
Ordered exponential
Encyclopedia
The ordered exponential (also called the path-ordered exponential) is a mathematical
object, defined in non-commutative algebra
s, which is equivalent to the exponential function
of the integral
in the commutative algebras. Therefore it is a function
, defined by means of a function from real number
s to a real or complex associative algebra
. In practice the values lie in matrix and operator algebras.
For the element A(t) from the algebra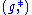 (set g with the non-commutative product *), where t is the "time parameter", the ordered exponential
(set g with the non-commutative product *), where t is the "time parameter", the ordered exponential 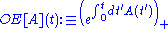 of A can be defined via one of several equivalent approaches:
of A can be defined via one of several equivalent approaches:
where the time moments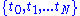 are defined as
are defined as 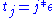 for
for 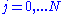 , and
, and 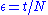 .
.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
object, defined in non-commutative algebra
Algebra
Algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning the study of the rules of operations and relations, and the constructions and concepts arising from them, including terms, polynomials, equations and algebraic structures...
s, which is equivalent to the exponential function
Exponential function
In mathematics, the exponential function is the function ex, where e is the number such that the function ex is its own derivative. The exponential function is used to model a relationship in which a constant change in the independent variable gives the same proportional change In mathematics,...
of the integral
Integral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
in the commutative algebras. Therefore it is a function
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
, defined by means of a function from real number
Real number
In mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
s to a real or complex associative algebra
Associative algebra
In mathematics, an associative algebra A is an associative ring that has a compatible structure of a vector space over a certain field K or, more generally, of a module over a commutative ring R...
. In practice the values lie in matrix and operator algebras.
For the element A(t) from the algebra
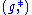 (set g with the non-commutative product *), where t is the "time parameter", the ordered exponential
(set g with the non-commutative product *), where t is the "time parameter", the ordered exponential 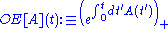 of A can be defined via one of several equivalent approaches:
of A can be defined via one of several equivalent approaches:
- As the limitLimit (mathematics)In mathematics, the concept of a "limit" is used to describe the value that a function or sequence "approaches" as the input or index approaches some value. The concept of limit allows mathematicians to define a new point from a Cauchy sequence of previously defined points within a complete metric...
of the ordered product of the infinitesimalInfinitesimalInfinitesimals have been used to express the idea of objects so small that there is no way to see them or to measure them. The word infinitesimal comes from a 17th century Modern Latin coinage infinitesimus, which originally referred to the "infinite-th" item in a series.In common speech, an...
exponentials: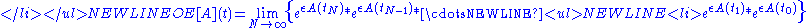
where the time moments
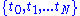 are defined as
are defined as 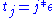 for
for 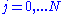 , and
, and 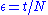 .
.- Via the initial value problemInitial value problemIn mathematics, in the field of differential equations, an initial value problem is an ordinary differential equation together with a specified value, called the initial condition, of the unknown function at a given point in the domain of the solution...
, where the OE[A](t) is the unique solution of the system of equations: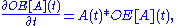
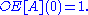
- Via an integral equationIntegral equationIn mathematics, an integral equation is an equation in which an unknown function appears under an integral sign. There is a close connection between differential and integral equations, and some problems may be formulated either way...
: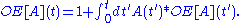
- Via Taylor seriesTaylor seriesIn mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point....
expansion: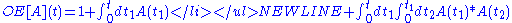
See also
- Related: Path-orderingPath-orderingIn theoretical physics, path-ordering is the procedure of ordering a product of many operators according to the value of one chosen parameter:...
describes essentially the same concept.
- Product integralProduct integralProduct integrals are a counterpart of standard integrals of infinitesimal calculus. They were first developed by the mathematician Vito Volterra in 1887 to solve systems of linear differential equations...
- Related: Path-ordering

