
Mevalonic aciduria
Encyclopedia
Mevalonate kinase deficiency, also called mevalonic aciduria, is an autosomal
recessive metabolic disorder that disrupts the biosynthesis
of cholesterol
and isoprenoids.
in the urine
, resulting from insufficient activity of the enzyme mevalonate kinase
(ATP:mevalonate 5-phosphotransferase; EC 2.7.1.36).
 The disorder was first described in 1985.
The disorder was first described in 1985.
Classified as an inborn error of metabolism
, mevalonate kinase deficiency usually results in developmental delay, hypotonia
, anemia
, hepatosplenomegaly
, various dysmorphic features, mental retardation
, an overall failure to thrive
and several other features.

Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
recessive metabolic disorder that disrupts the biosynthesis
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
of cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
and isoprenoids.
Diagnosis
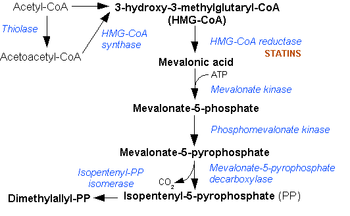
Mevalonate kinase deficiency causes an accumulation of mevalonic acidMevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid is a key organic compound in biochemistry. The anion of mevalonic acid, the predominant form in biological media, is known as mevalonate. This compound is of major pharmaceutical importance...
in the urine
Urine
Urine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
, resulting from insufficient activity of the enzyme mevalonate kinase
Mevalonate kinase
Mevalonate kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MVK gene. Mevalonate kinases are found in a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals...
(ATP:mevalonate 5-phosphotransferase; EC 2.7.1.36).

Classified as an inborn error of metabolism
Inborn error of metabolism
Inborn errors of metabolism comprise a large class of genetic diseases involving disorders of metabolism. The majority are due to defects of single genes that code for enzymes that facilitate conversion of various substances into others...
, mevalonate kinase deficiency usually results in developmental delay, hypotonia
Hypotonia
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone , often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength...
, anemia
Anemia
Anemia is a decrease in number of red blood cells or less than the normal quantity of hemoglobin in the blood. However, it can include decreased oxygen-binding ability of each hemoglobin molecule due to deformity or lack in numerical development as in some other types of hemoglobin...
, hepatosplenomegaly
Hepatosplenomegaly
Hepatosplenomegaly is the simultaneous enlargement of both the liver and the spleen . Hepatosplenomegaly can occur as the result of acute viral hepatitis or infectious mononucleosis, or it can be the sign of a serious and life threatening lysosomal storage disease...
, various dysmorphic features, mental retardation
Mental retardation
Mental retardation is a generalized disorder appearing before adulthood, characterized by significantly impaired cognitive functioning and deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors...
, an overall failure to thrive
Failure to thrive
Failure to thrive is a medical term which is used in both pediatric and adult human medicine, as well as veterinary medicine ....
and several other features.


