
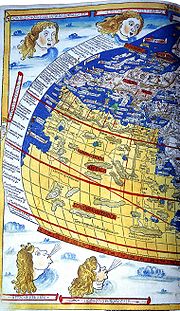
Nicolaus Germanus
Encyclopedia
Globe
A globe is a three-dimensional scale model of Earth or other spheroid celestial body such as a planet, star, or moon...
s depicting earth and sky in 1477, thus predating the Erdapfel
Erdapfel
The Erdapfel produced by Martin Behaim in 1492 is considered to be the oldest surviving terrestrial globe. It is constructed of a laminated linen ball in two halves, reinforced with wood and overlaid with a map painted by Georg Glockendon....
of Martin Behaim
Martin Behaim
Martin Behaim , was a German mariner, artist, cosmographer, astronomer, philosopher, geographer and explorer in service to the King of Portugal.-Biography:The Behaim family had immigrated to Nuremberg because of religious persecution around...
.
The places and dates of his birth and death as well as his exact name are unknown. He is also called "Donis", "Donnus", "Donmus" or "Donus", abbreviated forms of "Dominus". and is sometimes referred to as a monk
Monk
A monk is a person who practices religious asceticism, living either alone or with any number of monks, while always maintaining some degree of physical separation from those not sharing the same purpose...
of the Benedictine order possibly from Reichenbach Priory (Baden-Württemberg)
Reichenbach Priory (Baden-Württemberg)
Reichenbach Monastery or Priory was a house of the Benedictine Order, located at Klosterreichenbach, now part of Baiersbronn in Baden-Württemberg in Germany....
.
In 1477, two years after the opening of the Vatican Library
Vatican Library
The Vatican Library is the library of the Holy See, currently located in Vatican City. It is one of the oldest libraries in the world and contains one of the most significant collections of historical texts. Formally established in 1475, though in fact much older, it has 75,000 codices from...
, Germanus created a globe each for earth and sky, for which he was paid 200 ducat
Ducat
The ducat is a gold coin that was used as a trade coin throughout Europe before World War I. Its weight is 3.4909 grams of .986 gold, which is 0.1107 troy ounce, actual gold weight...
s on 11 December 1477 according to a receipt. An additional three ducats were paid the next day for the adding of the papal coat of arms, and four more on 20 December for two covers. The globes are listed in an inventory of 1481. The marchesa of Mantua
Mantua
Mantua is a city and comune in Lombardy, Italy and capital of the province of the same name. Mantua's historic power and influence under the Gonzaga family, made it one of the main artistic, cultural and notably musical hubs of Northern Italy and the country as a whole...
, Isabella, asked for copies in 1505 (Intendiamo, che ne la libraria dil papa sono due spere solide: In una è depicto el Mapamundo, in l'altra li Signi Celesti, cio è el Zodiaco [...])
The globes were kept in Salle Pontifica (Magna Secreta) until they were lost in the Sacco di Roma of 1527. The earth globe of Germanus is considered the first modern to be documented. During production, he invented the "Donis" map projection
Map projection
A map projection is any method of representing the surface of a sphere or other three-dimensional body on a plane. Map projections are necessary for creating maps. All map projections distort the surface in some fashion...
, in which parallels of latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
are made equidistant, but meridians
Meridian (geography)
A meridian is an imaginary line on the Earth's surface from the North Pole to the South Pole that connects all locations along it with a given longitude. The position of a point along the meridian is given by its latitude. Each meridian is perpendicular to all circles of latitude...
converge toward the poles.
External links
- Cosmographia Claudii Ptolomaei Alexandrini, 1467
- http://deposit.ddb.de/online/inkunabel/boe206.htm
- Mitteleuropakarte – Germania tota tabella – von Nicolaus Cusanus in der Redaktion von Nicolaus Germanus, ca. 1478, nach ihrer Inkunabeledition, Eystat 1491.
- Während der letzten Hälfte des 15. Jahrhunderts. fügt der deutsche Mönch Nicolaus Germanus die ersten modernen und korrigierten Landkarten zur Geographie des Ptolemäus hinzu.

