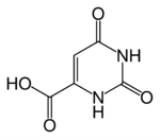
Pyrimidinecarboxylic acid
Encyclopedia
Orotic acid is a heterocyclic compound
and an acid
; it is also known as pyrimidinecarboxylic acid. Historically it was believed to be part of the Vitamin B complex and was called vitamin B13, but it is now known that it is not a vitamin
.
The compound is manufactured in the body by intestinal flora. It is sometimes used as a mineral carrier in some dietary supplements (to increase their bioavailability
), most commonly for lithium orotate
.
dihydroorate dehydrogenase, where it later combines with phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate
(PRPP) to form orotidylate (OMP). A distinguishing characteristic of pyrimidine synthesis is that the pyrimidine ring is fully synthesized before being attached to the ribose sugar, whereas purine synthesis happens by building the base directly on the sugar.
. It may be a symptom of an increased ammonia
load due to a metabolic disorder, such as a urea cycle disorder
.
In ornithine transcarbamoylase deficiency, a disorder of the urea cycle, excess carbamoyl phosphate is converted into orotic acid. This typically leads to increased urinary orotic acid excretion, because the orotic acid is not being properly utilized and must be eliminated.
Orotic acid can be mutagenic (causes mutation
s) in mammalian somatic cells. It is also mutagenic for bacteria and or yeast.
Heterocyclic compound
A heterocyclic compound is a cyclic compound which has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring. The counterparts of heterocyclic compounds are homocyclic compounds, the rings of which are made of a single element....
and an acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
; it is also known as pyrimidinecarboxylic acid. Historically it was believed to be part of the Vitamin B complex and was called vitamin B13, but it is now known that it is not a vitamin
Vitamin
A vitamin is an organic compound required as a nutrient in tiny amounts by an organism. In other words, an organic chemical compound is called a vitamin when it cannot be synthesized in sufficient quantities by an organism, and must be obtained from the diet. Thus, the term is conditional both on...
.
The compound is manufactured in the body by intestinal flora. It is sometimes used as a mineral carrier in some dietary supplements (to increase their bioavailability
Bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is used to describe the fraction of an administered dose of unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation, one of the principal pharmacokinetic properties of drugs. By definition, when a medication is administered...
), most commonly for lithium orotate
Lithium orotate
Lithium orotate, is a salt of orotic acid and lithium. It is available as the monohydrate, LiC5H3N2O4·H2O.Lithium orotate is generally marketed as a dietary supplement used in small doses to treat mental conditions including stress, bipolar disorder, alcoholism, ADHD, ADD, aggression, PTSD,...
.
Synthesis of orotate
Dihydroorotate is synthesized to orotic acid by the enzymeEnzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
dihydroorate dehydrogenase, where it later combines with phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate is a pentosephosphate.It is formed from ribose 5-phosphate by the enzyme ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase.It plays a role in transferring phospho-ribose groups in several reactions:...
(PRPP) to form orotidylate (OMP). A distinguishing characteristic of pyrimidine synthesis is that the pyrimidine ring is fully synthesized before being attached to the ribose sugar, whereas purine synthesis happens by building the base directly on the sugar.
Orotic acid diseases
A buildup of orotic acid can lead to orotic aciduriaOrotic aciduria
-Signs and symptoms:In addition to the characteristic excessive orotic acid in the urine, patients typically have megaloblastic anemia which cannot be cured by administration of vitamin B12 or folic acid....
. It may be a symptom of an increased ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
load due to a metabolic disorder, such as a urea cycle disorder
Urea cycle disorder
An urea cycle disorder or urea cycle defect is a genetic disorder caused by a deficiency of one of the enzymes in the urea cycle which is responsible for removing ammonia from the blood stream. The urea cycle involves a series of biochemical steps in which nitrogen, a waste product of protein...
.
In ornithine transcarbamoylase deficiency, a disorder of the urea cycle, excess carbamoyl phosphate is converted into orotic acid. This typically leads to increased urinary orotic acid excretion, because the orotic acid is not being properly utilized and must be eliminated.
Orotic acid can be mutagenic (causes mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s) in mammalian somatic cells. It is also mutagenic for bacteria and or yeast.

