Proper orbital elements
Encyclopedia

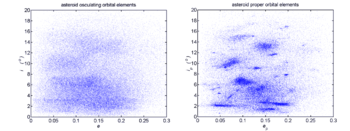
- proper semimajor axis (ap),
- proper eccentricity (ep), and
- proper inclination (ip).
The proper elements are to be contrasted with the osculating
Osculating orbit
In astronomy, and in particular in astrodynamics, the osculating orbit of an object in space is the gravitational Kepler orbit In astronomy, and in particular in astrodynamics, the osculating orbit of an object in space (at a given moment of time) is the gravitational Kepler orbit In astronomy,...
Keplerian orbital elements
Orbital elements
Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are generally considered in classical two-body systems, where a Kepler orbit is used...
observed at a particular time or epoch
Epoch (astronomy)
In astronomy, an epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity, such as celestial coordinates, or elliptical orbital elements of a celestial body, where these are subject to perturbations and vary with time...
, such as the semi-major axis
Semi-major axis
The major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter, a line that runs through the centre and both foci, its ends being at the widest points of the shape...
, eccentricity
Orbital eccentricity
The orbital eccentricity of an astronomical body is the amount by which its orbit deviates from a perfect circle, where 0 is perfectly circular, and 1.0 is a parabola, and no longer a closed orbit...
, and inclination
Inclination
Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit...
. Those osculating elements change in a quasi-periodic and (in principle) predictable manner due to such effects as perturbations from planets or other bodies, and precession (e.g. perihelion precession). In the Solar System
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
, such changes usually occur on timescales of thousands of years, while proper elements are meant to be practically constant over at least tens of millions of years.
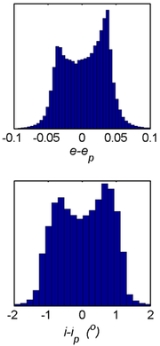
For most bodies, the osculating elements are relatively close to the proper elements because precession and perturbation effects are relatively small (See diagram). For over 99% of asteroid
Asteroid
Asteroids are a class of small Solar System bodies in orbit around the Sun. They have also been called planetoids, especially the larger ones...
s in the asteroid belt
Asteroid belt
The asteroid belt is the region of the Solar System located roughly between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter. It is occupied by numerous irregularly shaped bodies called asteroids or minor planets...
, the differences are less than 0.02 AU (for semi-major axis
Semi-major axis
The major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter, a line that runs through the centre and both foci, its ends being at the widest points of the shape...
a), 0.1 (for eccentricity e), and 2° (for inclination
Inclination
Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit...
i).
Nevertheless, this difference is non-negligible for any purposes where precision is of importance. As an example, the asteroid Ceres has osculating orbital elements (at epoch
Epoch (astronomy)
In astronomy, an epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity, such as celestial coordinates, or elliptical orbital elements of a celestial body, where these are subject to perturbations and vary with time...
November 26, 2005)
| a | e | i Inclination Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit... |
|---|---|---|
| 2.765515 AU Astronomical unit An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance.... |
0.080015 | 10.5868° |
while its proper orbital elements (independent of epoch) are
| ap | ep Orbital eccentricity The orbital eccentricity of an astronomical body is the amount by which its orbit deviates from a perfect circle, where 0 is perfectly circular, and 1.0 is a parabola, and no longer a closed orbit... | ip Inclination Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit... |
|---|---|---|
| 2.767096 AU | 0.116198 | 9.6474° |
A notable exception to this small-difference rule are asteroid
Asteroid
Asteroids are a class of small Solar System bodies in orbit around the Sun. They have also been called planetoids, especially the larger ones...
s lying in the Kirkwood gap
Kirkwood gap
A Kirkwood gap is a gap or dip in the distribution of main-belt asteroids with semi-major axis , as seen in the histogram below...
s, which are in strong orbital resonance with Jupiter.
To obtain proper elements for an object, one usually conducts a detailed simulation of its motion over timespans of several millions of years. Such a simulation must take into account many details of celestial mechanics including perturbations by the planets. Subsequently, one extracts quantities from the simulation which remain unchanged over this long timespan, and makes them the proper orbital elements. For example, the mean inclination, eccentricity, and semi-major axis.
Historically, various approximate analytic calculations were made, starting with those of Kiyotsugu Hirayama
Kiyotsugu Hirayama
was a Japanese astronomer, best known for his discovery that many asteroid orbits were more similar to one another than chance would allow, leading to the concept of asteroid families, now called "Hirayama families" in his honour....
in the early 20th century. Later analytic methods often included thousands of perturbing corrections for each particular object. Presently, the method of choice is to use a computer to numerically integrate the equations of celestial dynamics, and extract constants of motion directly from a numerical analysis of the predicted positions.
At present the most prominent use of proper orbital elements is in the study of asteroid families
Asteroid family
An asteroid family is a population of asteroids that share similar proper orbital elements, such as semimajor axis, eccentricity, and orbital inclination. The members of the families are thought to be fragments of past asteroid collisions...
, following in the footsteps of the pioneering work of Hirayama. As a Mars-crosser asteroid
Mars-crosser asteroid
A Mars-crosser is an asteroid whose orbit crosses that of Mars. The known numbered Mars-crossers are listed here. They include the two numbered Mars trojans 5261 Eureka and ....
132 Aethra
132 Aethra
Discovered by James Craig Watson in 1873, 132 Aethra is an M-type main-belt asteroid. It has a rather eccentric orbit that sometimes brings it closer to the Sun than the planet Mars. It was the first such Mars-crosser asteroid to be identified...
is the lowest numbered asteroid to not have any proper orbital elements.

