
Mixed-linkage glucan
Encyclopedia
Mixed-linkage glucan sometimes incorrectly referred to as beta-glucan
, is a hemicellulosic
polysaccharide
consisting of β-D(1-3) ad β-D(1-4) linked glucosyl residues
. MLG is highly prevalent within the Poales
, where it has important properties in the diet
. In addition, although thought to be confined to the Poales, MLG has been found to be highly prevalent in plants of the distantly evolutionarily related genus
Equisetum.
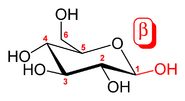 MLG is composed of β-D(1-3) and β-D(1-4)-linked glucosyl residues. Typically there are regions of 2-5 β-D(1-4)-linked residues separated by β-D(1-3)-linkages. The β-D(1-4)-linked residues form rigid regions of the structure while the β-D(1-3)-links are flexible.
MLG is composed of β-D(1-3) and β-D(1-4)-linked glucosyl residues. Typically there are regions of 2-5 β-D(1-4)-linked residues separated by β-D(1-3)-linkages. The β-D(1-4)-linked residues form rigid regions of the structure while the β-D(1-3)-links are flexible.
mixed-linkage glucan : xyloglucan endotransglucosylase
within Equiseta suggest that the role of MLG in each may be different.
Beta-glucan
β-Glucans are polysaccharides of D-glucose monomers linked by β-glycosidic bonds. β-glucans are a diverse group of molecules that can vary with respect to molecular mass, solubility, viscosity, and three-dimensional configuration...
, is a hemicellulosic
Hemicellulose
A hemicellulose is any of several heteropolymers , such as arabinoxylans, present along with cellulose in almost all plant cell walls. While cellulose is crystalline, strong, and resistant to hydrolysis, hemicellulose has a random, amorphous structure with little strength...
polysaccharide
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides are long carbohydrate molecules, of repeated monomer units joined together by glycosidic bonds. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure,...
consisting of β-D(1-3) ad β-D(1-4) linked glucosyl residues
Glycosidic bond
In chemistry, a glycosidic bond is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate....
. MLG is highly prevalent within the Poales
Poales
Poales is a large order of flowering plants in the monocotyledons, and includes families of plants such as the grasses, bromeliads, and sedges. Sixteen plant families are currently recognized by botanists to be part of Poales....
, where it has important properties in the diet
Diet (nutrition)
In nutrition, diet is the sum of food consumed by a person or other organism. Dietary habits are the habitual decisions an individual or culture makes when choosing what foods to eat. With the word diet, it is often implied the use of specific intake of nutrition for health or weight-management...
. In addition, although thought to be confined to the Poales, MLG has been found to be highly prevalent in plants of the distantly evolutionarily related genus
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
Equisetum.
Structure

Roles in the diet
MLGs exhibit the physiological properties of dietary fibres and the functional properties of viscous and gel-forming food hydrocolloids.Functions in planta
The prevalence of MLG within the poales and Equisetum suggests a definite role in their growth. However the presence of the enzymeEnzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
mixed-linkage glucan : xyloglucan endotransglucosylase
Mixed-linkage glucan : Xyloglucan endotransglucosylase
Mixed-linkage glucan : xyloglucan endotransglucosylase is a plant cell wall-modifying enzyme found in plants of the Equisetum genus. The enzyme is proposed, in vivo, to catalyse the endotransglucosylation of two different hemicellulose polysaccharides, mixed-linkage glucan and xyloglucan,...
within Equiseta suggest that the role of MLG in each may be different.

