Neoplasia
Encyclopedia
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
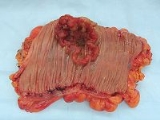
. The growth of neoplastic cells exceeds and is not coordinated with that of the normal tissues around it. The growth persists in the same excessive manner even after cessation of the stimuli. It usually causes a lump or tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
. Neoplasms may be benign, pre-malignant (carcinoma in situ
Carcinoma in situ
Carcinoma in situ is an early form of cancer that is defined by the absence of invasion of tumor cells into the surrounding tissue, usually before penetration through the basement membrane. In other words, the neoplastic cells proliferate in their normal habitat, hence the name "in situ"...
) or malignant (cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
).
In modern medicine, the term tumor means a neoplasm that has formed a lump. In the past, the term tumor was used differently. Some neoplasms do not cause a lump.
Types
A neoplasm can be benign, potentially malignant (pre-cancer), or malignant (cancerCancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
).
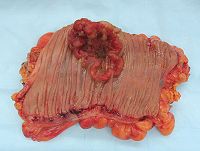
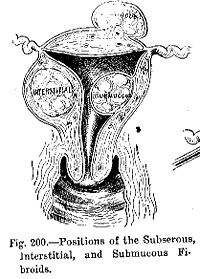
- Benign neoplasms include uterine fibroidsUterine fibroidsA uterine fibroid is a benign tumor that originates from the smooth muscle layer and the accompanying connective tissue of the uterus.Fibroids are the most common benign tumors in...
and melanocytic neviNevusNevus is the medical term for sharply-circumscribed and chronic lesions of the skin. These lesions are commonly named birthmarks and moles. Nevi are benign by definition...
(skin moles). They do not transform into cancerCancerCancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
. - Potentially malignant neoplasms include carcinoma in situCarcinoma in situCarcinoma in situ is an early form of cancer that is defined by the absence of invasion of tumor cells into the surrounding tissue, usually before penetration through the basement membrane. In other words, the neoplastic cells proliferate in their normal habitat, hence the name "in situ"...
. They do not invade and destroy but, given enough time, will transform into a cancerCancerCancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
. - Malignant neoplasms are commonly called cancerCancerCancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
. They invade and destroy the surrounding tissue, may form metastasesMetastasisMetastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
and eventually kill the host.
Difficulty of definition
Because neoplasia includes very different diseases, it is difficult to find an all-encompassing definition. The definition of the British oncologistOncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with cancer...
R.A. Willis is widely cited: A neoplasm is an abnormal mass of tissue, the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues, and persists in the same excessive manner after cessation of the stimulus which evoked the change.
This definition is criticized because some neoplasms, such as nevi, are not progressive.
Clonality
Neoplastic tumors often contain more than one type of cell, but their initiation and continued growth is usually dependent on a single population of neoplastic cells. These cells are presumed to be clonalClone (cell biology)
A clone is a group of identical cells that share a common ancestry, meaning they are derived from the same mother cell.Clonality implies the state of a cell or a substance being derived from one source or the other...
- that is, they are descended from a single progenitor cell.
Sometimes, the neoplastic cells all carry the same genetic
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
or epigenetic
Epigenetics
In biology, and specifically genetics, epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene expression or cellular phenotype caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence – hence the name epi- -genetics...
anomaly that becomes evidence for clonality. For lymphoid neoplasms, e.g. lymphoma
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a cancer in the lymphatic cells of the immune system. Typically, lymphomas present as a solid tumor of lymphoid cells. Treatment might involve chemotherapy and in some cases radiotherapy and/or bone marrow transplantation, and can be curable depending on the histology, type, and stage...
and leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia or leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called "blasts". Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases...
, clonality is proven by the amplification of a single rearrangement of their immunoglobulin gene (for B cell
B cell
B cells are lymphocytes that play a large role in the humoral immune response . The principal functions of B cells are to make antibodies against antigens, perform the role of antigen-presenting cells and eventually develop into memory B cells after activation by antigen interaction...
lesions) or T-cell receptor gene (for T cell
T cell
T cells or T lymphocytes belong to a group of white blood cells known as lymphocytes, and play a central role in cell-mediated immunity. They can be distinguished from other lymphocytes, such as B cells and natural killer cells , by the presence of a T cell receptor on the cell surface. They are...
lesions). The demonstration of clonality is now considered to be necessary to identify a lymphoid cell proliferation as neoplastic.
It is tempting to define neoplasms as clonal cellular proliferations but the demonstration of clonality is not always possible. Therefore, clonality is not required in the definition of neoplasia.
Neoplasia vs. tumor
TumorTumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
(Latin for swelling, one of the cardinal signs of inflammation) originally meant any form of swelling
Swelling (medical)
In medical parlance, swelling is the transient enlargement or protuberance in the body and may include tumors. According to cause, it may be congenital, traumatic, inflammatory, neoplastic or miscellaneous....
, neoplastic or not. Current English, however, both medical and non-medical, uses tumor as a synonym of neoplasm.
Some neoplasms do not form a tumor. These include leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia or leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called "blasts". Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases...
and most forms of carcinoma in situ
Carcinoma in situ
Carcinoma in situ is an early form of cancer that is defined by the absence of invasion of tumor cells into the surrounding tissue, usually before penetration through the basement membrane. In other words, the neoplastic cells proliferate in their normal habitat, hence the name "in situ"...
.

