
Nuclear magneton
Encyclopedia
The nuclear magneton is a physical constant
of magnetic moment
, defined by:
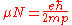
where:
In SI units, its value is approximately:
The nuclear magneton is the natural unit for expressing magnetic dipole moments of heavy particles such as nucleon
s and atomic nuclei
. On the contrary, the dipole moment of the electron, which is much higher as a consequence of much higher charge-to-mass ratio
, is usually expressed in corresponding units of the Bohr magneton.
Physical constant
A physical constant is a physical quantity that is generally believed to be both universal in nature and constant in time. It can be contrasted with a mathematical constant, which is a fixed numerical value but does not directly involve any physical measurement.There are many physical constants in...
of magnetic moment
Magnetic moment
The magnetic moment of a magnet is a quantity that determines the force that the magnet can exert on electric currents and the torque that a magnetic field will exert on it...
, defined by:
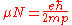
where:
- e is the elementary chargeElementary chargeThe elementary charge, usually denoted as e, is the electric charge carried by a single proton, or equivalently, the absolute value of the electric charge carried by a single electron. This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. To avoid confusion over its sign, e is sometimes called...
, - ħ is the reduced Planck constant,
- mp is the protonProtonThe proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
rest mass
In SI units, its value is approximately:
- μN =
The nuclear magneton is the natural unit for expressing magnetic dipole moments of heavy particles such as nucleon
Nucleon
In physics, a nucleon is a collective name for two particles: the neutron and the proton. These are the two constituents of the atomic nucleus. Until the 1960s, the nucleons were thought to be elementary particles...
s and atomic nuclei
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
. On the contrary, the dipole moment of the electron, which is much higher as a consequence of much higher charge-to-mass ratio
Mass-to-charge ratio
The mass-to-charge ratio ratio is a physical quantity that is widely used in the electrodynamics of charged particles, e.g. in electron optics and ion optics. It appears in the scientific fields of lithography, electron microscopy, cathode ray tubes, accelerator physics, nuclear physics, Auger...
, is usually expressed in corresponding units of the Bohr magneton.
External links
- Nuclear magneton, value from CODATA

