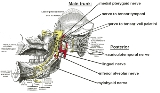
Mandibular nerve
Encyclopedia
The mandibular nerve is the largest of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve
.
through the foramen ovale
. The two roots then combine.
Immediately in the infratemporal fossa
beneath the base of the skull, the nerve gives off two branches from its medial side: a recurrent branch (nervus spinosus
) and the nerve to the medial pterygoid muscle
. The mandibular nerve then divides into two trunks, an anterior and a posterior.
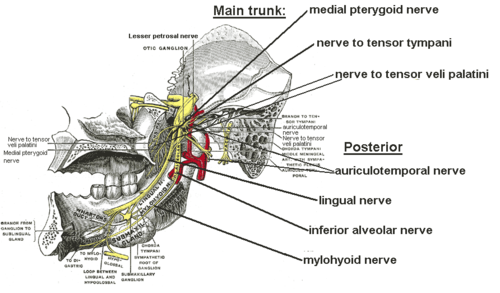 The mandibular nerve gives off the following branches:
The mandibular nerve gives off the following branches:
The mandibular nerve also gives off branches to the otic ganglion
Trigeminal nerve
The trigeminal nerve contains both sensory and motor fibres. It is responsible for sensation in the face and certain motor functions such as biting, chewing, and swallowing. Sensory information from the face and body is processed by parallel pathways in the central nervous system...
.
Roots
It is made up of two roots:- a large sensory root proceeding from the inferior angle of the trigeminal ganglionTrigeminal ganglionThe trigeminal ganglion is a sensory ganglion of the trigeminal nerve that occupies a cavity in the dura mater, covering the trigeminal impression near the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone.-Relations:It is somewhat crescentic in shape, with its convexity...
. - a small motor root (the motor part of the trigeminal), which passes beneath the ganglion, and unites with the sensory root, just after its exit through the foramen ovaleForamen ovale (skull)At the base of the skull the foramen ovale is one of the larger of the several holes that transmit nerves through the skull. The foramen ovale is situated in the posterior part of the sphenoid bone, posterolateral to the foramen rotundum.-Contents:Several nerves, arteries and veins pass through...
.
Path
The two roots (sensory and motor) exit the middle cranial fossaMiddle cranial fossa
The middle fossa, deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest....
through the foramen ovale
Foramen ovale (skull)
At the base of the skull the foramen ovale is one of the larger of the several holes that transmit nerves through the skull. The foramen ovale is situated in the posterior part of the sphenoid bone, posterolateral to the foramen rotundum.-Contents:Several nerves, arteries and veins pass through...
. The two roots then combine.
Immediately in the infratemporal fossa
Infratemporal fossa
The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity, situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch.* anteriorly, by the infratemporal surface of the maxilla and the ridge which descends from its zygomatic process...
beneath the base of the skull, the nerve gives off two branches from its medial side: a recurrent branch (nervus spinosus
Nervus spinosus
The meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve that supplies the dura mater.-Course:It enters the skull through the foramen spinosum with the middle meningeal artery....
) and the nerve to the medial pterygoid muscle
Medial pterygoid muscle
The medial pterygoid , is a thick, quadrilateral muscle of mastication.The mandibular branch of the fifth cranial nerve, the trigeminal nerve, innervates the medial pterygoid muscle.-Origin and insertion:...
. The mandibular nerve then divides into two trunks, an anterior and a posterior.
Branches

- From the main trunk of the nerve (before the division)
- nervus spinosusNervus spinosusThe meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve that supplies the dura mater.-Course:It enters the skull through the foramen spinosum with the middle meningeal artery....
(meningeal branch) - medial pterygoid nerve
- nerve to tensor tympaniTensor tympaniThe tensor tympani, the larger of the two muscles of the tympanic cavity, is contained in the bony canal above the osseous portion of the auditory tube...
- nerve to tensor veli palatini
- nerve to tensor tympani
- nervus spinosus
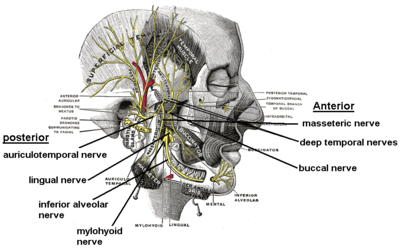
- From the anterior division
- masseteric nerveMasseteric nerveThe masseteric nerve passes laterally, above the Pterygoideus externus, in front of the temporomandibular articulation, and behind the tendon of the Temporalis; it crosses the mandibular notch with the masseteric artery, to the deep surface of the Masseter, in which it ramifies nearly as far as its...
- deep temporal nervesDeep temporal nervesThe deep temporal nerves, branches of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve, are two in number, anterior and posterior. They pass above the upper border of the pterygoideus externus and enter the deep surface of the temporalis.-Branches:...
(anterior and posterior) - buccal nerveBuccal nerveThe buccal nerve is a nerve in the face. It is a branch of the mandibular nerve and transmits sensory information from skin over the buccal membrane and from the second and third molar teeth.-Course:It courses between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle, underneath...
(a sensory nerve) - lateral pterygoid nerve
- masseteric nerve

- From the posterior division
- auriculotemporal nerveAuriculotemporal nerveThe auriculotemporal nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to various regions on the side of the head.-Origin:...
- lingual nerveLingual nerveThe lingual nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve , itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve, which supplies sensory innervation to the tongue...
- inferior alveolar nerveInferior alveolar nerveThe inferior alveolar nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve, which is itself the third branch of the trigeminal nerve .-Path:...
- motor branch to mylohyoidMylohyoidMylohyoid can refer to:* Mylohyoid muscle* Mylohyoid line* Mylohyoid nerve* Mylohyoid branch of inferior alveolar artery* Mylohyoid groove...
and anterior belly of digastric muscles (mylohyoid nerveMylohyoid nerveThe mylohyoid nerve is a nerve that innervates the mylohyoid muscle and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle.-Structure:...
)
- auriculotemporal nerve
The mandibular nerve also gives off branches to the otic ganglion
Otic ganglion
The otic ganglion is a small, oval shaped, flattened parasympathetic ganglion of a reddish-gray color, located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa. It gives innervation to the parotid gland for salivation....
Supplies
The mandibular nerve innervates:- mylohyoid muscleMylohyoid muscleThe mylohyoid muscle is a muscle running from the mandible to the hyoid bone, forming the floor of the oral cavity. It is named for its two attachments, with the prefix "mylo" coming from the Greek word for "molar". These muscles are mesodermal in origin...
and anterior belly of digastric muscleDigastric muscleThe digastric muscle is a small muscle located under the jaw. so digastric muscles are muscle fibers in ligament of treitz ,omohyoid , occipitofrontalis.... - mucous membraneMucous membraneThe mucous membranes are linings of mostly endodermal origin, covered in epithelium, which are involved in absorption and secretion. They line cavities that are exposed to the external environment and internal organs...
of the anterior two-thirds of the tongueTongueThe tongue is a muscular hydrostat on the floors of the mouths of most vertebrates which manipulates food for mastication. It is the primary organ of taste , as much of the upper surface of the tongue is covered in papillae and taste buds. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly... - the inside of the cheek (the buccal mucosa)
- teeth and mucoperiosteumMucoperiosteumMucoperiosteum is a compound structure consisting of mucous membrane and of periosteum.It can be found in the palate....
of mandibular teeth - skin of the temporal region
- auricula
- lower lipLipLips are a visible body part at the mouth of humans and many animals. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech...
, and chinChinIn the human anatomy, the chin is the lowermost part of the face.It is formed by the lower front of the mandible.People show a wide variety of chin structures. See Cleft chin.... - Muscles of masticationMuscles of masticationDuring mastication, four muscles of mastication are responsible for adduction and lateral motion of the jaw. Other muscles, usually associated with the hyoid such as the sternohyomastoid, are responsible for opening the jaw.-Muscles:*The masseter...
- the muscles tensor tympaniTensor tympaniThe tensor tympani, the larger of the two muscles of the tympanic cavity, is contained in the bony canal above the osseous portion of the auditory tube...
and tensor veli palatini
See also
- Ophthalmic nerveOphthalmic nerveThe ophthalmic nerve is one of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve. The ophthalmic nerve carries only sensory fibers.-Branches:*Nasociliary nerve**sensory root of ciliary ganglion**posterior ethmoidal nerve...
- Maxillary nerve
- Marginal mandibular branch of facial nerveMarginal mandibular branch of facial nerveThe marginal mandibular branch of facial nerve passes forward beneath the Platysma and Triangularis, supplying the muscles of the lower lip and chin, and communicating with the mental branch of the inferior alveolar nerve.-Muscles innervated :...

