
Norwegian railway signalling
Encyclopedia
The signalling system used on the rail transport in Norway
is regulated by the Regulations of December 4, 2001 no. 1336 about signals and signs on the state's railway network and connected private tracks.
The first signalling system on the Norwegian railway system was a mechanically operated semaphore system introduced at Drammen
station in 1893. The first electrically operated light signal system was delivered by AEG
in 1924. Today, only electrically operated light signals are used.
. Developed by Ascom Radiocom, it was only installed on the primary railway lines. The system allows radio communication between a train dispatcher, and train drivers and other users involved in railway operations. Scanet was also connected to the automatic train control
system. However, several lines lack the system, including the Arendal Line
, the Flåm Line, the Meråker Line, the Nordland Line, the Rauma Line, the Røros Line, the Inner Østfold Line, the northern part of the Gjøvik Line, and several tunnels along the Bergen Line and the Sørland Line. The Åsta accident
in 2000 spurred the need to give all parts of the railway coverage with train radio. On these lines, the dispatcher and drivers must communicate using the Nordic Mobile Telephone
(NMT 450) standard, which by 2002 was being planned terminated by Telenor
.
Scanet was replaced by Global System for Mobile Communication – Railway (GSM-R) between 2004 2007, with the systems first being installed on the lines without Scanet. The system, delivered by Nokia Siemens Networks
, was on time and on budget, and made Norway one of the first countries to fully implement the system throughout Europe. After GSM-R was fully implemented on 1 November, Scanet was gradually closed. The new system has been characterized as simpler to use and giving better audio quality than Scanet. The implementation cost 1.8 billion Norwegian krone
and covers the entire network.
. Other nearby countries reverse the role of the single green aspect and double green aspect.
. To prevent this, the yellow light would be proved to be operating before the green light is displayed (that is, the yellow is shown before the green, if the yellow fails, the green isn't shown and the signal stays totally dark).
warning system, also used on Perth
's suburban railway network.
Rail transport in Norway
The Norwegian railway system comprises 4,087 km of track of which 2,622 km is electrified and 242 km double track. There are 696 tunnels and 2760 bridges....
is regulated by the Regulations of December 4, 2001 no. 1336 about signals and signs on the state's railway network and connected private tracks.
The first signalling system on the Norwegian railway system was a mechanically operated semaphore system introduced at Drammen
Drammen
Drammen is a city in Buskerud County, Norway. The port and river city of Drammen is centrally located in the eastern and most populated part of Norway.-Location:...
station in 1893. The first electrically operated light signal system was delivered by AEG
AEG
Allgemeine Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft was a German producer of electrical equipment founded in 1883 by Emil Rathenau....
in 1924. Today, only electrically operated light signals are used.
Train radio
Between 1993 and 1996, NSB rolled out the analog train radio system ScanetScanet
Scanet is a defunct, analog train radio system used by the Norwegian State Railways and later the Norwegian National Rail Administration. The system was developed by Ascom Radiocom and was installed on the primary Norwegian railways between 1993 and 1996...
. Developed by Ascom Radiocom, it was only installed on the primary railway lines. The system allows radio communication between a train dispatcher, and train drivers and other users involved in railway operations. Scanet was also connected to the automatic train control
Automatic Train Control
Automatic Train Control is a train protection system for railways, ensuring the safe and smooth operation of trains on ATC-enabled lines. Its main advantages include making possible the use of cab signalling instead of track-side signals and the use of smooth deceleration patterns in lieu of the...
system. However, several lines lack the system, including the Arendal Line
Arendal Line
The Arendal Line is a long railway line between Arendal and Simonstad in Norway. At Nelaug, north of Arendal, the line intersects with the Sørland Line. The southern section is electrified and provides a feeder passenger service. The line originally ran north from Arendal to Treungen and the...
, the Flåm Line, the Meråker Line, the Nordland Line, the Rauma Line, the Røros Line, the Inner Østfold Line, the northern part of the Gjøvik Line, and several tunnels along the Bergen Line and the Sørland Line. The Åsta accident
Åsta accident
The Åsta accident was a railway accident that occurred at 13:12:25 on 4 January 2000 at Åsta in Åmot, south of Rena in Østerdalen, Norway. A train from Trondheim collided with a local train from Hamar on Rørosbanen resulting in an explosive fire...
in 2000 spurred the need to give all parts of the railway coverage with train radio. On these lines, the dispatcher and drivers must communicate using the Nordic Mobile Telephone
Nordic Mobile Telephone
NMT is the first fully automatic cellular phone system...
(NMT 450) standard, which by 2002 was being planned terminated by Telenor
Telenor
Telenor Group is the incumbent telecommunications company in Norway, with headquarters located at Fornebu, close to Oslo. Today, Telenor Group is mostly an international wireless carrier with operations in Scandinavia, Eastern Europe and Asia, working predominantly under the Telenor brand...
.
Scanet was replaced by Global System for Mobile Communication – Railway (GSM-R) between 2004 2007, with the systems first being installed on the lines without Scanet. The system, delivered by Nokia Siemens Networks
Nokia Siemens Networks
Nokia Siemens Networks is a global data networking and telecommunications equipment company headquartered in Espoo, Finland. It is a joint venture between Nokia of Finland and Siemens of Germany...
, was on time and on budget, and made Norway one of the first countries to fully implement the system throughout Europe. After GSM-R was fully implemented on 1 November, Scanet was gradually closed. The new system has been characterized as simpler to use and giving better audio quality than Scanet. The implementation cost 1.8 billion Norwegian krone
Norwegian krone
The krone is the currency of Norway and its dependent territories. The plural form is kroner . It is subdivided into 100 øre. The ISO 4217 code is NOK, although the common local abbreviation is kr. The name translates into English as "crown"...
and covers the entire network.
Signalling remedies
The following signalling remedies are used:- Signal flags
- Hand-held signal lamps
- Signal whistle
- The signal giver's arms
- Fixed light signals
- Fixed sound signals
- Signal signs
- Orientation poles
- Locomotive whistle
- Locomotive and train signal lamps
The fundamental meaning of the signal colors
- Red always indicates "stop".
- Violet indicates that the associated level crossing signal shows "Stop short of the level crossing".
- Yellow indicates "caution".
- Green indicates "permission to run".
- White indicates "clear line".
Main signals
| Signal | Meaning | Used in | |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Signal 20A – Stop – flashes | The train must stop short of the signal. | Station entry signals, block signals. |
  |
Signal 20B – Stop | The train must stop short of the signal. | Station exit signals, inner signals. |
  |
Signal 21 – Proceed (to diverging route) | The train can proceed, usually via one or more diverging switches Railroad switch A railroad switch, turnout or [set of] points is a mechanical installation enabling railway trains to be guided from one track to another at a railway junction.... . |
Station entry signals, station exit signals, inner signals, block signals. |
 |
Signal 22 – Proceed | The train can proceed, not via diverging switches. | Station entry signals, station exit signals, inner signals, block signals. |
Fail safe
If one of the green lights in signal 22 fails, the indication becomes the lower speed signal 21 – this is fail-safeFail-safe
A fail-safe or fail-secure device is one that, in the event of failure, responds in a way that will cause no harm, or at least a minimum of harm, to other devices or danger to personnel....
. Other nearby countries reverse the role of the single green aspect and double green aspect.
Distant signals
| Image | Signal | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
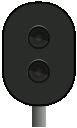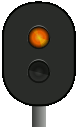 |
Signal 23 – Expect stop – flashes | The associated main signal shows signal 20A or 20B. |
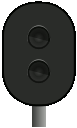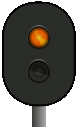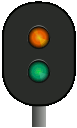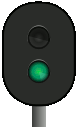 |
Signal 24 – Expect to proceed (to diverging route) – flashes | The associated main signal shows signal 21. |
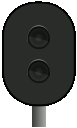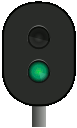 |
Signal 25 – Expect to proceed – flashes | The associated main signal shows signal 22. |
Wrong-side failure
If the yellow light in signal 24 fails, the signal displays a higher speed indication, which would be a wrong-side failureWrong-side failure
A wrong side failure describes a failure condition in a piece of railway signalling equipment that results in an unsafe state.A typical example would be a signal showing a 'proceed' aspect when it should be showing a 'stop' or 'danger' aspect, resulting in a "false clear"...
. To prevent this, the yellow light would be proved to be operating before the green light is displayed (that is, the yellow is shown before the green, if the yellow fails, the green isn't shown and the signal stays totally dark).
Warning systems
Norway uses the Ericsson ATPAutomatic Train Protection
Automatic Train Protection in Great Britain refers to either of two implementations of a train protection system installed in some trains in order to help prevent collisions through a driver's failure to observe a signal or speed restriction...
warning system, also used on Perth
Perth, Western Australia
Perth is the capital and largest city of the Australian state of Western Australia and the fourth most populous city in Australia. The Perth metropolitan area has an estimated population of almost 1,700,000....
's suburban railway network.

