
Planar projection
Encyclopedia
Planar projections are the subset of 3D graphical projections constructed by linearly mapping points in three dimensional space to points on a two-dimensional projection plane. The projected point on the plane is chosen such that it is collinear
with the corresponding three dimensional point and the centre of projection. The lines connecting these points are commonly referred to as projectors.
The centre of projection can be thought of as the location of the observer while the plane of projection is the surface on which the two dimensional projected image of the scene is recorded or from which it is viewed (e.g., photographic negative, photographic print, computer monitor). When the centre of projection is at a finite distance from the projection plane, a perspective
projection is obtained. When the centre of projection is at infinity, all the projectors are parallel, and the corresponding subset of planar projections are referred to as parallel projections.
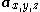 to give a point
to give a point 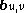 on the projection plane. These transformations consist of various compositions
on the projection plane. These transformations consist of various compositions
of the five transformations: orthographic projection
, rotation
, shear, translation
and perspective.
Line (geometry)
The notion of line or straight line was introduced by the ancient mathematicians to represent straight objects with negligible width and depth. Lines are an idealization of such objects...
with the corresponding three dimensional point and the centre of projection. The lines connecting these points are commonly referred to as projectors.
The centre of projection can be thought of as the location of the observer while the plane of projection is the surface on which the two dimensional projected image of the scene is recorded or from which it is viewed (e.g., photographic negative, photographic print, computer monitor). When the centre of projection is at a finite distance from the projection plane, a perspective
Perspective (graphical)
Perspective in the graphic arts, such as drawing, is an approximate representation, on a flat surface , of an image as it is seen by the eye...
projection is obtained. When the centre of projection is at infinity, all the projectors are parallel, and the corresponding subset of planar projections are referred to as parallel projections.
Mathematical formulation
Mathematically, planar projections are linear transformations acting on a point in three dimensional space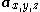 to give a point
to give a point 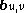 on the projection plane. These transformations consist of various compositions
on the projection plane. These transformations consist of various compositionsFunction composition
In mathematics, function composition is the application of one function to the results of another. For instance, the functions and can be composed by computing the output of g when it has an argument of f instead of x...
of the five transformations: orthographic projection
Orthographic projection
Orthographic projection is a means of representing a three-dimensional object in two dimensions. It is a form of parallel projection, where all the projection lines are orthogonal to the projection plane, resulting in every plane of the scene appearing in affine transformation on the viewing surface...
, rotation
Rotation (mathematics)
In geometry and linear algebra, a rotation is a transformation in a plane or in space that describes the motion of a rigid body around a fixed point. A rotation is different from a translation, which has no fixed points, and from a reflection, which "flips" the bodies it is transforming...
, shear, translation
Translation (geometry)
In Euclidean geometry, a translation moves every point a constant distance in a specified direction. A translation can be described as a rigid motion, other rigid motions include rotations and reflections. A translation can also be interpreted as the addition of a constant vector to every point, or...
and perspective.

