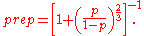
P-rep
Encyclopedia
In statistical
hypothesis testing, p-rep or prep has been proposed as a statistical alternative to the classic p-value
. Whereas a p-value is the probability of obtaining a result under the null hypothesis, p-rep computes the probability of replicating an effect. Whether it does so is heavily disputed – some have argued that the concept rests on a mathematical falsehood.
For a while, the Association for Psychological Science
recommended that articles submitted to Psychological Science
and their other journals report p-rep rather than the classic p-value, but this is no longer the case.
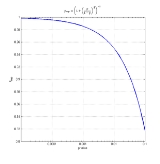
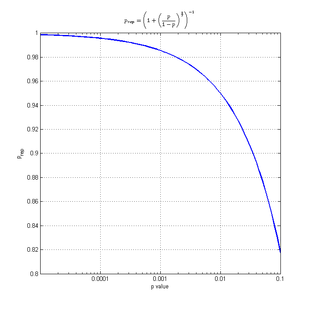 The value of the p-rep (prep) can be approximated based on the p-value (p) as follows:
The value of the p-rep (prep) can be approximated based on the p-value (p) as follows:
with the p-value makes it clear that this new measure doesn't bring any additional information on the significance of the result of a given experiment. However, according to Killeen who acknowledges this latter point, the main advantage of p-rep lies in the fact that it better captures the way experimenters naively
think and conceptualize p-values and statistical hypothesis testing
.
Among the criticisms of p-rep is the fact that it does not take prior probabilities into account. For example, if an experiment on some unlikely paranormal phenomenon produced a p-rep of 0.75, most right-thinking people would not believe the probability of a replication is 0.75. Instead they would conclude that it is much closer to 0. Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence, and p-rep ignores this. This consideration undermines the argument that p-rep is easier to understand than a classical p value. The fact that p-rep requires assumptions about prior probabilities for it to be valid makes its interpretation complex. The classical p merely states the probability of an outcome (or more extreme outcome) given a null hypothesis and therefore is valid without regard to prior probabilities. Killeen argues that new results should be evaluated in their own right, without the burden of history, with flat priors: that is what p-rep yields. A more pragmatic estimate of replicability would include prior knowledge, which the logic of p-rep permits, but which null testing does not.
Critics have also underscored mathematical errors in the original paper by Killeen. For example, the formula relating the effect size
s from two replications of a given experiment erroneously uses one of these random variable
s as a parameter
of the probability distribution
of the other while he previously hypothesized these two variables to be independent
.
These criticisms were addressed in his rejoinder.
A further criticism of the P-rep statistic involves the logic of experimentation. The purpose of replication in science is to adequately account for unmeasured factors in the testing environment, and in the case of human-subjects research: unmeasured participant variables and response biases, characteristics of the individual(s) conducting the experiment, and to replicate findings using different samples of participants. The idea that any value can, from one sample of data, meaningfully capture the likelihood of (by definition) unmeasured factors to affect the outcome, and thus the likelihhod of replicability, is a logical fallacy.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
hypothesis testing, p-rep or prep has been proposed as a statistical alternative to the classic p-value
P-value
In statistical significance testing, the p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic at least as extreme as the one that was actually observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. One often "rejects the null hypothesis" when the p-value is less than the significance level α ,...
. Whereas a p-value is the probability of obtaining a result under the null hypothesis, p-rep computes the probability of replicating an effect. Whether it does so is heavily disputed – some have argued that the concept rests on a mathematical falsehood.
For a while, the Association for Psychological Science
Association for Psychological Science
The Association for Psychological Science , previously the American Psychological Society, is a non-profit international organization whose mission is to promote, protect, and advance the interests of scientifically oriented psychology in research, application, teaching, and the improvement of...
recommended that articles submitted to Psychological Science
Psychological science
Psychological Science is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal of the Association for Psychological Science , published by SAGE Publications. It is one of the most influential journals in psychology.-Publishings:...
and their other journals report p-rep rather than the classic p-value, but this is no longer the case.
Calculation

Criticism
The fact that the p-rep has a one-to-one correspondenceBijection
A bijection is a function giving an exact pairing of the elements of two sets. A bijection from the set X to the set Y has an inverse function from Y to X. If X and Y are finite sets, then the existence of a bijection means they have the same number of elements...
with the p-value makes it clear that this new measure doesn't bring any additional information on the significance of the result of a given experiment. However, according to Killeen who acknowledges this latter point, the main advantage of p-rep lies in the fact that it better captures the way experimenters naively
Folk science
Folk science describes ways of understanding and predicting the natural and social world, without the use of rigorous methodologies . One could label all understanding of nature predating the Greeks as "folk science"....
think and conceptualize p-values and statistical hypothesis testing
Statistical hypothesis testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of making decisions using data, whether from a controlled experiment or an observational study . In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance alone, according to a pre-determined threshold...
.
Among the criticisms of p-rep is the fact that it does not take prior probabilities into account. For example, if an experiment on some unlikely paranormal phenomenon produced a p-rep of 0.75, most right-thinking people would not believe the probability of a replication is 0.75. Instead they would conclude that it is much closer to 0. Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence, and p-rep ignores this. This consideration undermines the argument that p-rep is easier to understand than a classical p value. The fact that p-rep requires assumptions about prior probabilities for it to be valid makes its interpretation complex. The classical p merely states the probability of an outcome (or more extreme outcome) given a null hypothesis and therefore is valid without regard to prior probabilities. Killeen argues that new results should be evaluated in their own right, without the burden of history, with flat priors: that is what p-rep yields. A more pragmatic estimate of replicability would include prior knowledge, which the logic of p-rep permits, but which null testing does not.
Critics have also underscored mathematical errors in the original paper by Killeen. For example, the formula relating the effect size
Effect size
In statistics, an effect size is a measure of the strength of the relationship between two variables in a statistical population, or a sample-based estimate of that quantity...
s from two replications of a given experiment erroneously uses one of these random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
s as a parameter
Parameter
Parameter from Ancient Greek παρά also “para” meaning “beside, subsidiary” and μέτρον also “metron” meaning “measure”, can be interpreted in mathematics, logic, linguistics, environmental science and other disciplines....
of the probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
of the other while he previously hypothesized these two variables to be independent
Statistical independence
In probability theory, to say that two events are independent intuitively means that the occurrence of one event makes it neither more nor less probable that the other occurs...
.
These criticisms were addressed in his rejoinder.
A further criticism of the P-rep statistic involves the logic of experimentation. The purpose of replication in science is to adequately account for unmeasured factors in the testing environment, and in the case of human-subjects research: unmeasured participant variables and response biases, characteristics of the individual(s) conducting the experiment, and to replicate findings using different samples of participants. The idea that any value can, from one sample of data, meaningfully capture the likelihood of (by definition) unmeasured factors to affect the outcome, and thus the likelihhod of replicability, is a logical fallacy.