
Old Louisiana State Capitol
Encyclopedia
The Louisiana's Old State Capitol is a building in Baton Rouge
, Louisiana
, United States
that housed the Louisiana State Legislature
from the mid-19th century until the current capitol tower building
was constructed in 1929.
It is built both to look like and function like a castle and has led some locals to call it the Louisiana Castle, the Castle of Baton Rouge, the Castle on the River or the Museum of Political History, though most people just call it the old capitol building. When someone says "Old State Capitol" in Louisiana they are probably talking about this building and not the two towns that were formerly the capital city; New Orleans and Donaldsonville.
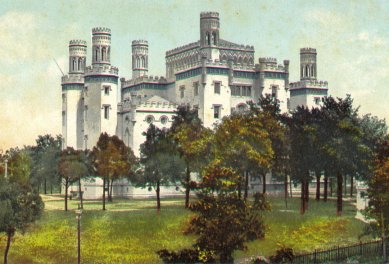 On September 21, 1847, the City of Baton Rouge donated to the state of Louisiana a $20,000 parcel of land for a state capitol building, taking the seat of the capitol away from the City of New Orleans. The land donated by the city for the capitol building stands high atop a Baton Rouge bluff facing the Mississippi River
On September 21, 1847, the City of Baton Rouge donated to the state of Louisiana a $20,000 parcel of land for a state capitol building, taking the seat of the capitol away from the City of New Orleans. The land donated by the city for the capitol building stands high atop a Baton Rouge bluff facing the Mississippi River
, a site that some believe was once marked by the red pole, or "le baton rouge," which French explorers claimed designated a Native American council meeting site. The state house itself is one of the most distinguished examples of Gothic Revival architecture in the United States.
New York architect James Dakin was hired to design the new Capitol building in Baton Rouge, and rather than mimic the federal Capitol Building in Washington, as so many other states had done, he conceived a Neo-Gothic medieval castle overlooking the Mississippi, complete with turrets and crenellations. Dakin referred to his design as "Castellated Gothic" due to its decoration with cast-iron, which was both cheaper and more durable than other building materials used at the time. In 1859, the Capitol was featured and favorably described in DeBow's Review
, the most prestigious periodical in the antebellum South. Mark Twain
, however, as a steamboat pilot in the 1850s, loathed the sight of it, "It is pathetic ... that a whitewashed castle, with turrets and things ... should ever have been built in this otherwise honorable place."
In 1862, during the Civil War, Union Admiral David Farragut
captured New Orleans and the seat of government retreated from Baton Rouge. The Union troops first used the "old gray castle," as it was once described, as a prison and then as a garrison for African-American troops under General Culver Grover. While used as a garrison the Old State Capitol caught fire twice. This, in turn, transformed the building into an empty, gutted shell abandoned by the Union troops. By 1882 the state house was totally reconstructed by architect and engineer William A. Freret, who is credited with the installation of the spiral staircase and stained glass dome, which are the focal points of the interior. The refurbished state house remained in use until 1932, when it was abandoned for the New Louisiana State Capitol
building. The Old State Capitol has since been used to house federally chartered veteran's organizations, and the seat of the Works Progress Administration
.
, The Louisiana Arts and Science Museum, St. Joseph Cathedral, Baton Rouge and the newly built and widely acclaimed Shaw Center
.
The museum inside the Old State Capitol houses many displays concerning political history in Louisiana. It is also the place where the gun that was used to kill Huey Long
is stored on display.
Admission is free and the building is wheelchair accessible. Museum hours are Tuesday through Saturday from 9 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. For more information, call 800-488-2968 or 225-342-0500.
Baton Rouge, Louisiana
Baton Rouge is the capital of the U.S. state of Louisiana. It is located in East Baton Rouge Parish and is the second-largest city in the state.Baton Rouge is a major industrial, petrochemical, medical, and research center of the American South...
, Louisiana
Louisiana
Louisiana is a state located in the southern region of the United States of America. Its capital is Baton Rouge and largest city is New Orleans. Louisiana is the only state in the U.S. with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are local governments equivalent to counties...
, United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
that housed the Louisiana State Legislature
Louisiana State Legislature
The Louisiana State Legislature is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Louisiana. It is bicameral body, comprising the lower house, the Louisiana House of Representatives with 105 representatives, and the upper house, the Louisiana Senate with 39 senators...
from the mid-19th century until the current capitol tower building
Louisiana State Capitol
The Louisiana State Capitol building is the capitol building of the state of Louisiana, located in Baton Rouge. The capitol houses the Louisiana State Legislature, the governor's office, and parts of the executive branch...
was constructed in 1929.
It is built both to look like and function like a castle and has led some locals to call it the Louisiana Castle, the Castle of Baton Rouge, the Castle on the River or the Museum of Political History, though most people just call it the old capitol building. When someone says "Old State Capitol" in Louisiana they are probably talking about this building and not the two towns that were formerly the capital city; New Orleans and Donaldsonville.
History
In 1846, the Louisiana Legislature in New Orleans decided to move the seat of government to Baton Rouge. As in many states, representatives from other parts of Louisiana feared a concentration of power in the state's largest city. In 1840, New Orleans' population was around 102,000, fourth largest in the U.S. The 1840 population of Baton Rouge, on the other hand, was only 2,269.
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
, a site that some believe was once marked by the red pole, or "le baton rouge," which French explorers claimed designated a Native American council meeting site. The state house itself is one of the most distinguished examples of Gothic Revival architecture in the United States.
New York architect James Dakin was hired to design the new Capitol building in Baton Rouge, and rather than mimic the federal Capitol Building in Washington, as so many other states had done, he conceived a Neo-Gothic medieval castle overlooking the Mississippi, complete with turrets and crenellations. Dakin referred to his design as "Castellated Gothic" due to its decoration with cast-iron, which was both cheaper and more durable than other building materials used at the time. In 1859, the Capitol was featured and favorably described in DeBow's Review
DeBow's Review
DeBow's Review was a widely circulated magazine of "agricultural, commercial, and industrial progress and resource" in the American South during the upper middle of the 19th century, from 1846 until 1884. It bore the name of its first editor, James Dunwoody Brownson DeBow DeBow's Review was a...
, the most prestigious periodical in the antebellum South. Mark Twain
Mark Twain
Samuel Langhorne Clemens , better known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American author and humorist...
, however, as a steamboat pilot in the 1850s, loathed the sight of it, "It is pathetic ... that a whitewashed castle, with turrets and things ... should ever have been built in this otherwise honorable place."
In 1862, during the Civil War, Union Admiral David Farragut
David Farragut
David Glasgow Farragut was a flag officer of the United States Navy during the American Civil War. He was the first rear admiral, vice admiral, and admiral in the United States Navy. He is remembered in popular culture for his order at the Battle of Mobile Bay, usually paraphrased: "Damn the...
captured New Orleans and the seat of government retreated from Baton Rouge. The Union troops first used the "old gray castle," as it was once described, as a prison and then as a garrison for African-American troops under General Culver Grover. While used as a garrison the Old State Capitol caught fire twice. This, in turn, transformed the building into an empty, gutted shell abandoned by the Union troops. By 1882 the state house was totally reconstructed by architect and engineer William A. Freret, who is credited with the installation of the spiral staircase and stained glass dome, which are the focal points of the interior. The refurbished state house remained in use until 1932, when it was abandoned for the New Louisiana State Capitol
Louisiana State Capitol
The Louisiana State Capitol building is the capitol building of the state of Louisiana, located in Baton Rouge. The capitol houses the Louisiana State Legislature, the governor's office, and parts of the executive branch...
building. The Old State Capitol has since been used to house federally chartered veteran's organizations, and the seat of the Works Progress Administration
Works Progress Administration
The Works Progress Administration was the largest and most ambitious New Deal agency, employing millions of unskilled workers to carry out public works projects, including the construction of public buildings and roads, and operated large arts, drama, media, and literacy projects...
.
Museum of Political History
Restored in the 1990s, the Old State Capitol is now the Museum of Political History. Most recently, the exterior façade has been refurbished with shades of tan stucco, in noticeable contrast to its former stone coloring. Numerous events are held there including an annual ball wherein the participants re-enact dances and traditions of French culture while wearing traditional 18th and 19th century dress. It is located in downtown Baton Rouge within walking distance to the new state capital tower and all of the many culturally significant buildings there. Some of these include the Old Louisiana Governor's MansionOld Louisiana Governor's Mansion
The Old Louisiana Governor's Mansion is located at 502 North Blvd. between Royal and St. Charles Streets in Baton Rouge and was used between 1930 and 1961; a new residence was completed in 1963. When the original Louisiana Governor's mansion was termite-infested during the beginning of Huey Long's...
, The Louisiana Arts and Science Museum, St. Joseph Cathedral, Baton Rouge and the newly built and widely acclaimed Shaw Center
Shaw Center for the Arts
The Shaw Center for the Arts is a 125,000 square foot performing art venue, fine arts museum, and education center located at 100 Lafayette Street in downtown Baton Rouge, Louisiana. It opened in 2005...
.
The museum inside the Old State Capitol houses many displays concerning political history in Louisiana. It is also the place where the gun that was used to kill Huey Long
Huey Long
Huey Pierce Long, Jr. , nicknamed The Kingfish, served as the 40th Governor of Louisiana from 1928–1932 and as a U.S. Senator from 1932 to 1935. A Democrat, he was noted for his radical populist policies. Though a backer of Franklin D...
is stored on display.
Admission is free and the building is wheelchair accessible. Museum hours are Tuesday through Saturday from 9 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. For more information, call 800-488-2968 or 225-342-0500.
External links
- Louisiana's Old State Capitol and Museum of Political History - official site
- Louisiana's Old State Capitol Foundation- official site
- Governor Henry Watkins Allen Memorial by La-Cemeteries
- Survey number HABS LA-1132 - Louisiana State Capitol, North Boulevard, Saint Philip, America & Front Streets, Baton Rouge, East Baton Rouge Parish, LA
- Baton Rouge Guide has information and photos on the old state capitol

