
Q-Chem
Encyclopedia
Q-Chem is an ab initio
computational chemistry
software program. Q-Chem can perform a number of general quantum chemistry
calculations, including Hartree-Fock
, density functional theory
(DFT), coupled cluster
(CC), configuration interaction
(for single electron excitations—CIS) and other advanced electronic structure methods. The Q-Chem computational engines are also included in Spartan
.
Ab initio quantum chemistry methods
Ab initio quantum chemistry methods are computational chemistry methods based on quantum chemistry. The term ab initiowas first used in quantum chemistry by Robert Parr and coworkers, including David Craig in a semiempirical study on the excited states of benzene.The background is described by Parr...
computational chemistry
Computational chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses principles of computer science to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses the results of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into efficient computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules and solids...
software program. Q-Chem can perform a number of general quantum chemistry
Quantum chemistry
Quantum chemistry is a branch of chemistry whose primary focus is the application of quantum mechanics in physical models and experiments of chemical systems...
calculations, including Hartree-Fock
Hartree-Fock
In computational physics and chemistry, the Hartree–Fock method is an approximate method for the determination of the ground-state wave function and ground-state energy of a quantum many-body system....
, density functional theory
Density functional theory
Density functional theory is a quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics and chemistry to investigate the electronic structure of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. With this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by...
(DFT), coupled cluster
Coupled cluster
Coupled cluster is a numerical technique used for describing many-body systems. Its most common use is as one of several quantum chemical post-Hartree–Fock ab initio quantum chemistry methods in the field of computational chemistry...
(CC), configuration interaction
Configuration interaction
Configuration interaction is a post-Hartree–Fock linear variational method for solving the nonrelativistic Schrödinger equation within the Born–Oppenheimer approximation for a quantum chemical multi-electron system. Mathematically, configuration simply describes the linear combination...
(for single electron excitations—CIS) and other advanced electronic structure methods. The Q-Chem computational engines are also included in Spartan
Spartan (software)
SPARTAN is a molecular modeling and computational chemistry application from . It contains code for molecular mechanics, semi-empirical methods, ab initio models, density functional models, post-Hartree-Fock models, and thermochemical recipes including T1....
.
Ground State Self-Consistent Field Methods
- Hartree-Fock Theory: Restricted, Unrestricted, and Restricted Open-Shell Formulations
-
-
- Analytical First Derivatives for Geometry Optimizations
- Analytical Second Derivatives for Harmonic Frequency Analysis
- Density Functional Theory
- Local Functionals and Gradient-Corrected Functionals
-
- Exchange Functionals: Slater, Becke '88 (B), GGA91 (Perdew '91, PW91), Gill '96, Gilbert and Gill '99 (GG99), Handy and Cohen's OPTX (HC_OPTX)
- Correlation Functionals VWN (#5 parameterization), Lee-Yang-Parr (LYP), LYP (EDF1 parameterization), Perdew-Zunger '81 (PZ81), Perdew '86 (P86), Wigner, GGA91 (Perdew '91, PW91)
- Exchange-correlation functional: EDF1 and Becke(EDF1), PBE functionals, user-definable exchange-correlation functionals
- Hybrid HF-DFT Functionals
-
- B3LYP, B3PW91, B3LYP5(using the VWN5 functional), User-definable hybrid functionals
- Meta GGA Functionals: BMK, M05, M05-2X, M06, M06-2X, M06-L, and M06-HF
- Chai and Head-Gordon's Long-Range Corrected Hybrid Functionals:
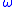 B97,
B97, 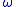 B97X,
B97X, 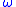 B97X-D, and
B97X-D, and 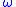 B97X-2
B97X-2
- Numerical-Grid Based Numerical Quadrature Schemes
-
- SG-0 standard grid
- SG-1 standard grid
- Lebedev and Gauss-Legendre Angular Quadrature Schemes
- Incremental Density Function Theory
- Analytical First Derivatives for Geometry Optimizations
- Analytical Second Derivatives for Harmonic Frequency Analysis
- Linear Scaling Methods
- Fourier Transform Coulomb Method (FTC)
- Continuous Fast Multipole Method (CFMM)
- Linear-Scaling HF-exchange method (LinK)
- Linear Scaling Grid Based Integration for Exchange-Correlation Functional Evaluation
- Linear Scaling NMR Chemical Shifts
- Q-Chem's AOINTS Package for Two Electron Integrals
- Incorporates the latest advances in high performance integrals technology
- COLD PRISM
- J Matrix engine
-
Post-Hartree-Fock methods
-
-
- MP2, MP3, , MP4, MP4SDQ, Local MP2- TRIM (triatomics in molecules) and DIM (diatomics in molecules) techniques, RI-MP2
- Coupled-Cluster MethodsCoupled clusterCoupled cluster is a numerical technique used for describing many-body systems. Its most common use is as one of several quantum chemical post-Hartree–Fock ab initio quantum chemistry methods in the field of computational chemistry...
: CCSD, CCSD(T), CCSD(2), QCISDQuadratic configuration interactionQuadratic configuration interaction is an extension of Configuration interaction that corrects for size-consistency errors in the all singles and double excitation CI methods ....
, QCISD(T), QCISD2, EOM-CCSD,
-

