Particle collection in wet scrubbers
Encyclopedia
Wet scrubber
s capture relatively small dust particles with large liquid droplets. In most wet scrubbing systems, droplets produced are generally larger than 50 micrometres (in the 150 to 500 micrometres range). As a point of reference, human hair ranges in diameter from 50 to 100 micrometres. The size distribution of particles
to be collected is source specific.
For example, particles produced by mechanical means (crushing or grinding) tend to be large (above 10 micrometres); whereas, particles produced from combustion or a chemical reaction will have a substantial portion of small (i.e. less than 5 micrometres) and submicrometre particles.
The most critical sized particles are those in the 0.1 to 0.5 micrometres range because they are the most difficult for wet scrubbers to collect.
Droplets are produced by several methods:
These droplets collect particles by using one or more of several collection mechanisms such as impaction, direct interception, diffusion
, electrostatic attraction, condensation
, centrifugal force
and gravity. However, impaction and diffusion
are the main ones.
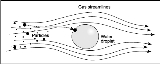
 In a wet scrubbing system, dust particles will tend to follow the streamlines of the exhaust stream
In a wet scrubbing system, dust particles will tend to follow the streamlines of the exhaust stream
. However, when liquid droplets are introduced into the exhaust stream, particles cannot always follow these streamlines as they diverge around the droplet (Figure 1). The particle's mass causes it to break away from the streamlines and impact
or hit the droplet.
Impaction increases as the diameter of the particle increases and as the relative velocity between the particle and droplets increases. As particles get larger they are less likely to follow the gas streamlines around droplets. Also, as particles move faster relative to the
liquid droplet, there is a greater chance that the particle will hit a droplet. Impaction is the predominant collection mechanism for scrubbers having gas stream velocities greater than 0.3 m/s (1 ft/s) (Perry 1973).
Most scrubber
s operate with gas stream velocities well above 0.3 m/s. Therefore, at these velocities, particles having diameters greater than 1.0 µm are collected by this mechanism.
Impaction also increases as the size of the liquid droplet decreases because the presence of more droplets within the vessel increases the probability that particles will impact on the droplets.
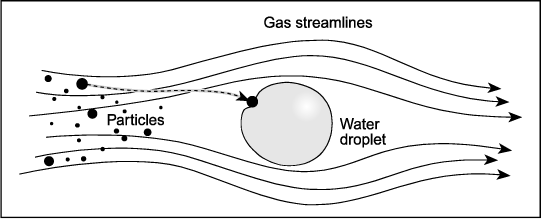
 Very small particles (less than 0.1 µm in diameter) experience random movement
Very small particles (less than 0.1 µm in diameter) experience random movement
in an exhaust stream. These particles are so tiny that they are bumped by gas molecules as they move in the exhaust stream. This bumping, or bombardment, causes them to first move one way and then another in a random manner, or to diffuse
, through the gas. This irregular motion can cause the particles to collide with a droplet and be collected (Figure 2). Because of this, diffusion is the primary collection mechanism in wet scrubbers for particles smaller than 0.1 µm.
The rate of diffusion depends on the following:
For both impaction and diffusion, collection efficiency increases with an increase in relative velocity (liquid- or gas-pressure input) and a decrease in liquid-droplet size.
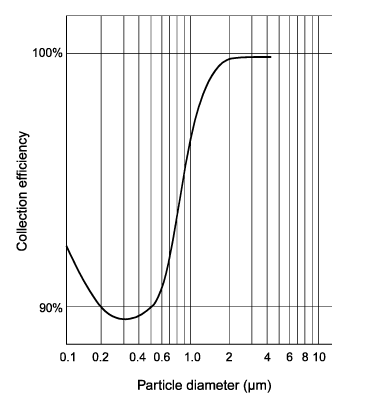 However, collection by diffusion increases as particle size decreases. This mechanism enables certain scrubbers to effectively remove the very tiny particles (less than 0.1 µm).
However, collection by diffusion increases as particle size decreases. This mechanism enables certain scrubbers to effectively remove the very tiny particles (less than 0.1 µm).
In the particle size range of approximately 0.1 to 1.0 µm, neither of these two collection mechanisms (impaction or diffusion) dominates. This relationship is illustrated in Figure 3.
to enhance particle collection without increasing power consumption.
In electrostatic attraction, particles are captured by first inducing a charge on them. Then, the charged particles are either attracted to each other, forming larger, easier-to-collect particles, or they are collected on a surface.
Condensation
of water vapor on particles promotes collection by adding mass to the particles. Other mechanisms such as gravity, centrifugal force
, and direct interception slightly affect particle collection.
Wet scrubber
The term wet scrubber describes a variety of devices that remove pollutants from a furnace flue gas or from other gas streams. In a wet scrubber, the polluted gas stream is brought into contact with the scrubbing liquid, by spraying it with the liquid, by forcing it through a pool of liquid, or by...
s capture relatively small dust particles with large liquid droplets. In most wet scrubbing systems, droplets produced are generally larger than 50 micrometres (in the 150 to 500 micrometres range). As a point of reference, human hair ranges in diameter from 50 to 100 micrometres. The size distribution of particles
Particle size distribution
The particle-size distribution of a powder, or granular material, or particles dispersed in fluid, is a list of values or a mathematical function that defines the relative amounts of particles present, sorted according to size...
to be collected is source specific.
For example, particles produced by mechanical means (crushing or grinding) tend to be large (above 10 micrometres); whereas, particles produced from combustion or a chemical reaction will have a substantial portion of small (i.e. less than 5 micrometres) and submicrometre particles.
The most critical sized particles are those in the 0.1 to 0.5 micrometres range because they are the most difficult for wet scrubbers to collect.
Droplets are produced by several methods:
- Injecting liquid at high pressure through specially designed nozzleNozzleA nozzle is a device designed to control the direction or characteristics of a fluid flow as it exits an enclosed chamber or pipe via an orifice....
s - Aspirating the particle-laden gas stream through a liquid pool
- Submerging a whirling rotorTurbineA turbine is a rotary engine that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work.The simplest turbines have one moving part, a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades, or the blades react to the flow, so that they move and...
in a liquid pool.
These droplets collect particles by using one or more of several collection mechanisms such as impaction, direct interception, diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
, electrostatic attraction, condensation
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition....
, centrifugal force
Centrifugal force
Centrifugal force can generally be any force directed outward relative to some origin. More particularly, in classical mechanics, the centrifugal force is an outward force which arises when describing the motion of objects in a rotating reference frame...
and gravity. However, impaction and diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
are the main ones.
Impaction

Exhaust gas
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline/petrol, diesel fuel, fuel oil or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an exhaust pipe, flue gas stack or propelling nozzle.It often disperses...
. However, when liquid droplets are introduced into the exhaust stream, particles cannot always follow these streamlines as they diverge around the droplet (Figure 1). The particle's mass causes it to break away from the streamlines and impact
or hit the droplet.
Impaction increases as the diameter of the particle increases and as the relative velocity between the particle and droplets increases. As particles get larger they are less likely to follow the gas streamlines around droplets. Also, as particles move faster relative to the
liquid droplet, there is a greater chance that the particle will hit a droplet. Impaction is the predominant collection mechanism for scrubbers having gas stream velocities greater than 0.3 m/s (1 ft/s) (Perry 1973).
Most scrubber
Scrubber
Scrubber systems are a diverse group of air pollution control devices that can be used to remove some particulates and/or gases from industrial exhaust streams. Traditionally, the term "scrubber" has referred to pollution control devices that use liquid to wash unwanted pollutants from a gas stream...
s operate with gas stream velocities well above 0.3 m/s. Therefore, at these velocities, particles having diameters greater than 1.0 µm are collected by this mechanism.
Impaction also increases as the size of the liquid droplet decreases because the presence of more droplets within the vessel increases the probability that particles will impact on the droplets.
Diffusion

Brownian motion
Brownian motion or pedesis is the presumably random drifting of particles suspended in a fluid or the mathematical model used to describe such random movements, which is often called a particle theory.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has several real-world applications...
in an exhaust stream. These particles are so tiny that they are bumped by gas molecules as they move in the exhaust stream. This bumping, or bombardment, causes them to first move one way and then another in a random manner, or to diffuse
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
, through the gas. This irregular motion can cause the particles to collide with a droplet and be collected (Figure 2). Because of this, diffusion is the primary collection mechanism in wet scrubbers for particles smaller than 0.1 µm.
The rate of diffusion depends on the following:
- The relative velocity between the particle and droplet
- The particle diameter
- The liquid-droplet diameter.
For both impaction and diffusion, collection efficiency increases with an increase in relative velocity (liquid- or gas-pressure input) and a decrease in liquid-droplet size.

In the particle size range of approximately 0.1 to 1.0 µm, neither of these two collection mechanisms (impaction or diffusion) dominates. This relationship is illustrated in Figure 3.
Other collection mechanisms
In recent years, some scrubber manufacturers have utilized other collection mechanisms such as electrostatic attraction and condensationCondensation
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition....
to enhance particle collection without increasing power consumption.
In electrostatic attraction, particles are captured by first inducing a charge on them. Then, the charged particles are either attracted to each other, forming larger, easier-to-collect particles, or they are collected on a surface.
Condensation
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition....
of water vapor on particles promotes collection by adding mass to the particles. Other mechanisms such as gravity, centrifugal force
Centrifugal force
Centrifugal force can generally be any force directed outward relative to some origin. More particularly, in classical mechanics, the centrifugal force is an outward force which arises when describing the motion of objects in a rotating reference frame...
, and direct interception slightly affect particle collection.
External links
- The Encyclopedia Of Filters - Dust Collection An overview of the science of dust collection systems, including Wet Scrubbers.

