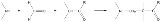
Mannich reaction
Overview
Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis,...
which consists of an amino alkylation of an acidic proton placed next to a carbonyl
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups....
functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
with formaldehyde
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula CH2O. It is the simplest aldehyde, hence its systematic name methanal.Formaldehyde is a colorless gas with a characteristic pungent odor. It is an important precursor to many other chemical compounds, especially for polymers...
and ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
or any primary or secondary amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
. The final product is a β-amino-carbonyl compound also known as a Mannich base
Mannich base
A mannich base is a beta-amino-ketone, which is formed in the reaction of an amine, formaldehyde and a carbon acid . The Mannich base is an endproduct in the Mannich reaction, which is nucleophilic addition reaction of a non-enolizable aldehyde and any primary or secondary amine to produce...
. Reactions between aldimine
Aldimine
In organic chemistry, an aldimine is an imine that is an analog of an aldehyde.As such, aldimines have the general formula R–CH=N–R. Aldimines are similar to ketimines, which are analogs of ketones.An important subset of aldimines are the Schiff bases,...
s and α-methylene carbonyls are also considered Mannich reactions because these imines form between amines and aldehydes.
The reaction is named after chemist
Chemist
A chemist is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties such as density and acidity. Chemists carefully describe the properties they study in terms of quantities, with detail on the level of molecules and their component atoms...
Carl Mannich
Carl Mannich
Carl Ulrich Franz Mannich was a German Chemist. From 1927 to 1943 he was Professor for pharmaceutical chemistry at the University of Berlin...
.
The Mannich reaction is an example of nucleophilic addition
Nucleophilic addition
In organic chemistry, a nucleophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where in a chemical compound a π bond is removed by the creation of two new covalent bonds by the addition of a nucleophile....
of an amine to a carbonyl
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups....
group followed by dehydration to the Schiff base
Schiff base
A Schiff base, named after Hugo Schiff, is a compound with a functional group that contains a carbon-nitrogen double bond with the nitrogen atom connected to an aryl or alkyl group, not hydrogen....
.

