
Planck postulate
Encyclopedia
The Planck Postulate one of the fundamental principles of quantum mechanics
, is the postulate that the energy of oscillators in a black body
is quantized, and is given by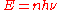 ,
,
where is an integer 1, 2, 3, ...,
is an integer 1, 2, 3, ..., 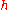 is Planck's constant, and
is Planck's constant, and  (the Greek letter nu, not the Latin letter v) is the frequency of the oscillator.
(the Greek letter nu, not the Latin letter v) is the frequency of the oscillator.
The Planck Postulate was introduced by Max Planck
in his derivation of his law of black body radiation in 1900. This assumption allowed Planck to derive a formula for the entire spectrum
of the radiation emitted by a black body
. Planck was unable to justify this assumption based on classical physics
; he considered quantization as being purely a mathematical trick, rather than (as we now know) a fundamental change in our understanding of the world.
In 1905 in one of his three most important papers, Albert Einstein
adapted the Planck postulate to explain the photoelectric effect
, but Einstein proposed that the energy of photons themselves was quantized, and that quantization was not merely a feature of microscopic oscillators. Planck's postulate was further applied to understanding the Compton effect, and was applied by Niels Bohr
to explain the emission spectrum
of the hydrogen
atom
and derive the correct value of the Rydberg constant
.
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
, is the postulate that the energy of oscillators in a black body
Black body
A black body is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation. Because of this perfect absorptivity at all wavelengths, a black body is also the best possible emitter of thermal radiation, which it radiates incandescently in a characteristic, continuous spectrum...
is quantized, and is given by
 ,
,where
 is an integer 1, 2, 3, ...,
is an integer 1, 2, 3, ..., 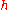 is Planck's constant, and
is Planck's constant, and  (the Greek letter nu, not the Latin letter v) is the frequency of the oscillator.
(the Greek letter nu, not the Latin letter v) is the frequency of the oscillator.The Planck Postulate was introduced by Max Planck
Max Planck
Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck, ForMemRS, was a German physicist who actualized the quantum physics, initiating a revolution in natural science and philosophy. He is regarded as the founder of the quantum theory, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918.-Life and career:Planck came...
in his derivation of his law of black body radiation in 1900. This assumption allowed Planck to derive a formula for the entire spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
of the radiation emitted by a black body
Black body
A black body is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation. Because of this perfect absorptivity at all wavelengths, a black body is also the best possible emitter of thermal radiation, which it radiates incandescently in a characteristic, continuous spectrum...
. Planck was unable to justify this assumption based on classical physics
Classical physics
What "classical physics" refers to depends on the context. When discussing special relativity, it refers to the Newtonian physics which preceded relativity, i.e. the branches of physics based on principles developed before the rise of relativity and quantum mechanics...
; he considered quantization as being purely a mathematical trick, rather than (as we now know) a fundamental change in our understanding of the world.
In 1905 in one of his three most important papers, Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who developed the theory of general relativity, effecting a revolution in physics. For this achievement, Einstein is often regarded as the father of modern physics and one of the most prolific intellects in human history...
adapted the Planck postulate to explain the photoelectric effect
Photoelectric effect
In the photoelectric effect, electrons are emitted from matter as a consequence of their absorption of energy from electromagnetic radiation of very short wavelength, such as visible or ultraviolet light. Electrons emitted in this manner may be referred to as photoelectrons...
, but Einstein proposed that the energy of photons themselves was quantized, and that quantization was not merely a feature of microscopic oscillators. Planck's postulate was further applied to understanding the Compton effect, and was applied by Niels Bohr
Niels Bohr
Niels Henrik David Bohr was a Danish physicist who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum mechanics, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922. Bohr mentored and collaborated with many of the top physicists of the century at his institute in...
to explain the emission spectrum
Emission spectrum
The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the element's atoms or the compound's molecules when they are returned to a lower energy state....
of the hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
and derive the correct value of the Rydberg constant
Rydberg constant
The Rydberg constant, symbol R∞, named after the Swedish physicist Johannes Rydberg, is a physical constant relating to atomic spectra in the science of spectroscopy. Rydberg initially determined its value empirically from spectroscopy, but Niels Bohr later showed that its value could be calculated...
.

