Maximum magnitude
Encyclopedia
An important parameter in the calculation of seismic hazard
, maximum magnitude (expressed as Moment magnitude scale
) is also one of the more contentious. The choice of the value can greatly influence the final outcome of the results, yet this is most likely a size of earthquake
that has not yet occurred in the region under study.
 The seismic hazard calculation involves a double integration (integral
The seismic hazard calculation involves a double integration (integral
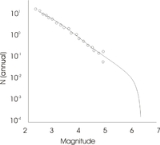
) over the region, combined with the expected number (earthquake frequency) of earthquakes, from the smallest to the largest. The integration must close at the maximum magnitude. The figure shows a typical 'Earthquake frequency' plot for a given region.
This is a typical plot for continent
al interiors. The circles represent actual earthquake data. Note that the dataset is complete for small magnitudes, but becomes erratic for the larger. At about M5, there are no records, simply because the historical record is usually too short. In some cases paleoseismology can fill some of the gap, but this is rare for continental regions.
The last part of the curve, perhaps the most important part, can be filled in by inference. This would come from studying similar geology throughout the world (using analogs to extend time), or by a study of fault mechanics
. For example, large-scale studies have been conducted for Stable Continental Regions (SCR's), which are defined defined "as regions of continental crust that have not experienced any major tectonism, magmatism, basement metamorphism or anorogenic intrusion since the early Creataceous, and no rifting or major extension or transtension since the Paleogene." http://earthquake.usgs.gov/scitech/scr_catalog.html
Finally there is the common question of what is the maximum magnitude for the whole world. http://www.seismo.nrcan.gc.ca/questions/faq_e.php Unfortunately, it cannot really be answered, since this earthquake has most likely not happened in the historical record, and we cannot search beyond the earth for analogs. Answers can again be inferred using the finite size of the world's plates (plate tectonics), and the possible limits of the various magnitude scales http://eqseis.geosc.psu.edu/~cammon/HTML/Classes/IntroQuakes/notes/earthquake_size.html. The specific value, however, is not directly relevant to most people, since, except for tsunami
s, the local shaking effects come to a maximum at about M8, and greater earthquakes simply extend the rupture distance.
Seismic hazard
Seismic hazard refers to the study of expected earthquake ground motions at the earth's surface, and its likely effects on existing natural conditions and man-made structures for public safety considerations; the results of such studies are published as seismic hazard maps, which identify the...
, maximum magnitude (expressed as Moment magnitude scale
Moment magnitude scale
The moment magnitude scale is used by seismologists to measure the size of earthquakes in terms of the energy released. The magnitude is based on the seismic moment of the earthquake, which is equal to the rigidity of the Earth multiplied by the average amount of slip on the fault and the size of...
) is also one of the more contentious. The choice of the value can greatly influence the final outcome of the results, yet this is most likely a size of earthquake
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
that has not yet occurred in the region under study.

Integral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
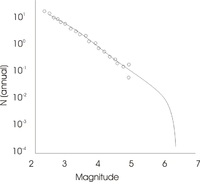
) over the region, combined with the expected number (earthquake frequency) of earthquakes, from the smallest to the largest. The integration must close at the maximum magnitude. The figure shows a typical 'Earthquake frequency' plot for a given region.
This is a typical plot for continent
Continent
A continent is one of several very large landmasses on Earth. They are generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, with seven regions commonly regarded as continents—they are : Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia.Plate tectonics is...
al interiors. The circles represent actual earthquake data. Note that the dataset is complete for small magnitudes, but becomes erratic for the larger. At about M5, there are no records, simply because the historical record is usually too short. In some cases paleoseismology can fill some of the gap, but this is rare for continental regions.
The last part of the curve, perhaps the most important part, can be filled in by inference. This would come from studying similar geology throughout the world (using analogs to extend time), or by a study of fault mechanics
Fault mechanics
Fault mechanics is a field of study that investigates the behavior of geologic faults.Behind every good earthquake is some weak rock. Whether the rock remains weak becomes an important point in determining the potential for bigger earthquakes....
. For example, large-scale studies have been conducted for Stable Continental Regions (SCR's), which are defined defined "as regions of continental crust that have not experienced any major tectonism, magmatism, basement metamorphism or anorogenic intrusion since the early Creataceous, and no rifting or major extension or transtension since the Paleogene." http://earthquake.usgs.gov/scitech/scr_catalog.html
Finally there is the common question of what is the maximum magnitude for the whole world. http://www.seismo.nrcan.gc.ca/questions/faq_e.php Unfortunately, it cannot really be answered, since this earthquake has most likely not happened in the historical record, and we cannot search beyond the earth for analogs. Answers can again be inferred using the finite size of the world's plates (plate tectonics), and the possible limits of the various magnitude scales http://eqseis.geosc.psu.edu/~cammon/HTML/Classes/IntroQuakes/notes/earthquake_size.html. The specific value, however, is not directly relevant to most people, since, except for tsunami
Tsunami
A tsunami is a series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, typically an ocean or a large lake...
s, the local shaking effects come to a maximum at about M8, and greater earthquakes simply extend the rupture distance.

