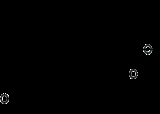
Moronic acid
Encyclopedia
Moronic acid is a natural triterpene
. Moronic acid can be extracted from Rhus javanica, a sumac plant traditionally believed to hold medicinal applications. The molecule has also been extracted from Mistletoe
(Phoradendron reichenbachianum
).
Bevirimat
, a derivative of the related triterpenoid
betulinic acid
, is under development as an anti-HIV drug; however, moronic acid has shown better antiviral profiles in vitro
than bevirimat. A particular moronic acid derivative
showed potent anti-HIV activity with EC50
values of 0.0085 μM against NL4-3, 0.021 μM against PI-R (a multiple protease inhibitor resistant strain), and 0.13 μM against FHR-2 (an HIV strain resistant to bevirimat). This derivative has become a new lead for clinical trials and is also active against herpes simplex virus 1.
Terpene
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds, produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers, though also by some insects such as termites or swallowtail butterflies, which emit terpenes from their osmeterium. They are often strong smelling and thus may have had a protective...
. Moronic acid can be extracted from Rhus javanica, a sumac plant traditionally believed to hold medicinal applications. The molecule has also been extracted from Mistletoe
Mistletoe
Mistletoe is the common name for obligate hemi-parasitic plants in several families in the order Santalales. The plants in question grow attached to and within the branches of a tree or shrub.-Mistletoe in the genus Viscum:...
(Phoradendron reichenbachianum
Phoradendron
Phoradendron is a genus of mistletoes, native to warm temperate and tropical regions of the Americas. Traditionally, the genus has been placed in the family Viscaceae, but recent genetic research acknowledged by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group shows this family to be correctly placed within a larger...
).
Bevirimat
Bevirimat
Bevirimat is an anti-HIV drug derived from a betulinic acid-like compound, first isolated from Syzygium claviflorum, a Chinese herb. It is believed to inhibit HIV by a novel mechanism, so-called maturation inhibition. It is not currently U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved, but is...
, a derivative of the related triterpenoid
Triterpenoid
Triterpenoids are terpenoid derviatives of triterpene molecules.They may have useful anti-cancer properties.Notable examples*Betulinic acid, possible anti-cancer drug*Bardoxolone methyl, inflammation modulator*Triterpenoid saponins...
betulinic acid
Betulinic acid
Betulinic acid is a naturally occurring pentacyclic triterpenoid which has anti-retroviral, anti-malarial, and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as a more recently discovered potential as an anticancer agent, by inhibition of topoisomerase...
, is under development as an anti-HIV drug; however, moronic acid has shown better antiviral profiles in vitro
In vitro
In vitro refers to studies in experimental biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological context in order to permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms. Colloquially, these experiments...
than bevirimat. A particular moronic acid derivative
Derivative (chemistry)
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by some chemical or physical process. In the past it was also used to mean a compound that can be imagined to arise from another compound, if one atom is replaced with another atom or group of atoms, but modern...
showed potent anti-HIV activity with EC50
EC50
The term half maximal effective concentration refers to the concentration of a drug, antibody or toxicant which induces a response halfway between the baseline and maximum after some specified exposure time...
values of 0.0085 μM against NL4-3, 0.021 μM against PI-R (a multiple protease inhibitor resistant strain), and 0.13 μM against FHR-2 (an HIV strain resistant to bevirimat). This derivative has become a new lead for clinical trials and is also active against herpes simplex virus 1.
External links
- CTD's Moronic acid page from the Comparative Toxicogenomics DatabaseComparative Toxicogenomics DatabaseThe Comparative Toxicogenomics Database is a public website and research tool that curates scientific data describing relationships between chemicals, genes, and human diseases....
- NLM/NIH Medical Subject Heading
- KEGG Terpinoid Synthesis Pathway
- Molecules with silly names

