
Markov additive process
Encyclopedia
In applied probability
, a Markov additive process (MAP) {(X(t),J(t)) : t ≥ 0} is a bivariate Markov process
whose transition probability measure is translation invariant
in the additive component X(t). That is to say, the evolution of X(t) is governed by J(t) in the sense that for any f and g we require
Çinlar uses the unique structure of the MAP to prove that, given a gamma process with a shape parameter that is a function of Brownian motion
, the resulting lifetime is distributed according to the Weibull distribution.
Kharoufeh presents a compact transform expression for the failure distribution for wear processes of a component degrading according to a Markovian environment inducing state-dependent continuous linear wear by using the properties of a MAP and assuming the wear process to be temporally homogeneous and that the environmental process has a finite state space
.
Applied probability
Much research involving probability is done under the auspices of applied probability, the application of probability theory to other scientific and engineering domains...
, a Markov additive process (MAP) {(X(t),J(t)) : t ≥ 0} is a bivariate Markov process
Markov process
In probability theory and statistics, a Markov process, named after the Russian mathematician Andrey Markov, is a time-varying random phenomenon for which a specific property holds...
whose transition probability measure is translation invariant
Invariant (mathematics)
In mathematics, an invariant is a property of a class of mathematical objects that remains unchanged when transformations of a certain type are applied to the objects. The particular class of objects and type of transformations are usually indicated by the context in which the term is used...
in the additive component X(t). That is to say, the evolution of X(t) is governed by J(t) in the sense that for any f and g we require
-
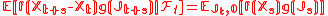 .
.
Çinlar uses the unique structure of the MAP to prove that, given a gamma process with a shape parameter that is a function of Brownian motion
Brownian motion
Brownian motion or pedesis is the presumably random drifting of particles suspended in a fluid or the mathematical model used to describe such random movements, which is often called a particle theory.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has several real-world applications...
, the resulting lifetime is distributed according to the Weibull distribution.
Kharoufeh presents a compact transform expression for the failure distribution for wear processes of a component degrading according to a Markovian environment inducing state-dependent continuous linear wear by using the properties of a MAP and assuming the wear process to be temporally homogeneous and that the environmental process has a finite state space
State space
In the theory of discrete dynamical systems, a state space is a directed graph where each possible state of a dynamical system is represented by a vertex, and there is a directed edge from a to b if and only if ƒ = b where the function f defines the dynamical system.State spaces are...
.

