
Normality (chemistry)
Encyclopedia
In chemistry
, the normality of a solution is defined as the molar concentration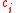 divided by an equivalence factor
divided by an equivalence factor 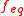 :
:
(H2SO4) is a diprotic acid
. Since only 0.5 mol of H2SO4 are needed to produce 1 mol of H+, the equivalence factor is:
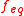 (H2SO4) = 0.5
(H2SO4) = 0.5
If the concentration of a sulfuric acid solution is c(H2SO4) = 1 mol/L, then its normality is 2 N. It can also be called a "2 normal" solution.
Similarly, for a solution with c(H3PO4) = 1 mol/L, the normality is 3 N because phosphoric acid
contains 3 acidic H atoms.
. The same solution can possess different normalities for different reactions. The definition of the equivalence factor varies depending on the type of chemical reaction that is discussed: It may refer to equations, bases, redox species, precipitating ions, or isotopes. For example, a solution of Mg2+ that is 2 N with respect to a Cl- ion, is only 1 N with respect to an O2- ion. Since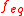 may not be unequivocal, IUPAC and NIST discourage the use of normality.
may not be unequivocal, IUPAC and NIST discourage the use of normality.
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, the normality of a solution is defined as the molar concentration
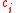 divided by an equivalence factor
divided by an equivalence factor 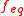 :
:- normality
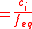
Units
The unit symbol "N" is used to denote "mol/L" when referring to normality. Alternatively, the symbol "Eq/L" is sometimes used. Although losing favor, medical reporting of serum concentrations in "mEq/L" (=0.001 N) still occurs.Usage
There are three common areas where normality is used as a measure of reactive species in solution:- In acid-base chemistry, normality is used to express the concentration of protons (H+) or hydroxide ions (OH-) in a solution. Here,
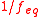 is an integerIntegerThe integers are formed by the natural numbers together with the negatives of the non-zero natural numbers .They are known as Positive and Negative Integers respectively...
is an integerIntegerThe integers are formed by the natural numbers together with the negatives of the non-zero natural numbers .They are known as Positive and Negative Integers respectively...
value. Each solute can produce one or more equivalents of reactive species when dissolved. - In redoxRedoxRedox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
reactions, the equivalence factor describes the number of electronElectronThe electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s that an oxidizing or reducing agent can accept or donate. Here,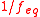 can have a fractional (non-integer) value.
can have a fractional (non-integer) value. - In precipitationPrecipitation (chemistry)Precipitation is the formation of a solid in a solution or inside anothersolid during a chemical reaction or by diffusion in a solid. When the reaction occurs in a liquid, the solid formed is called the precipitate, or when compacted by a centrifuge, a pellet. The liquid remaining above the solid...
reactions, the equivalence factor measures the number of ions which will precipitate in a given reaction. Here,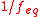 is an integer value.
is an integer value.
Examples
Normality can be used for acid-base titrations. For example, sulfuric acidSulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
(H2SO4) is a diprotic acid
Diprotic acid
A diprotic acid is an acid such as H2SO4 that contains within its molecular structure two hydrogen atoms per molecule capable of dissociating in water. The complete dissociation of diprotic acids is of the same form as sulfuric acid:The dissociation does not happen all at once due to the two...
. Since only 0.5 mol of H2SO4 are needed to produce 1 mol of H+, the equivalence factor is:
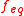 (H2SO4) = 0.5
(H2SO4) = 0.5If the concentration of a sulfuric acid solution is c(H2SO4) = 1 mol/L, then its normality is 2 N. It can also be called a "2 normal" solution.
Similarly, for a solution with c(H3PO4) = 1 mol/L, the normality is 3 N because phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid, also known as orthophosphoric acid or phosphoric acid, is a mineral acid having the chemical formula H3PO4. Orthophosphoric acid molecules can combine with themselves to form a variety of compounds which are also referred to as phosphoric acids, but in a more general way...
contains 3 acidic H atoms.
Criticism
Normality is an ambiguous measure of the concentration of a solution. It needs a definition of the equivalence factor, which depends on the definition of equivalentsEquivalent (chemistry)
The equivalent , sometimes termed the molar equivalent, is a unit of amount of substance used in chemistry and the biological sciences.The equivalent is formally defined as the amount of a substance which will either:...
. The same solution can possess different normalities for different reactions. The definition of the equivalence factor varies depending on the type of chemical reaction that is discussed: It may refer to equations, bases, redox species, precipitating ions, or isotopes. For example, a solution of Mg2+ that is 2 N with respect to a Cl- ion, is only 1 N with respect to an O2- ion. Since
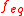 may not be unequivocal, IUPAC and NIST discourage the use of normality.
may not be unequivocal, IUPAC and NIST discourage the use of normality.

