit
might be non-zero. It turns out that in the strict adiabatic limit  is the "Berry curvature" (mathematically known as ``two-form"). Using the notations
is the "Berry curvature" (mathematically known as ``two-form"). Using the notations 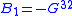 and
and 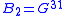 we can rewrite the formula for the amount of pumped particles as
we can rewrite the formula for the amount of pumped particles as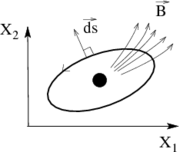
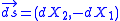 as illustrated. The advantage of this point of view is in the intuition that it gives for the result:
as illustrated. The advantage of this point of view is in the intuition that it gives for the result: 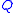 is related to the flux of a field
is related to the flux of a field 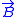 which is created (so to say) by "magnetic charges" in
which is created (so to say) by "magnetic charges" in  space. In practice the calculation of
space. In practice the calculation of 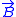 is done using the following formula:
is done using the following formula:This formula can be regarded as the quantum adiabatic limit of the Kubo formula. The eigenstates of the system are labeled by the index
 . These are in general many body states, and the energies are in general many body energies. At finite temperatures a thermal average over
. These are in general many body states, and the energies are in general many body energies. At finite temperatures a thermal average over 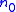 is implicit. The field
is implicit. The field  can be regarded as the rotor of "vector potential"
can be regarded as the rotor of "vector potential"  (mathematically known as the "one-form"). Namely,
(mathematically known as the "one-form"). Namely, 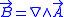 . The ``Berry phase" which is acquired by a wavefunction at the end of a closed cycle is
. The ``Berry phase" which is acquired by a wavefunction at the end of a closed cycle is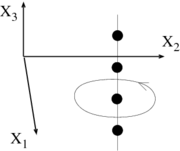
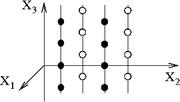
Accordingly one can argue that the "magnetic charge" that generates (so to say) the
 field consists of quantized "Dirac monopoles". It follows from gauge invariance that the degeneracies of the system are arranged as vertical Dirac chains. The "Dirac monopoles" are situated at
field consists of quantized "Dirac monopoles". It follows from gauge invariance that the degeneracies of the system are arranged as vertical Dirac chains. The "Dirac monopoles" are situated at  points where
points where 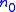 has a degeneracy with another level. The Dirac monopoles picture is useful for charge transport analysis: the amount of transported charge is determined by the number of the Dirac chains encircled by the pumping cycle. Optionally it is possible to evaluate the transported charge per pumping cycle from the Berry phase by differentiating it with respect to the Aharonov–Bohm flux through the device.
has a degeneracy with another level. The Dirac monopoles picture is useful for charge transport analysis: the amount of transported charge is determined by the number of the Dirac chains encircled by the pumping cycle. Optionally it is possible to evaluate the transported charge per pumping cycle from the Berry phase by differentiating it with respect to the Aharonov–Bohm flux through the device.The scattering approach to quantum pumping
The Ohmic conductance of a mesoscopic device that is connected by leads to reservoirs is given by the Landauer formula: in dimensionless units the Ohmic conductance of an open channel equals its transmission. The extension of this scattering point of view in the context of quantum pumping leads to the Brouwer-Buttiker-Pretre-Thomas (BPT) formula which relates the geometric conductance to the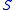 matrix of the pump:
matrix of the pump:Here
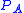 is a projector that restrict the trace operations to the open channels of the lead where the current is measured. This BPT formula has been originally derived using a scattering approach, but later its relation to the Kubo formula has been worked out.
is a projector that restrict the trace operations to the open channels of the lead where the current is measured. This BPT formula has been originally derived using a scattering approach, but later its relation to the Kubo formula has been worked out.The effect of Interactions
A very recent work considers the role of interactions in the stirring of Bose condensed particles. Otherwise the rest of the literature concerns primarily electronic devices. Typically the pump is modeled as a quantum dot. The effect of electron-electron interactions within the dot region is taken into account in the Coulomb blockade regime or in the Kondo regime. In the former case charge transport is quantized even in the case of small back scattering. Deviation from the exact quantized value is related to dissipation. In the Kondo regime, as the temperature is lowered, the pumping effect is modified. There are also works that consider interactions over the whole system (including the leads) using the Luttinger liquid model.See also
- Quantum mechanicsQuantum mechanicsQuantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
- Brownian ratchetBrownian ratchetIn the philosophy of thermal and statistical physics, the Brownian ratchet, or Feynman-Smoluchowski ratchet is a thought experiment about an apparent perpetual motion machine first analysed in 1912 by Polish physicist Marian Smoluchowski and popularised by American Nobel laureate physicist Richard...
- Geometric phaseGeometric phaseIn classical and quantum mechanics, the geometric phase, Pancharatnam–Berry phase , Pancharatnam phase or most commonly Berry phase, is a phase acquired over...
(section Stochastic pump effect)