
Prism coupler
Encyclopedia
Introduction
The prism coupler was the first device used to couple a substantial fraction of the power contained in a laser beam into a thin film without the need for precision polishing of the edge of the film and sub-micron accuracy in the alignment of the beam and the edge of the film. Using a prism coupler, the beam coupled into a thin film can have a diameter hundreds of times the thickness of the film. Invention of the coupler contributed to the initiation of a field of study known as Integrated Optics. The physical concepts underlying operation of the coupler are described below.Coupler Configuration
Fig. 1 illustrates a prism coupler used to couple the power from an incident laser beam into a thin film. The film lies on a substrate like a glass microscope slide and might have a thickness of the order of the wavelength of the incident light. If the refractive index of the film is greater than that of the glass slide, the film can serve as a dielectric planar waveguide for light.The prism coupler consists of a near cube of high refractive index glass and a second thin film at the bottom that contacts the waveguide film and serves the function of partially containing the guided wave over the coupling distance. For reasons described below, we may refer to the thin film at the bottom of the prism as the tunneling layer. The tunneling layer must have a lower refractive index than the waveguide film and may actually be implemented as a layer of air. The thickness of the tunneling layer might be in the range of tens to hundreds of nanometers.
In operation, the prism, with tunneling layer down, is pressed against the waveguide film lying on the glass slide. The beam enters the front face of the prism and strikes the tunneling layer somewhat more than half a beam width away from the face opposite the entry face of the prism. The ranking of refractive indices of the four regions of the combined coupler and waveguide structure must be as follows: the refractive index of the glass slide and the tunneling later must be lowest, next is the refractive index of the guide film, and highest is the index of the prism. Figures 2 and 3 are photographs showing early experiments involving, respectively, prism coupling into a thin film, and coupling in and out of a thin film. Light scattered from the guided wave, clamps holding the prisms, and a beam reflected from the front face of the prism are visible in the photographs.
Theory of the Prism Coupler
A convenient way to gain a qualitative, as well as a quantitative, understanding of how the prism coupler works may be obtained using the reciprocity theorem. The reciprocity theorem permits the relative power coupled into the thin film by an incident beam to be computed from the solution to a reciprocal problem. In the reciprocal problem, a waveguide mode in the film, travelling to the left in Fig. 1, is incident on the prism coupler. Barring significant scattering at the prism interface, the waveguide mode in the reciprocal problem retains its form as a mode and propagates under the prism, losing power as it propagates due to radiation into the prism. The power in the prism emerges as a collimated beam at an angle determined by the propagation constant of the waveguide mode and the refractive index of the prism. Radiation into the prism occurs because the evanescent tail of the waveguide mode touches the bottom of the prism. The waveguide mode “tunnels” through the tunneling layer.Efficient coupling of light into the film occurs when the beam incident from the left shown in Fig. 1, evaluated at the bottom face of the prism, has the same shape as the radiated beam in the reciprocal problem. When the power in both the incident beam and the reciprocal waveguide mode is normalized, the fractional coupling amplitude is expressed as an integral over the product of the incident wave and the radiated reciprocal field. The integral is a surface integral taken over the bottom face of the prism. From such an integral we deduce three key features: (1) To couple in a significant fraction of the incident power, the incident beam must arrive at the angle that renders it phase matched to the waveguide mode. (2) The transverse behavior of the waveguide mode launched in the film (transverse to the direction of propagation) will be essentially that of the incident beam. (3) If the thickness of the tunneling layer is adjusted appropriately, it is possible, in principle, to couple nearly all the light in the beam into the waveguide film.
Suppressing the transverse part of the representation for the fields, and taking x as direction to the left in Fig. 1, the waveguide mode in the reciprocal problem takes the monotonically decreasing form [exp( -∫α(x)dx + iβwx)], where α(x) is the attenuation rate and βw is the propagation constant of the waveguide mode. The associated transverse field at the bottom of the prism takes the form A α1/2(x) [exp -∫α(x)dx + iβwx], with A a normalization constant. The transverse field of the incident beam will have the form f(x)[exp –iβinx] where f(x) is a normalized Gaussian, or other beam form, and βin is the longitudinal component of the propagation constant of the incident beam. When βin = βw, integration of A f(x)α1/2(x) [exp -∫α(x)dx] yields the coupling amplitude. Adjusting α(x) permits the coupling to approach unity, barring significant geometry dependent diffractive effects.
Alternative Ways to Understand the Prism Coupler
The Goos-Hänchen shift describes the displacement of the center point of an optical beam when it undergoes total reflection from the interface between two semi-infinite regions of different refractive index. The displacement is generally of the order of the wavelength of light. If the reflection of a beam from a sandwich structure that consists of a semi-infinite prism, a tunneling layer, a waveguide film layer, and a semi-infinite glass slide is investigated, the shift will be found to be much larger as a consequence of the excitation of the guided wave. Terminating the upper (prism) region just beyond the mid-point of the incident beam traps the light of the beam in the waveguide mode in the film.Excitation of the guided wave by an incident beam can also be viewed as a problem in coupled modes, the modes being the waveguide mode and a representation for the incident beam. Power introduced into one branch of a coupled mode structure can transfer to the other branch along the structure.
Measurement Applications of Prism Couplers
Prism couplers are instruments used to measure the refractive indexRefractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
/birefringence
Birefringence
Birefringence, or double refraction, is the decomposition of a ray of light into two rays when it passes through certain anisotropic materials, such as crystals of calcite or boron nitride. The effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who saw it in calcite...
and thickness of dielectric
Dielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
and polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
films. Since refractive indices of a material depend upon the wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
of the electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
transmitted, a monochromatic laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
is used in conjunction with a prism of known refractive index. The laser beam is directed through a side of the prism, bent, and is normally reflected back out the opposite side into a photo detector. However, at certain values of the incident angle theta, the beam does not reflect back out, but instead is transmitted through the base into the film sample. These angles are called mode angles. A computer-driven rotary table varies the incident angle of the laser. The first mode angle found determines the refractive index, and the angle difference from one mode to the next determines the sample thickness.
Prism couplers also allow for coupling light in and out of a waveguide without exposing the cross-section of the waveguide (edge coupling). To achieve this a phase matching condition is required between the propagation constant of the mth mode in the waveguide
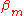 and the incident light at an angle
and the incident light at an angle  normal from the waveguide surface.
normal from the waveguide surface.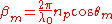
where
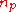 is the index of refraction of the prism.
is the index of refraction of the prism.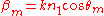
where
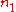 is the index of air (~1) and
is the index of air (~1) and 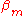 is the propagation constant of the waveguide. . In order to have a guided mode,
is the propagation constant of the waveguide. . In order to have a guided mode,  . This would imply that
. This would imply that 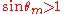 , which is not possible.
, which is not possible.

