
Orthognathic surgery
Encyclopedia
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
to correct conditions of the jaw
Jaw
The jaw is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term jaws is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serving to open and close it and is part of the body plan of...
and face
Face
The face is a central sense organ complex, for those animals that have one, normally on the ventral surface of the head, and can, depending on the definition in the human case, include the hair, forehead, eyebrow, eyelashes, eyes, nose, ears, cheeks, mouth, lips, philtrum, temple, teeth, skin, and...
related to structure, growth, sleep apnea
Sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by abnormal pauses in breathing or instances of abnormally low breathing, during sleep. Each pause in breathing, called an apnea, can last from a few seconds to minutes, and may occur 5 to 30 times or more an hour. Similarly, each abnormally low...
, TMJ disorders, malocclusion
Malocclusion
A malocclusion is a misalignment of teeth or incorrect relation between the teeth of the two dental arches. The term was coined by Edward Angle, the "father of modern orthodontics", as a derivative of occlusion, which refers to the manner in which opposing teeth meet.-Presentation:Most people have...
problems owing to skeletal disharmonies, or other orthodontic problems that cannot be easily treated with braces. Originally coined by Dr. Harold Hargis, D.M.D., it is also used in treatment of congenital conditions like cleft palate. Bones can be cut and re-aligned, then held in place with either screws or plates and screws.
Indications
- Gross jaw discrepancies (Anteroposterior , Vertical and /or Transverse discrepancies).
- Facial skeletal discrepancies associated with documented sleep apnea, airway defects, and soft tissue discrepancies.
- Facial skeletal discrepancies associated with documented temporomandibular joint pathology.
Surgery
Orthognathic surgery is performed by either an oral and maxillofacial surgeon, plastic surgeon, or ENT in collaboration with an orthodontist. It often includes braces before and after surgery, and retainers after the final removal of braces. Orthognathic surgery is often needed after reconstruction of cleft palate or other major craniofacialCraniofacial
Craniofacial may be used to describe certain congenital malformations, injuries, surgeons who subspecialize in this area, multi-disciplinary medical-surgical teams that treat and do research on disorders affecting this region, and organizations with interest in...
anomalies. Careful coordination between the surgeon and orthodontist is essential to ensure that the teeth will fit correctly after the surgery.
Planning
Planning for the surgery usually involves input from a multidisciplinary team. Involved professionals are oral and maxillofacial surgeons, plastic surgeons, ENT surgeons, orthodontists, and speech and language therapist. As the surgery usually results in a noticeable change in the patient's face a psychological assessment is occasionally required to assess patient's need for surgery and its predicted effect on the patient.Radiographs and photographs are taken to help in the planning and there is software to predict the shape of the patient's face after surgery, which is useful both for planning and for explaining the surgery to the patient and the patient's family. Advanced software can allow the patient to see the predicted results of the surgery.
The main goals of orthognathic surgery are to achieve a correct bite, an aesthetic face and an enlarged airway. While correcting the bite is important, if the face is not considered the resulting bony changes might lead to an unaesthetic result. Orthognathic surgery is also available as a very successful treatment (90-100%) for obstructive sleep apnea. Great care needs to be taken during the planning phase to maximize airway patency.
Procedure
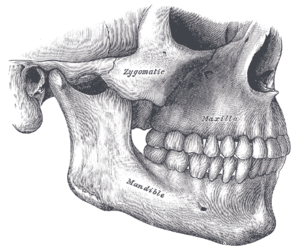
The surgery might involve one jaw or the two jaws during the same procedure. The modification is done by making cuts in the bones of the mandible and / or maxillaMaxilla
The maxilla is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper jaw. This is similar to the mandible , which is also a fusion of two halves at the mental symphysis. Sometimes The maxilla (plural: maxillae) is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper...
and repositioning the cut pieces in the desired alignment. Usually surgery is performed under general anaesthetic
General anaesthetic
A general anaesthetic is a drug that brings about a reversible loss of consciousness. These drugs are generally administered by an anaesthesia provider to induce or maintain general anaesthesia to facilitate surgery...
and using nasal tube for intubation
Intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic or rubber tube into the trachea to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs...
rather than the more commonly used oral tube; this is to allow wiring the teeth together during surgery. The surgery often does not involve cutting the skin, and instead, the surgeon is often able to go through the inside of the mouth.
Cutting the bone is called osteotomy
Osteotomy
An osteotomy is a surgical operation whereby a bone is cut to shorten, lengthen, or change its alignment. It is sometimes performed to correct a hallux valgus, or to straighten a bone that has healed crookedly following a fracture. It is also used to correct a coxa vara, genu valgum, and genu varum...
and in case of performing the surgery on the two jaws at the same time it is called a bi-maxillary osteotomy (two jaws bone cutting) or a maxillomandibular advancement
Maxillomandibular advancement
Maxillomandibular Advancement or orthognathic surgery, also sometimes called Bimaxillary Advancement , or Maxillomandibular Osteotomy , is a surgical procedure which moves the jaw top and bottom forward....
. The bone cutting is traditionally done using special electrical saws and burs, and manual chisels. Recently a machine that can make the bone cuts using ultra-sound waves has been introduced; this is yet to be used on a wide scale. The maxilla can be adjusted using a "Lefort I
LeFort fracture
Le Fort fractures are types of facial fractures involving the maxillary bone and surrounding structures in a usually bilateral and either horizontal, pyramidal or transverse way. LeFort fractures are classic in facial trauma...
" level osteotomy (most common). Sometimes the midface can be mobilised as well by using a Lefort II
LeFort fracture
Le Fort fractures are types of facial fractures involving the maxillary bone and surrounding structures in a usually bilateral and either horizontal, pyramidal or transverse way. LeFort fractures are classic in facial trauma...
, or Lefort III
LeFort fracture
Le Fort fractures are types of facial fractures involving the maxillary bone and surrounding structures in a usually bilateral and either horizontal, pyramidal or transverse way. LeFort fractures are classic in facial trauma...
osteotomy. These techniques are utilized extensively for children suffering from certain craniofacial abnormalities such as Crouzon syndrome
Crouzon syndrome
Crouzon syndrome is a genetic disorder known as a branchial arch syndrome. Specifically, this syndrome affects the first branchial arch, which is the precursor of the maxilla and mandible...
.
The jaws will be wired together (inter-maxillary fixation) using stainless steel wires during the surgery to insure the correct re-positioning of the bones. This in most cases is released before the patient wakes up. Some surgeons prefer to wire the jaws shut.
Complications
Like any other surgery, there can be some complications like bleeding, swelling, infection, nausea and vomiting. There could also be some numbness in the face due to nerve damage. The numbness may be either temporary, or, more rarely, permanent. In general, complications of this surgery occur, but not frequently.If the surgery involved the upper jaw, then the surgery could have an effect on the shape of the patient's nose. This can be minimised by careful planning and accurate execution of the surgical plan. Sometimes, this is considered part of the benefit.
Post operation
After orthognathic surgery, patients are often required to adhere to an all-liquid diet. After time, soft food can be introduced, and then hard food. Diet is very important after the surgery, to accelerate the healing process. Weight loss due to lack of appetite and the liquid diet is common, but should be avoided if possible. Normal recovery time can range from a few weeks for minor surgery, to up to a year for more complicated surgery.For some surgeries, pain may be minimal due to minor nerve damage and lack of feeling. Doctors will prescribe pain medication and prophylactic antibiotics to the patient. There is often a large amount of swelling around the jaw area, and in some cases bruising. Most of the swelling will disappear in the first few weeks, but some may remain for a few months.
The surgeon will see the patient for check-ups frequently, to check on the healing, check for infection, and to make sure nothing has moved. The frequency of visits will decrease over time. If the surgeon is unsatisfied with the way the bone is mending, he may recommend additional surgery to rectify whatever may have shifted. It is very important to avoid any chewing until the surgeon is satisfied with the healing.
See also
- Craniofacial surgeryCraniofacial surgeryCraniofacial surgery is a surgical subspecialty of maxillofacial surgery, plastic surgery, and ENT that deals with congenital and acquired deformities of the skull, face, and jaws. Although craniofacial treatment often involves manipulation of bone, craniofacial surgery is not tissue-specific,...
- Oral and maxillofacial surgeryOral and maxillofacial surgeryOral and maxillofacial surgery is surgery to correct a wide spectrum of diseases, injuries and defects in the head, neck, face, jaws and the hard and soft tissues of the oral and maxillofacial region. It is an internationally recognized surgical specialty...
- OrthodonticsOrthodonticsOrthodontics, orthodontia, or orthodonture is the first specialty of dentistry that is concerned with the study and treatment of malocclusions , which may be a result of tooth irregularity, disproportionate jaw relationships, or both...
- SurgerySurgerySurgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...

