
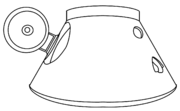
Merkur (spacecraft)
Encyclopedia

Spacecraft
A spacecraft or spaceship is a craft or machine designed for spaceflight. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, earth observation, meteorology, navigation, planetary exploration and transportation of humans and cargo....
designed as the reentry capsule for the TKS spacecraft
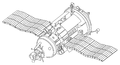
TKS spacecraft
TKS spacecraft was a Soviet spacecraft design in the late 1960s intended to supply the military Almaz space station. The spacecraft was designed for manned or autonomous cargo resupply use...
. The name Merkur, assigned to the spacecraft by Western sources, is technically a misnomer; it was never referred to as such by its creator or design engineers and the name never appeared in any soviet documentation.
Its official designation was 11F74. Although the shape of the pressurized portion of the capsule was vaguely like that of the Command Module of Project Apollo
Project Apollo
The Apollo program was the spaceflight effort carried out by the United States' National Aeronautics and Space Administration , that landed the first humans on Earth's Moon. Conceived during the Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower, Apollo began in earnest after President John F...
the reentry orientation rockets, parachute, and soft landing engines were located on section attached to the top of the capsule. Inside, the VA was completely different from the Apollo CM. Although it also could carry a crew of three, it was designed for occupation only during the launching and landing phases of the missions. Like the American spacecraft, it had a Launch Escape System
Launch escape system
A Launch Escape System is a top-mounted rocket connected to the crew module of a crewed spacecraft and used to quickly separate the crew module from the rest of the rocket in case of emergency. Since the escape rockets are above the crew module, an LES typically uses separate nozzles which are...
, a rocket bolted to its nose which was discarded shortly after launch.
Cosmonaut Alexei Leonov called the Almaz Return Capsule "our Apollo," though as a military program, it had no connection to the Soviet manned lunar program.
But in its purpose the VA was more like certain planned military derivatives of the spacecraft of Project Gemini
Project Gemini
Project Gemini was the second human spaceflight program of NASA, the civilian space agency of the United States government. Project Gemini was conducted between projects Mercury and Apollo, with ten manned flights occurring in 1965 and 1966....
. Like the USAF's Gemini B, planned in the 1960s to carry crew to the Manned Orbiting Laboratory
Manned Orbiting Laboratory
The Manned Orbiting Laboratory , originally referred to as the Manned Orbital Laboratory, was part of the United States Air Force's manned spaceflight program, a successor to the cancelled Boeing X-20 Dyna-Soar military reconnaissance space plane project...
which would be orbited by the same rocket just below the capsule itself, the VA had a small circular hatch in the heat shield.
The VA was to be launched manned attached to the TKS
TKS spacecraft
TKS spacecraft was a Soviet spacecraft design in the late 1960s intended to supply the military Almaz space station. The spacecraft was designed for manned or autonomous cargo resupply use...
and Almaz
Almaz
The Almaz program was a series of military space stations launched by the Soviet Union under cover of the civilian Salyut DOS-17K program after 1971....
Space Station by the Proton rocket
Proton rocket
Proton is an expendable launch system used for both commercial and Russian government space launches. The first Proton rocket was launched in 1965 and the launch system is still in use as of 2011, which makes it one of the most successful heavy boosters in the history of spaceflight...
and then remain unoccupied until the end of the mission when it would serve as the reentry vehicle.
Although it was never launched as part of the Almaz station, four TKS were launched with VA capsules (one lone flight and three to dockings with space stations: 1 to Salyut 6
Salyut 6
Salyut 6 , DOS-5, was a Soviet orbital space station, the eighth flown as part of the Salyut programme. Launched on 29 September 1977 by a Proton rocket, the station was the first of the 'second-generation' type of space station. Salyut 6 possessed several revolutionary advances over the earlier...
, 2 to Salyut 7
Salyut 7
Salyut 7 was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first manned in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Various crew and modules were used over its lifetime, including a total of 12 manned and 15 unmanned launches...
) were launched in the 1980s, although with no crew aboard. The VA capsule on the fourth TKS was modified as a no-reentry laboratory segment.
The VA capsules were also launched in pairs four times. Although one of these flights was aborted due to the carrier rocket failure, the upper capsule was equipped with a Launch Escape System which carried this capsule away from the exploding rocket.
Cosmos 881 and Cosmos 882
Orbital test of a pair of two VA capsules in 1976-12-15 that started jointly and reentered separately.VA #009
Launched at 1977-08-04. Launch vehicle failure on a suborbital test of two VA capsule.Cosmos 997 and Cosmos 998
On 1978-03-30 pair of two VA capsules that started jointly and reentered separatelyCosmos 1100 and Cosmos 1101
On 1979-05-23 pair of two VA capsules that started jointly and reentered separatelySpecifications
- Habitable Volume: 4.56 m3
- Gross mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb)
- Payload: 1,880 kg (4,140 lb)
- Height: 3.64 m (11.94 ft)
- Diameter: 2.79 m (9.15 ft)
- First date: 12/15/1976
- Last date: 5/22/1979
- Number: 9
External links
- The Almaz Space Station Program
- http://www.russianspaceweb.com/almaz.html
Sources
- http://www.russianspaceweb.com/almaz_ops4.html

