
Locomotives of New Zealand
Encyclopedia
Locomotives of New Zealand currently in operation owned by KiwiRail
consist of 172 diesel-electric locomotive
s, 22 electric locomotive
s, 3 railcar
s, and 103 shunting locomotives. There are also 19 diesel multiple unit
s in Auckland, owned by the Auckland Regional Transport Authority (ARTA), 71 electric multiple unit
s owned by the Greater Wellington Regional Council, and diesel-electric and steam locomotive
s and railcars in working order owned by private companies or preservation societies.
All New Zealand
's main-line locomotives are 1067 mm (3 foot 6 inch) gauge.
, which comprised 146 locomotives.
KiwiRail await the delivery of 20 new Chinese built
diesel electric locomotives, due to arrive in mid 2012.
Steam locomotives (which were retired from regular service by the end of October 1971) were originally categorised with just a single letter, such as the "F class
". When a new class was built as an enhancement of an old class, the old class's letter was re-used, followed by a superscript upper-case letter. For example, the 1906 A class
was followed by the AA
and AB
classes.
Diesel-electric and electric locomotive classifications originally consisted of an upper-case D or E respectively followed by a second and sometimes a third (sub-class) letter. The second and third letters are sometimes represented as smaller-sized upper case (for example, as seen on many locomotive cab-side number plates).
Diesel and diesel-electric classes appear to have originally been classified, after the first class letter ('D' as alluded to above), by the second letter being allocated to indicate the country of manufacture (for example DA
for the American EMD designs, which were also, later, built in Canada and Australia; DE
for England or 'English Electric'; DJ
for the Mitsubishi units from Japan). Whilst this was a reasonable starting point, such issues as the introduction of 'sister models' and sub-classing caused by rebuild and refurbishment resulted in the pragmatic, contiguous use of other class letters. For example the eight cylinder version of the DA class became the DB class
, and was later rebuilt as the DBR. When the DA class rebuilding began, the rebuilt locomotives became the DC class
. Following the DJ there was a large gap in the classification continuum as NZR took a different tack and catalogued their new GE power as the DX class
and then (because the original DFs
had since been withdrawn) new Canadian-built EMD units took over that classification
.
There are exceptions, and new classes were not always given the classification that alphabetically followed that of the previous class that had most recently been acquired. If an entire class had been withdrawn from service and the classification no longer in use, it was sometimes re-used; for example, two A classes exist, one from 1873
and one from 1906
.
(EMD units imported from Queensland), QR (EMD units imported from Queensland and placed into service unrebuilt - this non-standard classification originally intended to be temporary as these units were intended to eventually undergo rebuild). Most diesel-electric shunting locomotives have a three-letter classification with DS as the first two letters, following on from the original diesel-electric shunting class that was known simply as the DS class
.
For electric locomotives the second letter often referred to where the locomotive was based, such as EC
in Christchurch
, EO
in Otira
and EW
in Wellington
. The ED
and EF
classes were an exception. The EM class
in Wellington possibly stands for Electric Motor. ET is Electric Trailer. The DM class
units were an exception to this.
Almost all railcar
s were classified RM
(Rail Motor), and individual classes were known by alternate names such as the Vulcan railcars
of the South Island
and the Wairarapa railcars
that ran over the Rimutaka Incline to the Wairarapa
.
In the 1970s the first different livery appeared. Eleven members of the DJ class
were painted "Southerner Blue" (mainly dark blue) to haul the Southerner express in the South Island. The Silver Fern
railcars appeared in stainless steel, and the DX class
, appearing in 1972, were painted "clockwork orange" (orange and yellow). In 1978, the rebuilt DC class
appeared in "fruit salad" (red, yellow, grey and black), and many locomotives followed suit. Following the split of New Zealand Rail Limited
from the New Zealand Railways Corporation
in 1991, a modified livery of blue, yellow, grey and black appeared. For the first time, locomotives wore the name of their operator - New Zealand Rail - in prominent view. This livery was continued after 1993 when NZ Rail was privatised, and was slightly modified when the company was renamed Tranz Rail
in 1995 by replacing the NZ Rail logo with the new Tranz Rail logo. In 2001 a new livery to promote level crossing
safety was trialed on DC 4323. This colour scheme was nicknamed "bumble bee"
because of its black and yellow colours. Following the takeover of Tranz Rail by Australia's Toll Holdings
in 2004, Toll Rail
's livery appeared, nicknamed "corn cob", consisting of green and yellow. That same year, DC class (and now DFT/DFB class) locomotives being used on Auckland commuter services began wearing the MAXX livery, which was dark blue and yellow with a MAXX logo on the side. When the government bought back Toll and introduced KiwiRail, it also introduced its own livery, consisting of grey and red (a second version later followed). Most of today's locomotives are painted in "fruit salad", blue, "bumble bee"
, "corn cob" or KiwiRail.
's royal train in the early 1950s.)
. For purposes here, they are classified under their common names.
Experimental railcars included the following:
Steam locomotive notes:
KiwiRail
KiwiRail Holdings Limited is the rail operations subsidiary of the New Zealand Railways Corporation, which trades as KiwiRail. Headquartered in Wellington, New Zealand, KiwiRail is the largest rail transport operator in New Zealand. Since July 2010 John Spencer has been the Chairman...
consist of 172 diesel-electric locomotive
Diesel locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railroad locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine, a reciprocating engine operating on the Diesel cycle as invented by Dr. Rudolf Diesel...
s, 22 electric locomotive
Electric locomotive
An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or an on-board energy storage device...
s, 3 railcar
Railcar
A railcar, in British English and Australian English, is a self-propelled railway vehicle designed to transport passengers. The term "railcar" is usually used in reference to a train consisting of a single coach , with a driver's cab at one or both ends. Some railways, e.g., the Great Western...
s, and 103 shunting locomotives. There are also 19 diesel multiple unit
Diesel multiple unit
A diesel multiple unit or DMU is a multiple unit train consisting of multiple carriages powered by one or more on-board diesel engines. They may also be referred to as a railcar or railmotor, depending on country.-Design:...
s in Auckland, owned by the Auckland Regional Transport Authority (ARTA), 71 electric multiple unit
Electric multiple unit
An electric multiple unit or EMU is a multiple unit train consisting of self-propelled carriages, using electricity as the motive power. An EMU requires no separate locomotive, as electric traction motors are incorporated within one or a number of the carriages...
s owned by the Greater Wellington Regional Council, and diesel-electric and steam locomotive
Steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a railway locomotive that produces its power through a steam engine. These locomotives are fueled by burning some combustible material, usually coal, wood or oil, to produce steam in a boiler, which drives the steam engine...
s and railcars in working order owned by private companies or preservation societies.
All New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
's main-line locomotives are 1067 mm (3 foot 6 inch) gauge.
Classification details
The locomotives of KiwiRail and its predecessors are divided into classes. Each class was designed to perform specific duties. A class can be as small as one individual locomotive, and the largest class to run on New Zealand rails was the DA classNZR DA class
The NZR Da diesel-electric mainline locomotive class ran on the New Zealand railway system between 1955 and 1989. With 146 locomotives, it was the most numerous class to operate in New Zealand, just five more than the AB class steam locomotive....
, which comprised 146 locomotives.
KiwiRail await the delivery of 20 new Chinese built
NZR DL class
The NZR DL class is a class of diesel-electric locomotives manufactured for KiwiRail by Dalian Locomotive and Rolling Stock Company with engines from MTU...
diesel electric locomotives, due to arrive in mid 2012.
Steam locomotives (which were retired from regular service by the end of October 1971) were originally categorised with just a single letter, such as the "F class
NZR F class
The NZR F class was the first important class of steam locomotive built to operate on New Zealand's railway network after the national gauge of 1067 millimetres was adopted. The first locomotives built for the new 1067 mm railways were two E class double Fairlies for the Dunedin and Port Chalmers...
". When a new class was built as an enhancement of an old class, the old class's letter was re-used, followed by a superscript upper-case letter. For example, the 1906 A class
NZR A class (1906)
The A class were steam locomotives built in 1906 with a 4-6-2 wheel arrangement for New Zealand's national railway network, and described by some as the most handsome engines to run on New Zealand rails. The class should not be confused with the older and more obscure A class of 1873. They were...
was followed by the AA
NZR Aa class
The AA class consisted of ten steam locomotives built to operate on New Zealand's national rail network. Built to a similar design to the A class of 1906, they had a wheel arrangement of 4-6-2 and were suited to hauling freight services. Ordered and built in 1914, all ten entered service in New...
and AB
NZR Ab class
The NZR AB class was a class of 4-6-2 Pacific tender steam locomotive that operated on New Zealand's national railway system. Originally an improvement on the 1906 A class, 141 were built between 1915 and 1927 by NZR's Addington Workshops, A & G Price Limited of Thames, New Zealand, and North...
classes.
Diesel-electric and electric locomotive classifications originally consisted of an upper-case D or E respectively followed by a second and sometimes a third (sub-class) letter. The second and third letters are sometimes represented as smaller-sized upper case (for example, as seen on many locomotive cab-side number plates).
Diesel and diesel-electric classes appear to have originally been classified, after the first class letter ('D' as alluded to above), by the second letter being allocated to indicate the country of manufacture (for example DA
NZR DA class
The NZR Da diesel-electric mainline locomotive class ran on the New Zealand railway system between 1955 and 1989. With 146 locomotives, it was the most numerous class to operate in New Zealand, just five more than the AB class steam locomotive....
for the American EMD designs, which were also, later, built in Canada and Australia; DE
NZR DE class
The NZR DE class is a New Zealand class of shunting diesel-electric locomotives. The New Zealand Railways intended to replace steam locomotives for shunting duties with this class...
for England or 'English Electric'; DJ
NZR DJ class
The NZR DJ class locomotive is a class of diesel-electric locomotive used in New Zealand. The class were purchased from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries with a modernisation loan from the World Bank to replace steam locomotives in the South Island, where most of the class members worked most of their...
for the Mitsubishi units from Japan). Whilst this was a reasonable starting point, such issues as the introduction of 'sister models' and sub-classing caused by rebuild and refurbishment resulted in the pragmatic, contiguous use of other class letters. For example the eight cylinder version of the DA class became the DB class
NZR DB class
The NZR Db diesel-electric locomotive class was built in 1965-1966. They were a lighter version of the Da class to operate on secondary North Island lines from which the Da was excluded due to its weight. One of the principal lines which the Db dominated was the East Coast Main Trunk to Tauranga...
, and was later rebuilt as the DBR. When the DA class rebuilding began, the rebuilt locomotives became the DC class
NZR DC class
The NZR DC class locomotive is the most common class of locomotive currently in operation on the New Zealand rail network. Primarily employed to haul freight trains operated by KiwiRail, the class is also used for long-distance passenger trains operated by Tranz Scenic and suburban passenger trains...
. Following the DJ there was a large gap in the classification continuum as NZR took a different tack and catalogued their new GE power as the DX class
NZR DX class
The NZR DX class is a class of 49 Co-Co diesel-electric locomotives that currently operates on New Zealand's national railway network.Built by General Electric in Erie, Pennsylvania, United States, they were introduced to New Zealand between 1972 and 1976. The class is based on the General Electric...
and then (because the original DFs
NZR DF class (1954)
The NZR DF class of 1954 was the first class of mainline diesel-electric locomotives built for New Zealand's national railway network, built by English Electric...
had since been withdrawn) new Canadian-built EMD units took over that classification
NZR DF class (1979)
The NZR DF class of 1979 is a class of 30 Co-Co diesel-electric locomotives built by General Motors Diesel of Canada between 1979 and 1981. Between 1992 and 1997, all the locomotives were rebuilt as the DFT class, a turbocharged version of the DF....
.
There are exceptions, and new classes were not always given the classification that alphabetically followed that of the previous class that had most recently been acquired. If an entire class had been withdrawn from service and the classification no longer in use, it was sometimes re-used; for example, two A classes exist, one from 1873
NZR A class (1873)
The A class was the second class of steam locomotive ordered to work on New Zealand's national railways. It should not be confused with the more numerous A class 4-6-2 tender locomotives of 1906. Initially ordered by the Public Works Department for use in the construction of lines, the A class...
and one from 1906
NZR A class (1906)
The A class were steam locomotives built in 1906 with a 4-6-2 wheel arrangement for New Zealand's national railway network, and described by some as the most handsome engines to run on New Zealand rails. The class should not be confused with the older and more obscure A class of 1873. They were...
.
Traffic Monitoring System
Following the introduction of the computer-based Traffic Monitoring System (TMS) and consequent renumbering, classes were identified by the two upper-case letters with the first letter remaining D or E respectively and sub-classes being indicated by a third upper-case letter, such as DAA (DA modified for hump shunting), DAR (DA with rebuilt superstructure), DFT (DF with turbo-conversion), DXR (rebuilt DX), DQNZR DQ class
The NZR DQ and QR class locomotives are two classes of mainline diesel-electric locomotives in New Zealand and Tasmania, Australia. Originally Queensland Rail 1460 and 1502 class, they were purchased by New Zealand Rail Limited in 1995 to be rebuilt, as a cheaper alternative to buying new...
(EMD units imported from Queensland), QR (EMD units imported from Queensland and placed into service unrebuilt - this non-standard classification originally intended to be temporary as these units were intended to eventually undergo rebuild). Most diesel-electric shunting locomotives have a three-letter classification with DS as the first two letters, following on from the original diesel-electric shunting class that was known simply as the DS class
NZR DS class
The NZR DS class is a class of 16 diesel shunting locomotives built by the Vulcan Foundry and supplied by the Drewry Car Co from 1949 - 1955.-Operation:The locomotives were largely allocated to shunting yards, and later industrial service.-Withdrawal:...
.
For electric locomotives the second letter often referred to where the locomotive was based, such as EC
NZR EC class
The NZR EC class were a class of electric locomotive used in Christchurch, New Zealand. They replaced steam locomotives on trains through the Lyttelton rail tunnel between Lyttelton and Christchurch.-Introduction:...
in Christchurch
Christchurch
Christchurch is the largest city in the South Island of New Zealand, and the country's second-largest urban area after Auckland. It lies one third of the way down the South Island's east coast, just north of Banks Peninsula which itself, since 2006, lies within the formal limits of...
, EO
NZR EO class (1923)
The New Zealand Railways EO class of 1923 were electric locomotives used on the steep Otira to Arthur's Pass section of the Midland Line. They were primarily for pulling trains through the 8.5 km Otira Tunnel to avoid the buildup of steam, smoke and soot....
in Otira
Otira
Otira is a small township seven kilometres north of Arthur's Pass in the central South Island of New Zealand. It is on the western approach to the pass, a saddle between the Otira and Bealey Rivers high in the Southern Alps...
and EW
NZR EW class
The NZR EW class locomotive was a class of electric locomotive used in Wellington, New Zealand. The classification 'EW' was due to their being electric locomotives allocated to Wellington.- Introduction :...
in Wellington
Wellington
Wellington is the capital city and third most populous urban area of New Zealand, although it is likely to have surpassed Christchurch due to the exodus following the Canterbury Earthquake. It is at the southwestern tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Rimutaka Range...
. The ED
NZR ED class
The NZR ED class locomotive was a class of electric locomotive used in Wellington, New Zealand. They were built by English Electric and New Zealand Railways between 1938 and 1940, and hauled mainly passenger trains on the Wellington region's 1500 V DC electrification, and banked freight trains on...
and EF
NZR EF class
The NZR EF class is a class of 22 25 kV AC electric locomotives that operate on the North Island Main Trunk between Palmerston North and Te Rapa in New Zealand...
classes were an exception. The EM class
NZR EM class (Electric Multiple Unit)
The NZR EM/ET class is a type of electric multiple unit used on suburban services in Wellington, New Zealand. They are owned by the Greater Wellington Regional Council and operated by Tranz Metro, a division of national railway operator KiwiRail....
in Wellington possibly stands for Electric Motor. ET is Electric Trailer. The DM class
NZR DM class (Electric Multiple Unit)
The NZR DM/D class is a type of electric multiple unit used on the rail passenger network of Wellington, New Zealand formed of DM power cars and D trailers...
units were an exception to this.
Almost all railcar
Railcar
A railcar, in British English and Australian English, is a self-propelled railway vehicle designed to transport passengers. The term "railcar" is usually used in reference to a train consisting of a single coach , with a driver's cab at one or both ends. Some railways, e.g., the Great Western...
s were classified RM
NZR RM class
The RM class is the classification used by the New Zealand Railways Department and its successors given to most railcars and railbuses that have operated on New Zealand's national rail network. As NZR and its successors has operated many diverse types of railcars, alternate names have been given...
(Rail Motor), and individual classes were known by alternate names such as the Vulcan railcars
NZR RM class (Vulcan)
The NZR RM class Vulcan railcars were operated by the New Zealand Railways Department in the South Island of New Zealand. All New Zealand railcars were classified as RM, and these were known as Vulcan railcars, from the name of the manufacturer, Vulcan Foundry of Britain. - Background :On 9 May...
of the South Island
South Island
The South Island is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand, the other being the more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, to the south and east by the Pacific Ocean...
and the Wairarapa railcars
NZR RM class (Wairarapa)
The NZR RM class Wairarapa railcar was the first truly successful class of railcars to operate on New Zealand's national rail network...
that ran over the Rimutaka Incline to the Wairarapa
Wairarapa
Wairarapa is a geographical region of New Zealand. It occupies the south-eastern corner of the North Island, east of metropolitan Wellington and south-west of the Hawke's Bay region. It is lightly populated, having several rural service towns, with Masterton being the largest...
.
Liveries
New Zealand's locomotives have appeared in several different liveries over the ages. Steam locomotives were mainly black. When the railcars and first-generation diesels came in, they were painted in "carnation red" with a white or yellow stripe.In the 1970s the first different livery appeared. Eleven members of the DJ class
NZR DJ class
The NZR DJ class locomotive is a class of diesel-electric locomotive used in New Zealand. The class were purchased from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries with a modernisation loan from the World Bank to replace steam locomotives in the South Island, where most of the class members worked most of their...
were painted "Southerner Blue" (mainly dark blue) to haul the Southerner express in the South Island. The Silver Fern
NZR RM class (Silver Fern)
This article is about the New Zealand railcar service and the railcars themselves. For other uses, see Silver Fern .The NZR RM class Silver Fern is a class of railcar in New Zealand. The three air-conditioned and sound-proofed 723-kW 96-seater diesel-electric twin-set railcars were built by...
railcars appeared in stainless steel, and the DX class
NZR DX class
The NZR DX class is a class of 49 Co-Co diesel-electric locomotives that currently operates on New Zealand's national railway network.Built by General Electric in Erie, Pennsylvania, United States, they were introduced to New Zealand between 1972 and 1976. The class is based on the General Electric...
, appearing in 1972, were painted "clockwork orange" (orange and yellow). In 1978, the rebuilt DC class
NZR DC class
The NZR DC class locomotive is the most common class of locomotive currently in operation on the New Zealand rail network. Primarily employed to haul freight trains operated by KiwiRail, the class is also used for long-distance passenger trains operated by Tranz Scenic and suburban passenger trains...
appeared in "fruit salad" (red, yellow, grey and black), and many locomotives followed suit. Following the split of New Zealand Rail Limited
Tranz Rail
Tranz Rail, formally Tranz Rail Holdings Ltd , was the main rail operator in New Zealand from 1991 until it was purchased by Toll Holdings in 2003.- Formation :...
from the New Zealand Railways Corporation
New Zealand Railways Corporation
KiwiRail Network, formerly ONTRACK , is the infrastructure arm of KiwiRail. The ONTRACK trading name was introduced in 2004 after the government repurchased all of New Zealand's rail infrastructure from Toll NZ. It does not operate revenue rolling stock...
in 1991, a modified livery of blue, yellow, grey and black appeared. For the first time, locomotives wore the name of their operator - New Zealand Rail - in prominent view. This livery was continued after 1993 when NZ Rail was privatised, and was slightly modified when the company was renamed Tranz Rail
Tranz Rail
Tranz Rail, formally Tranz Rail Holdings Ltd , was the main rail operator in New Zealand from 1991 until it was purchased by Toll Holdings in 2003.- Formation :...
in 1995 by replacing the NZ Rail logo with the new Tranz Rail logo. In 2001 a new livery to promote level crossing
Level crossing
A level crossing occurs where a railway line is intersected by a road or path onone level, without recourse to a bridge or tunnel. It is a type of at-grade intersection. The term also applies when a light rail line with separate right-of-way or reserved track crosses a road in the same fashion...
safety was trialed on DC 4323. This colour scheme was nicknamed "bumble bee"
Bumble-Bee (livery)
Bumble-Bee is an informal term describing a New Zealand railway locomotive livery found in common usage amongst the railfan community....
because of its black and yellow colours. Following the takeover of Tranz Rail by Australia's Toll Holdings
Toll Holdings
TOLL , properly TOLL Holdings Limited, is Australia's largest transport company, based in Melbourne, Victoria. The company has operations in road, rail, sea and air in 55 countries....
in 2004, Toll Rail
Toll NZ
Toll Group Limited is a New Zealand trucking company. A subsidiary of the Australian company Toll Holdings, it has its headquarters in Auckland. It carries out operations by road and in the air, and formerly by rail and sea....
's livery appeared, nicknamed "corn cob", consisting of green and yellow. That same year, DC class (and now DFT/DFB class) locomotives being used on Auckland commuter services began wearing the MAXX livery, which was dark blue and yellow with a MAXX logo on the side. When the government bought back Toll and introduced KiwiRail, it also introduced its own livery, consisting of grey and red (a second version later followed). Most of today's locomotives are painted in "fruit salad", blue, "bumble bee"
Bumble-Bee (livery)
Bumble-Bee is an informal term describing a New Zealand railway locomotive livery found in common usage amongst the railfan community....
, "corn cob" or KiwiRail.
List of Locomotive Classes
This is a list of all classes of locomotives that operate or have operated on New Zealand's national railway network. It does not include locomotives used on private industrial lines or bush tramways. It is believed to be complete, and is sorted in alphabetical order rather than within type. Articles on specific individual classes can be accessed from this page.Diesel-electric locomotives
(This list includes shunting classes. Some shunting classes worked on revenue services as well as performing yard shunting duties, most notably the DE class when it hauled Queen Elizabeth IIElizabeth II of the United Kingdom
Elizabeth II is the constitutional monarch of 16 sovereign states known as the Commonwealth realms: the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Jamaica, Barbados, the Bahamas, Grenada, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, Tuvalu, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Belize,...
's royal train in the early 1950s.)
| Image | Class | Numbers | Number in class | Year(s) introduced | Year(s) withdrawn | Power output | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMS (1980) | pre-1980 | TMS (1980) | pre-1980 | ||||||
| DA NZR DA class The NZR Da diesel-electric mainline locomotive class ran on the New Zealand railway system between 1955 and 1989. With 146 locomotives, it was the most numerous class to operate in New Zealand, just five more than the AB class steam locomotive.... |
DA | 86 - 996 | 1400 - 1545 | 146 | 1955 - 1967 | 1971 - 1990 | 1060 kW | 85 rebuilt as DC class, 5 as DAA, 1 as DAR | |
| DAA NZR DA class The NZR Da diesel-electric mainline locomotive class ran on the New Zealand railway system between 1955 and 1989. With 146 locomotives, it was the most numerous class to operate in New Zealand, just five more than the AB class steam locomotive.... |
DAA | 11 - 63 | 1400 - 1404, 1406 | 5 | 1971 | 1989 | 1060 kW | DA class refitted for low speed running | |
| DAR NZR DA class The NZR Da diesel-electric mainline locomotive class ran on the New Zealand railway system between 1955 and 1989. With 146 locomotives, it was the most numerous class to operate in New Zealand, just five more than the AB class steam locomotive.... |
517 | 1 | 1989 | 2009? | 1060 kW | Modified DA designed for heavy duty shunting | |||
| DB NZR DB class The NZR Db diesel-electric locomotive class was built in 1965-1966. They were a lighter version of the Da class to operate on secondary North Island lines from which the Da was excluded due to its weight. One of the principal lines which the Db dominated was the East Coast Main Trunk to Tauranga... |
DB | 1001 - 1180 | 1000 - 1016 | 17 | 1965 - 1966 | 1980 - 1989 | 705 kW | 10 rebuilt as DBR | |
 |
DBR NZR DB class The NZR Db diesel-electric locomotive class was built in 1965-1966. They were a lighter version of the Da class to operate on secondary North Island lines from which the Da was excluded due to its weight. One of the principal lines which the Db dominated was the East Coast Main Trunk to Tauranga... |
1199 - 1295 | 10 | 1980 - 1982 | still in use | 705 kW | Rebuilt DB | ||
| DC NZR DC class The NZR DC class locomotive is the most common class of locomotive currently in operation on the New Zealand rail network. Primarily employed to haul freight trains operated by KiwiRail, the class is also used for long-distance passenger trains operated by Tranz Scenic and suburban passenger trains... |
DC | 4006 - 4951 | 1551 - 1599 | 85 | 1978 - 1983 | still in use | 1100 kW 1230 kW | Rebuilt DA, two types, one with 12-645C engines, and one with 12-645E engines. | |
 |
DCP NZR DC class The NZR DC class locomotive is the most common class of locomotive currently in operation on the New Zealand rail network. Primarily employed to haul freight trains operated by KiwiRail, the class is also used for long-distance passenger trains operated by Tranz Scenic and suburban passenger trains... |
4277 - 4945 | 14 | still in use | 1230 kW | DC designated for passenger services | |||
 |
DE NZR DE class The NZR DE class is a New Zealand class of shunting diesel-electric locomotives. The New Zealand Railways intended to replace steam locomotives for shunting duties with this class... |
DE | 1308 - 1458 | 501 - 515 | 15 | 1952 | 1987 - 1989 | 490 kW | One in service for Taieri Gorge Railway Taieri Gorge Railway The Taieri Gorge Railway is a railway line and tourist train operation based at Dunedin Railway Station in the South Island of New Zealand... . |
| DF (1954) NZR DF class (1954) The NZR DF class of 1954 was the first class of mainline diesel-electric locomotives built for New Zealand's national railway network, built by English Electric... |
1500 - 1510 (1954) 1300 - 1309 (1960) |
10 | 1954 | 1972 - 1975 | 1120 kW | New Zealand's first mainline diesel locomotive | |||
 |
DF NZR DF class (1979) The NZR DF class of 1979 is a class of 30 Co-Co diesel-electric locomotives built by General Motors Diesel of Canada between 1979 and 1981. Between 1992 and 1997, all the locomotives were rebuilt as the DFT class, a turbocharged version of the DF.... |
DF (1979) | 6006 - 6317 | 1651 - 1670 | 30 | 1979 - 1981 | 1992 - 1997 | 1230 kW | All rebuilt as DFT |
| DFB NZR DF class (1979) The NZR DF class of 1979 is a class of 30 Co-Co diesel-electric locomotives built by General Motors Diesel of Canada between 1979 and 1981. Between 1992 and 1997, all the locomotives were rebuilt as the DFT class, a turbocharged version of the DF.... |
7010 - 7307 | 10 | 2006 | still in use | 1800 kW | Upgraded DFT | |||
| DFM NZR DF class (1979) The NZR DF class of 1979 is a class of 30 Co-Co diesel-electric locomotives built by General Motors Diesel of Canada between 1979 and 1981. Between 1992 and 1997, all the locomotives were rebuilt as the DFT class, a turbocharged version of the DF.... |
7036 - 7226 | 3 | still in use | 1800 kW | Upgraded DFT | ||||
 |
DFT NZR DF class (1979) The NZR DF class of 1979 is a class of 30 Co-Co diesel-electric locomotives built by General Motors Diesel of Canada between 1979 and 1981. Between 1992 and 1997, all the locomotives were rebuilt as the DFT class, a turbocharged version of the DF.... |
7008 - 7348 | 30 | 1992 - 1997 | still in use | 1800 kW | Rebuilt DF | ||
 |
DG NZR DG class The NZR DG and DH class locomotives were a class of diesel-electric locomotives used on New Zealand's national rail network, built by English Electric.- Introduction :... |
DG | 2007 - 2468 | 750 - 791 | 42 | 1955 - 1956 | 1983 | 560 kW | 11 were rebuilt from 1956 DH class |
| DH (1956) NZR DG class The NZR DG and DH class locomotives were a class of diesel-electric locomotives used on New Zealand's national rail network, built by English Electric.- Introduction :... |
766, 772, 777 - 783 | 11 | 1956 | 1968 | 560 kW | Variant of DG class; all rebuilt as DG | |||
| DH NZR DH class The NZR DH class is a type of diesel-electric shunting locomotive in New Zealand. The class consists of six heavy shunt U10B type loco built by General Electric in the US in 1978... |
DH | 2816 - 2868 | 900 - 905 | 6 | 1978 | still in use | 672 kW | ||
| DI NZR DI class The DI class locomotive was a class of diesel-electric locomotive in New Zealand. They were built by English Electric Australia. The class is very similar to the Queensland Rail 1620 Class... |
DI | 1808 - 1843 | 1100 - 1104 | 5 | 1966 | 1988 - 1989 | 755 kW | ||
 |
DJ NZR DJ class The NZR DJ class locomotive is a class of diesel-electric locomotive used in New Zealand. The class were purchased from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries with a modernisation loan from the World Bank to replace steam locomotives in the South Island, where most of the class members worked most of their... |
DJ | 3009 - 3689 | 1200 - 1263 | 64 | 1968 - 1969 | 1986 - 1991 | 672 kW | Six in service for Taieri Gorge Railway |
| DL NZR DL class The NZR DL class is a class of diesel-electric locomotives manufactured for KiwiRail by Dalian Locomotive and Rolling Stock Company with engines from MTU... |
9008 - 9204 | 20 | 2010 | 20 in service; 20 on order | 2700 kW | ||||
 |
DQ NZR DQ class The NZR DQ and QR class locomotives are two classes of mainline diesel-electric locomotives in New Zealand and Tasmania, Australia. Originally Queensland Rail 1460 and 1502 class, they were purchased by New Zealand Rail Limited in 1995 to be rebuilt, as a cheaper alternative to buying new... |
6007 -6036, 6324 - 6416 | 15 | 1995 | still in use | 1120 kW | Rebuilt QR; originally from Queensland | ||
 |
DSC NZR DSC class The NZR DSC class is a heavy shunting locomotive used throughout New Zealand. The class was built in seven batches, the first 18 locomotives being built by British Thomson-Houston of the United Kingdom, with the remainder being built by New Zealand Railways.... |
DSC | 2000 - 2759 | 400 - 469 | 70 | 1959 - 1967 | still in use | 315 kW | |
 |
DSG NZR DSG class The NZR DSG class is a type of diesel-electric shunting locomotive used in New Zealand. The class shares a central cab design with the smaller DSC class shunting locomotive, and is twin-engined... |
3005 - 3304 | 24 | 1981 - 1983 | still in use | 700 kW | |||
 |
DSJ NZR DSJ class The NZR DSJ class is a class of diesel-electric shunting locomotive used on the New Zealand rail network. The class has a very similar overall design to the DSG class, but is instead single-engined, has a cab that is offset from the centre, and is both shorter and lighter than its twin-engined... |
4004 - 4060 | 5 | 1984 - 1985 | still in use | 350 kW | |||
 |
DX NZR DX class The NZR DX class is a class of 49 Co-Co diesel-electric locomotives that currently operates on New Zealand's national railway network.Built by General Electric in Erie, Pennsylvania, United States, they were introduced to New Zealand between 1972 and 1976. The class is based on the General Electric... |
DX | 5016 - 5520 | 2600 - 2648 | 49 | 1972 - 1975 | All Rebuilt as DXC & DXB | 2050 kW | 2 rebuilt as DXR |
 |
DXB NZR DX class The NZR DX class is a class of 49 Co-Co diesel-electric locomotives that currently operates on New Zealand's national railway network.Built by General Electric in Erie, Pennsylvania, United States, they were introduced to New Zealand between 1972 and 1976. The class is based on the General Electric... |
5016 - 5166 & 5448 | 12 | still in use | 2050 kW | Upgraded DX | |||
 |
DXC NZR DX class The NZR DX class is a class of 49 Co-Co diesel-electric locomotives that currently operates on New Zealand's national railway network.Built by General Electric in Erie, Pennsylvania, United States, they were introduced to New Zealand between 1972 and 1976. The class is based on the General Electric... |
5172 - 5520 5039 | 28 | still in use | 2050 kW | DX class upgraded especially for Midland Line coal trains (C = coal) | |||
| DXH NZR DX class The NZR DX class is a class of 49 Co-Co diesel-electric locomotives that currently operates on New Zealand's national railway network.Built by General Electric in Erie, Pennsylvania, United States, they were introduced to New Zealand between 1972 and 1976. The class is based on the General Electric... |
0 | All rebuilt as DXB and DXC | 2050 kW | Upgraded DX | |||||
 |
DXR NZR DX class The NZR DX class is a class of 49 Co-Co diesel-electric locomotives that currently operates on New Zealand's national railway network.Built by General Electric in Erie, Pennsylvania, United States, they were introduced to New Zealand between 1972 and 1976. The class is based on the General Electric... |
8007, 8022 | 2 | 1993, 2006 | still in use | 2050 kW | Rebuilt DX | ||
| EB NZR EB class The EB class was a class of five battery electric locomotives built to perform shunting duties at the workshops of New Zealand's national rail network. The first was built in 1925 and began its working life in Frankton, though four years later, it was transferred to Christchurch's Addington... |
EB | 1809 - 1821 | 25 - 29 | 5 | 1925, 1929 | 1976 - 1980 | 23 kW | Originally battery-electric | |
| QR NZR DQ class The NZR DQ and QR class locomotives are two classes of mainline diesel-electric locomotives in New Zealand and Tasmania, Australia. Originally Queensland Rail 1460 and 1502 class, they were purchased by New Zealand Rail Limited in 1995 to be rebuilt, as a cheaper alternative to buying new... |
2027 - 2102, 3032 | 25 | 1995 | 2005 | 1120 kW | Originally from Queensland; 15 rebuilt as DQ | |||
Diesel-mechanical and diesel-hydraulic locomotives
- DSNZR DS classThe NZR DS class is a class of 16 diesel shunting locomotives built by the Vulcan Foundry and supplied by the Drewry Car Co from 1949 - 1955.-Operation:The locomotives were largely allocated to shunting yards, and later industrial service.-Withdrawal:...
- DSA
- DSB
- TRNZR TR classThe NZR TR class is a class of diesel shunting locomotives built by many different manufacturers. Many of these locomotives have been withdrawn, but some are still in service. The first locomotives of this class were built by the Drewry Car Co in 1936, and had 52 kW or 90 kW petrol engines...
Electric locomotives
| Image | Class | Numbers | Number in class | Year(s) introduced | Year(s) withdrawn | Voltage | Power output | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMS (1980) | pre-1980 | TMS (1980) | pre-1980 | |||||||
 |
EO NZR EA class The NZR Ea class were used by New Zealand Railways between 1968 and 1997 on the OtiraArthur's Pass section of the Midland line in the South Island, through the Otira Tunnel... |
EA | 39 - 74 | 1 - 5 | 5 | 1968 | still in use | 1500V DC overhead | 960 kW | Originally EA, reclassified EO in 1980 |
 |
EC NZR EC class The NZR EC class were a class of electric locomotive used in Christchurch, New Zealand. They replaced steam locomotives on trains through the Lyttelton rail tunnel between Lyttelton and Christchurch.-Introduction:... |
7 - 12 | 6 | 1928 - 1929 | 1970 | 1500V DC overhead | 885 kW | |||
 |
ED NZR ED class The NZR ED class locomotive was a class of electric locomotive used in Wellington, New Zealand. They were built by English Electric and New Zealand Railways between 1938 and 1940, and hauled mainly passenger trains on the Wellington region's 1500 V DC electrification, and banked freight trains on... |
ED | 15, 21 | 101 - 110 | 10 | 1938 | 1969 - 1981 | 1500V DC overhead | 670 kW | |
 |
EF NZR EF class The NZR EF class is a class of 22 25 kV AC electric locomotives that operate on the North Island Main Trunk between Palmerston North and Te Rapa in New Zealand... |
30007 - 30249 | 22 | 1986 - 1988 | still in use | 25kV 50Hz AC 25 kV AC The 25 kV Alternating current railway electrification system is commonly used in railways worldwide, especially for high-speed rail.-Overview:This electrification system is ideal for railways that cover long distances and/or carry heavy traffic... overhead |
3000 kW | Originally Class 30, reclassified EF | ||
 |
EO NZR EO class (1923) The New Zealand Railways EO class of 1923 were electric locomotives used on the steep Otira to Arthur's Pass section of the Midland Line. They were primarily for pulling trains through the 8.5 km Otira Tunnel to avoid the buildup of steam, smoke and soot.... |
2 - 6 | 5 | 1923 | 1968 | 1500V DC overhead | 510 kW | |||
 |
EW NZR EW class The NZR EW class locomotive was a class of electric locomotive used in Wellington, New Zealand. The classification 'EW' was due to their being electric locomotives allocated to Wellington.- Introduction :... |
EW | 107 - 171 | 1800 - 1806 | 7 | 1952 | 1988 | 1500V DC overhead | 1340 kW | |
Battery electric locomotives
- ENZR E class (1922)The NZR E class battery-electric locomotive represented the third unique type of locomotive to be given the E classification in New Zealand. The first was the E class of nine Double Fairlie steam locomotives of 1872-75; the second E class consisted of a Mallet compound made in 1906; and as both...
- EBNZR EB classThe EB class was a class of five battery electric locomotives built to perform shunting duties at the workshops of New Zealand's national rail network. The first was built in 1925 and began its working life in Frankton, though four years later, it was transferred to Christchurch's Addington...
(later converted to diesel-electric)
Electric Multiple Units
All electric multiple units (as of 2010) operate on 1500V DC overhead.| Image | Class | Number in class | In service | Formation | Passenger capacity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
DM/D | 49 | 1938 - present | D - DM (two-car) D - DM - D (three-car) |
132 (two-car) 204 (three-car) |
Planned to be withdrawn in 2011 |
 |
EM/ET | 44 | 1982 - present | EM - ET | 148 | |
| FP/FT | 49 (planned) | 2010 (planned) | FP - FT | 147 | Named Matangi, after the Māori Maori language Māori or te reo Māori , commonly te reo , is the language of the indigenous population of New Zealand, the Māori. It has the status of an official language in New Zealand... word for "wind". |
Railcars
All railcars, unless otherwise stated, are designated RM classNZR RM class
The RM class is the classification used by the New Zealand Railways Department and its successors given to most railcars and railbuses that have operated on New Zealand's national rail network. As NZR and its successors has operated many diverse types of railcars, alternate names have been given...
. For purposes here, they are classified under their common names.
| Image | Class | Number in class | In service | Power type | Passenger capacity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 88-seater NZR RM class (88 seater) The NZR RM class 88-seaters were a class of railcar used in New Zealand, known unofficially as 'articulateds', 'twinsets', 'Drewrys' and 'Fiats'. They were purchased to replace steam-hauled provincial passenger trains and mixed trains... |
35 | 1955 - 1978 | Diesel-mechanical | 88 | Also known as Fiat or twinset; 14 were converted to AC class articulated carriages | |
| Silver Fern NZR RM class (Silver Fern) This article is about the New Zealand railcar service and the railcars themselves. For other uses, see Silver Fern .The NZR RM class Silver Fern is a class of railcar in New Zealand. The three air-conditioned and sound-proofed 723-kW 96-seater diesel-electric twin-set railcars were built by... |
3 | 1972 - present | Diesel-electric | 96 | Used for excursions | |
 |
Standard NZR RM class (Standard) The NZR RM class Standard railcars were a class of railcar operated by the New Zealand Railways Department in the North Island of New Zealand. Officially classified as RM like all other railcar classes in New Zealand, they acquired the designation of 'Standard' to differentiate them from others... |
6 | 1938 - 1972 | Diesel-mechanical | 48 - 52 | |
| Vulcan NZR RM class (Vulcan) The NZR RM class Vulcan railcars were operated by the New Zealand Railways Department in the South Island of New Zealand. All New Zealand railcars were classified as RM, and these were known as Vulcan railcars, from the name of the manufacturer, Vulcan Foundry of Britain. - Background :On 9 May... |
9 | 1940 - 1978 | Diesel-mechanical | 48 - 50 | ||
 |
Wairarapa NZR RM class (Wairarapa) The NZR RM class Wairarapa railcar was the first truly successful class of railcars to operate on New Zealand's national rail network... |
7 | 1936 - 1956 | Diesel-mechanical | 25 - 49 |
Experimental railcars included the following:
- Clayton steam railcarNZR RM class (Clayton)The NZR RM class Clayton steam railcar was a unique railcar that operated on New Zealand's national rail network and one of only two steam railcars to operate in New Zealand - the other being 1925's RM class Sentinel-Cammell...
- Edison battery-electric railcarNZR RM class (Edison battery-electric)The NZR RM class Edison battery-electric railcar was a popular and successful railcar that ran in Canterbury, New Zealand for eight years. The prototype was arguably the first successful railcar in New Zealand but it was not developed into a class...
- Leyland diesel railbusNZR RM class (Leyland diesel)The NZR RM class Leyland diesel railcar or Midland railcar was the first diesel-powered vehicle to enter revenue service on New Zealand's national rail network. Two were built, RM 20 and RM 21, and they commenced service in August 1936 as temporary short-use vehicles that would operate until...
- Leyland experimental petrol railcarNZR RM class (Leyland petrol)The Leyland experimental petrol railcar was a unique railcar built and trialled in New Zealand in 1925. It should not be confused with the two much smaller Leyland diesel railbuses of 1936....
- MacEwan-Pratt petrol railcarNZR RM class (MacEwan-Pratt)The NZR RM class MacEwan-Pratt petrol railcar was the first railcar to run on New Zealand's national rail network, though it was never used in revenue service. It was built in 1912 at a time when the New Zealand Railways Department was seeking alternative methods of providing rural passenger...
- Model T Ford railcarNZR RM class (Model T Ford)The NZR RM class Model T Ford railcar was a type of railcar that operated on New Zealand's national rail network. Only two were built, classified as RM 4 and RM 5, and they were experimental railcars designed in an attempt to offer improved passenger services on quiet country branch lines that...
- Sentinel-Cammell steam railcarNZR RM class (Sentinel-Cammell)The NZR RM class Sentinel-Cammell steam railcar was a steam-powered railcar operated by the New Zealand Railways Department . It was the only one of its type to operate in New Zealand, and one of only two steam railcars trialled in the country; the other was the Clayton steam railcar.-Overview:In...
Diesel Multiple Units
| Image | Class | Number in class | In service | Formation | Passenger capacity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
ADK/ADB NZR ADK class (Diesel Multiple Unit) The ADK class consists of nine diesel multiple unit cars each coupled to an ADB class trailer, operating on Auckland's suburban rail network. The Auckland Regional Council owns these units, and they are operated by Veolia.- History :... |
9 | 1993 - present | ADK - ADB | 134 | Originally from Western Australia Western Australia Western Australia is a state of Australia, occupying the entire western third of the Australian continent. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Great Australian Bight and Indian Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east and South Australia to the south-east... The tenth trailer car is stored at Westfield |
 |
ADL/ADC NZR ADL class (Diesel Multiple Unit) The ADL class consists of ten diesel multiple unit cars each coupled to an ADC class trailer, built by Goninan for the Western Australian Government Railways in the early 1980s. They were purchased by New Zealand Rail Limited in 1993 to replace suburban carriage trains used in Auckland... |
10 | 1993 - present | ADL - ADC | 128 | Originally from Western Australia Western Australia Western Australia is a state of Australia, occupying the entire western third of the Australian continent. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Great Australian Bight and Indian Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east and South Australia to the south-east... |
Steam locomotives
| Image | Class | Numbers | Number in class | Year(s) introduced | Year(s) withdrawn | Whyte notation Whyte notation The Whyte notation for classifying steam locomotives by wheel arrangement was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte and came into use in the early twentieth century encouraged by an editorial in American Engineer and Railroad Journal... |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
A of 1873 NZR A class (1873) The A class was the second class of steam locomotive ordered to work on New Zealand's national railways. It should not be confused with the more numerous A class 4-6-2 tender locomotives of 1906. Initially ordered by the Public Works Department for use in the construction of lines, the A class... |
14 | 1873 | 1905 | 0-4-0T | ||
| A of 1906 NZR A class (1906) The A class were steam locomotives built in 1906 with a 4-6-2 wheel arrangement for New Zealand's national railway network, and described by some as the most handsome engines to run on New Zealand rails. The class should not be confused with the older and more obscure A class of 1873. They were... |
58 | 1906 | 1969 | 4-6-2 4-6-2 4-6-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .These locomotives are also known as Pacifics... |
Includes 30 locomotives reclassified from AD | ||
| AA NZR Aa class The AA class consisted of ten steam locomotives built to operate on New Zealand's national rail network. Built to a similar design to the A class of 1906, they had a wheel arrangement of 4-6-2 and were suited to hauling freight services. Ordered and built in 1914, all ten entered service in New... |
10 | 1914 | 1957 | 4-6-2 4-6-2 4-6-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .These locomotives are also known as Pacifics... |
|||
| AB NZR Ab class The NZR AB class was a class of 4-6-2 Pacific tender steam locomotive that operated on New Zealand's national railway system. Originally an improvement on the 1906 A class, 141 were built between 1915 and 1927 by NZR's Addington Workshops, A & G Price Limited of Thames, New Zealand, and North... |
141 | 1915 | 1969 | 4-6-2 4-6-2 4-6-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .These locomotives are also known as Pacifics... |
New Zealand's most prolific class of steam locomotive; 10 rebuilt from WAB class | ||
| AD NZR A class (1906) The A class were steam locomotives built in 1906 with a 4-6-2 wheel arrangement for New Zealand's national railway network, and described by some as the most handsome engines to run on New Zealand rails. The class should not be confused with the older and more obscure A class of 1873. They were... |
30 | 1910 | 1916 | 4-6-2 4-6-2 4-6-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .These locomotives are also known as Pacifics... |
Reclassified A in 1916 | ||
| B of 1874 NZR B class (1874) The NZR B class of 1874 was the first of two steam locomotive classes to be designated as B by the Railways Department that then oversaw New Zealand's national rail network... |
2 | 1874 | 1890 | 0-4-4-0T Double Fairlie Fairlie A Fairlie is a type of articulated steam locomotive that has the driving wheels on bogies. The locomotive may be double-ended or single ended... |
|||
| B of 1899 NZR B class (1899) The B class of 1899 was a class of steam locomotives that operated on New Zealand's national rail network. An earlier B class of Double Fairlies had entered service in 1874, but as they had departed from the ownership of the New Zealand Railways by the end of 1896, the B classification was free... |
10 | 1899 | 1967 | 4-8-0 4-8-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. The type was nicknamed the Mastodon or Twelve-wheeler in North America.... |
Three rebuilt as WE class | ||
| BA NZR Ba class The BA class was a class of steam locomotive built by the New Zealand Railways Department for use on New Zealand's national rail network. The first BA entered service in November 1911, with the last of the 11 class members introduced on 14 May 1913.... |
10 | 1911 | 1969 | 4-8-0 4-8-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. The type was nicknamed the Mastodon or Twelve-wheeler in North America.... |
|||
| BB NZR Bb class The BB class of steam locomotives comprised 30 engines operated by New Zealand Railways in the North Island of New Zealand. Similar in design and appearance to the preceding B and BA classes, the first BB class locomotive entered service in February 1915, with the last to commence operations doing... |
30 | 1915 | 1968 | 4-8-0 4-8-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. The type was nicknamed the Mastodon or Twelve-wheeler in North America.... |
|||
| BC NZR Bc class The BC class comprised a single steam locomotive that operated on New Zealand's national rail network. Built for the Wellington and Manawatu Railway and classified simply as No... |
1 | 1902 | 1927 | 2-8-2 2-8-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... |
Originally from Wellington & Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | ||
 |
C NZR C class (1873) The C class consists of a number of tank locomotives built to operate on New Zealand's national rail network during its infancy. It is sometimes referred to as the little C class or the original C class to distinguish it from the C class of 1930.... of 1873 |
16 | 1873 | 1920 | 0-4-0ST original 0-4-2ST rebuild |
||
| C NZR C class (1930) The C class consisted of twenty-four steam locomotives built to perform shunting duties on New Zealand's national rail network. It is sometimes known as the big C class to differentiate it from the C class of 1873.-History and construction:... of 1930 |
24 | 1930 | 1968 | 2-6-2 2-6-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, six coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
|||
 |
D of 1874 NZR D class (1874) The NZR D class was a class of tank steam locomotives that operated on New Zealand's national railway network. The first members of the class entered service in 1874, and all had left the service of NZR by the end of 1927, which allowed the D classification to be used again in 1929.- Introduction... |
35 | 1874 | 1927 | 2-4-0T | ||
_josephine_otago_settlers_museum.jpg) |
E of 1872 NZR E class (1872) The NZR E class of Double Fairlie steam locomotives were two different types of Fairlie locomotive, and were the first classes to take that designation, followed by the E class Mallet compound locomotive of 1906 and then the E class battery electric locomotive of 1922... |
8 | 1872 | 1906 | 0-4-4-0T Double Fairlie Fairlie A Fairlie is a type of articulated steam locomotive that has the driving wheels on bogies. The locomotive may be double-ended or single ended... |
||
 |
E of 1906 NZR E class (1906) The E class comprised a single steam locomotive operated by New Zealand Railways from 1906 until 1917. Classified as E 66 and nicknamed Pearson's Dream after its designer, it was an experimental Mallet locomotive designed to work on the Rimutaka Incline... |
1 | 1906 | 1917 | 2-6-6-2T Mallet Mallet locomotive The Mallet Locomotive is a type of articulated locomotive, invented by a Swiss engineer named Anatole Mallet .... |
||
| F NZR F class The NZR F class was the first important class of steam locomotive built to operate on New Zealand's railway network after the national gauge of 1067 millimetres was adopted. The first locomotives built for the new 1067 mm railways were two E class double Fairlies for the Dunedin and Port Chalmers... |
88 | 1872 | 1964 | 0-6-0T | |||
| FA | 13 | 1892 | 1943 | 0-6-2T | |||
| FB | 13 | 1897 | 1943 | 0-6-2T | |||
| G of 1874 | 4 | 1874 | 1918 | 4-4-0ST | |||
 |
G of 1928 NZR G class (1928) The NZR G class was a type of Garratt steam locomotive used in New Zealand, the only such Garratt type steam locomotives ever used by New Zealand Government Railways. They were ordered to deal with traffic growth over the heavy gradients of the North Island Main Trunk and to do away with the use of... |
3 | 1928 | 1937 | 4-6-2+2-6-4 4-6-2+2-6-4 A 4-6-2+2-6-4, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, is a Garratt articulated locomotive.Other equivalent classifications are:... Garratt Garratt A Garratt is a type of steam locomotive that is articulated in three parts. Its boiler is mounted on the centre frame, and two steam engines are mounted on separate frames, one on each end of the boiler. Articulation permits larger locomotives to negotiate curves and lighter rails that might... |
All rebuilt as G of 1937 | |
| G of 1937 NZR G class (1928) The NZR G class was a type of Garratt steam locomotive used in New Zealand, the only such Garratt type steam locomotives ever used by New Zealand Government Railways. They were ordered to deal with traffic growth over the heavy gradients of the North Island Main Trunk and to do away with the use of... |
6 | 1937 | 1956 | 4-6-2 4-6-2 4-6-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .These locomotives are also known as Pacifics... |
Rebuilt from G of 1928 | ||
 |
H NZR H class The NZR H class locomotive was a unique class of locomotive used by the New Zealand Railways Department on the famous Rimutaka Incline, the three-mile section of 1 in 15 gradient between Cross Creek and Summit, over the Rimutaka Ranges... |
199 - 204 | 6 | 1878 | 1955 | 0-4-2T Fell Fell mountain railway system The Fell system uses a raised centre rail between the two running rails on steeply-graded railway lines to provide extra traction and braking, or braking alone. Trains are propelled by wheels or braked by shoes pressed horizontally onto the centre rail, as well as by means of the normal running... |
Includes H 199, the only remaining Fell locomotive in the world |
| J of 1874 NZR J class (1874) The J class were steam locomotives with the wheel arrangement of 2-6-0 that were built in 1874 to operate on the railway network of New Zealand. They should not be confused with the more famous J class of 1939... |
32 | 1874 | 1935 | 2-6-0 2-6-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and no trailing wheels. This arrangement is commonly called a Mogul... |
|||
 |
J of 1939 NZR J class (1939) The NZR J class steam locomotives were a class of locomotive used in New Zealand. Following the success of the K class on NZR main lines, there was an urgent need for a modern, powerful locomotive capable of running over secondary lines laid with lighter rails. Thus a new "Mountain" 4-8-2 type... |
1200 - 1239 | 40 | 1939 | 1971 | 4-8-2 4-8-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... |
12 were rebuilt as JB class |
 |
JA NZR Ja class The NZR JA class were a type of 4-8-2 steam locomotive used on the New Zealand railway network. The class was built in two batches, with the second batch possessing some differences from the first... |
1240 - 1290 | 51 | 1946 - 1956 | 1964 - 1971 | 4-8-2 4-8-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... |
Includes JA 1274 - the last NZR steam locomotive built. |
| JB NZR JB class The NZR JB class steam locomotives were all originally members of the J class of 1939. Built by North British Locomotive Works, Scotland, they all initially burned coal and wore distinctive bullet-like streamlining.- Conversion to oil burning :... |
12 | 4-8-2 4-8-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... |
Oil-burning variant of 1939 J class. 12 locomotives rebuilt from J class. | ||||
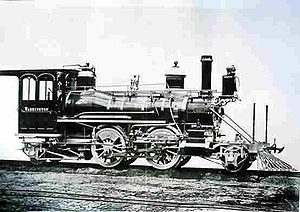 |
K of 1877 NZR K class (1877) The NZR Rogers K class was the first example of American-built locomotives to be used on New Zealand's railways. Their success coloured locomotive development in New Zealand until the end of steam.-History:... |
8 | 1877 | 1927 | 2-4-2 2-4-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-4-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... |
||
| K NZR K class (1932) The NZR K class of 1932 was a class of mixed traffic 4-8-4 steam locomotives that operated on New Zealand's railway network. The locomotives were developed following the failure of the G class Garratts... of 1932 |
900 - 929 | 30 | 1932 | 1967 | 4-8-4 4-8-4 Under the Whyte notation classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-4 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles .Other equivalent classifications are:UIC classification: 2D2... |
||
 |
KA NZR Ka class The NZR KA class of 1939 was a class of mixed traffic 4-8-4 steam locomotives that operated on New Zealand's railway network. They were built after the success of the K class to meet the increasing traffic demands of the New Zealand Railways Department... |
930 - 964 | 35 | 1939 - 1950 | 1964 - 1967 | 4-8-4 4-8-4 Under the Whyte notation classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-4 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles .Other equivalent classifications are:UIC classification: 2D2... |
Modified version of K with roller bearings and ACFI feedwater heaters |
| KB NZR Kb class The NZR KB class of 1939 was a class of mixed traffic steam locomotives that operated on New Zealand's railway network. They were built by the New Zealand Railways Department after the success of the K class to meet the increasing traffic demands on the Midland Line in the South Island... |
965 - 970 | 6 | 1939 | 1968 | 4-8-4 4-8-4 Under the Whyte notation classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-4 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles .Other equivalent classifications are:UIC classification: 2D2... |
KA class fitted with trailing-wheel boosters | |
| L | 10 | 1877 | 1901 - 1939 | 2-4-0T 4-4-0T 4-4-2T |
|||
 |
LA NZR La class The NZR LA class was a class of steam locomotives used by the New Zealand Railways Department and the New Zealand Midland Railway Company. They were built by Nasmyth, Wilson and Company in 1887 for New Zealand Midland Railway Company, and were taken over by NZR in 1900, when the government acquired... |
5 | 1887 - 1892 | 1920 - 1928 | 4-4-0T | Originally from New Zealand Midland Railway (nationalised 1900) | |
| M | 4 | 1875 | 1919 - 1928 | 0-6-0T 2-4-4T |
|||
 |
N NZR N class The N class were 12 steam locomotives that operated on the national rail network of New Zealand. They were built in three batches, including one batch of two engines for the private Wellington and Manawatu Railway Company, the WMR, by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1885, 1891, and 1901... |
12 | 1885 | 1934 | 2-6-2 2-6-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, six coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
Two originally from Wellington & Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | |
| NA NZR Na class The NA class was a class of two steam locomotives that operated on the privately owned Wellington and Manawatu Railway and then the publicly owned national rail network in New Zealand... |
2 | 1894 | 1929 | 2-6-2 2-6-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, six coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
Originally from Wellington & Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | ||
| NC NZR Nc class The NZR NC class was a class of two steam locomotives built by Baldwin Locomotive Works built for service on New Zealand's private Wellington and Manawatu Railway... |
2 | 1902 | 1931 | 2-6-2 2-6-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, six coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
Originally from Wellington & Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | ||
| O NZR O class The O class consisted of six steam locomotives that operated on New Zealand's national rail network. Ordered from the Baldwin Locomotive Works of Pennsylvania in 1885, three arrived in time to begin work in December 1885, while two more were placed in service in January 1886 and the sixth in... |
6 | 1885 | 1922 | 2-8-0 2-8-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels... |
|||
| OA NZR Oa class The OA class, built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works for the Wellington and Manawatu Railway in New Zealand, consisted of a solitary steam locomotive. Ordered in 1894, it entered service in August of that year as No. 13 and was the first narrow gauge Vauclain compound in the world... |
1 | 1894 | 1929 | 2-8-0 2-8-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels... |
Originally from Wellington & Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | ||
| OB NZR Ob class The OB class was the first class of steam locomotives constructed by the Baldwin Locomotive Works for the Wellington and Manawatu Railway in New Zealand. The class consisted of two locomotives ordered in 1888, and they entered service in September of that year as WMR No.'s 11 and 12... |
2 | 1888 | 1931 | 2-8-0 2-8-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels... |
Originally from Wellington & Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | ||
| OC NZR Oc class The OC class, built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works for the Wellington and Manawatu Railway in New Zealand, consists of a solitary steam locomotive. Ordered in 1896 as an externally similar but more powerful version of the OA class locomotive ordered in 1894, it entered service in June 1897 as No.... |
1 | 1896 | 1930 | 2-8-0 2-8-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels... |
Originally from Wellington & Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | ||
| P of 1876 NZR P class (1876) The P class was a class of two tank locomotives built to work on the government-owned national rail network of New Zealand in 1876. Their wheel arrangement was 0-6-0T under the Whyte notation system and they were initially ordered by the Otago Provincial Council, but they were soon incorporated... |
2 | 1876 | 1885 | 0-6-0ST | |||
| P of 1885 NZR P class (1885) The P class was a class of steam locomotives built to haul freight trains on the national rail network of New Zealand. The class consisted of ten individual locomotives ordered from the British company of Nasmyth, Wilson and Company in 1885, but miscommunications about the weight limitations... |
10 | 1885 | 1930 | 2-8-0 2-8-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels... |
|||
| Q of 1878 | 2 | 1878 | 1898 | 2-4-4T | |||
| Q of 1901 NZR Q class (1901) The NZR Q class was an important steam locomotive not only in the history of New Zealand's railway network but also in worldwide railways in general. Designed by New Zealand Government Railways' Chief Mechanical Engineer A. L. Beattie and ordered from the Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1901, they... |
13 | 1901 | 1957 | 4-6-2 4-6-2 4-6-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .These locomotives are also known as Pacifics... |
The world's first 4-6-2 Pacific 4-6-2 4-6-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .These locomotives are also known as Pacifics... locomotive |
||
| R NZR R class The NZR R class was a class of early 0-6-4T single Fairlie steam locomotives operated by New Zealand's Railways Department between 1879 and 1936.-Introduction:... |
18 | 1878 | 1936 | 0-6-4T Single Fairlie Fairlie A Fairlie is a type of articulated steam locomotive that has the driving wheels on bogies. The locomotive may be double-ended or single ended... |
|||
| S NZR S class The NZR S class was a class of seven 0-6-4T single Fairlie steam locomotives used in New Zealand.The locomotives were ordered by the New Zealand Railways Department in 1880, and delivered from the Avonside engine works in 1881–1882. They were considerably larger than the earlier R class, and all... |
7 | 1880 | 1927 | 0-6-4T Single Fairlie Fairlie A Fairlie is a type of articulated steam locomotive that has the driving wheels on bogies. The locomotive may be double-ended or single ended... |
|||
| T NZR T class The NZR T class was a class of steam locomotive used in New Zealand.-History:By the late 1870s there was a distinct need for a powerful type of locomotive to operate the steep section of the Main South Line between Dunedin and Oamaru... |
6 | 1879 | 1928 | 2-8-0 2-8-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels... |
|||
| U | 9 | 1894 | 1959 | 4-6-0 4-6-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles in a leading truck, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and no trailing wheels. This wheel arrangement became the second-most popular... |
|||
| UA | 6 | 1899 | 1937 | 4-6-0 4-6-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles in a leading truck, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and no trailing wheels. This wheel arrangement became the second-most popular... |
|||
| UB | 22 | 1901 | 1957 | 4-6-0 4-6-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles in a leading truck, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and no trailing wheels. This wheel arrangement became the second-most popular... |
|||
| UC | 10 | 1901 | 1959 | 4-6-0 4-6-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles in a leading truck, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and no trailing wheels. This wheel arrangement became the second-most popular... |
|||
| UD NZR UD class The NZR UD class was a class of two 4-6-0 steam locomotivesbuilt by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1904 for the Wellington and Manawatu Railway Company... |
2 | 1904 | 1931 | 4-6-0 4-6-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles in a leading truck, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and no trailing wheels. This wheel arrangement became the second-most popular... |
Originally from Wellington & Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | ||
 |
V NZR V class The NZR V class steam locomotive was used on New Zealand's railway network from 1885 onwards.-Introduction:The heavy increase in traffic by the early 1880s necessitated a design for a new class of passenger locomotive. The V class was conceived as an enlarged version of the 2-4-2 NZR K class of... |
13 | 1885 | 1937 | 2-6-2 2-6-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, six coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
Three originally from Wellington & Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | |
| W NZR W class The NZR W class consisted of two steam locomotives built at the Addington Railway Workshops in Christchurch, New Zealand by the New Zealand Railways Department.... |
192, 238 | 2 | 1889 | 1959 | 2-6-2T | Includes W 192, the first NZR locomotive built in New Zealand. | |
| WA | 11 | 1892 | 1962 | 2-6-2T | |||
| WAB NZR Wab class The WAB class locomotives were steam locomotives designed, built and used by New Zealand Railways Department. Their wheel arrangement is described by the Whyte notation 4-6-4T. The locomotives were designed by NZR chief draughtsman S.H. Jenkinson as tank versions of the AB class 4-6-2 Pacific... |
30 | 1918 - 1927 | 1947 - 1969 | 4-6-4T | 14 rebuilt from WS class; 10 rebuilt as AB class | ||
| WB NZR Wb class The NZR WB class was a class of tank locomotives that operated in New Zealand. Built in 1898 by the Baldwin Locomotive Works, the twelve members of the class entered service during the first five months of 1899... |
12 | 1898 | 1957 | 2-6-2T | |||
| WD NZR Wd class The NZR WD class was a class of tank locomotive built by Baldwin Locomotive Works to operate on New Zealand's national rail network. Essentially a more advanced version of 1898's WB class, the eighteen members of the WD class were ordered in 1901 and most entered service that year, though three... |
18 | 1901 | 1936 | 2-6-4T | |||
| WE | 3 | 1902 | 1969 | 4-6-4T | Rebuilt from B of 1899; equipped with Fell Fell mountain railway system The Fell system uses a raised centre rail between the two running rails on steeply-graded railway lines to provide extra traction and braking, or braking alone. Trains are propelled by wheels or braked by shoes pressed horizontally onto the centre rail, as well as by means of the normal running... centre rail braking for use on Rimutaka and Rewanui Inclines. |
||
| WF NZR Wf class The NZR WF class were steam locomotives designed, built and used by New Zealand Railways Department. Their wheel arrangement is described by the Whyte notation 2-6-4T and the first members of the class entered service in 1904. The locomotives were tank engines designed by the Railways Department's... |
41 | 1904 | 1969 | 2-6-4T | |||
| WG | 20 | 1910 | 1964 | 4-6-4T | 14 rebuilt as WW class | ||
| WH NZR WH class The NZR WH class was a class of three steam locomotives built by Manning Wardle built for service on New Zealand's private Wellington and Manawatu Railway . They did not acquire their WH classification until 1908 when the publicly owned New Zealand Railways Department purchased the WMR and its... |
3 | 1884 | 1927 | 2-4-2T | Originally from Wellington & Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | ||
| WJ NZR WJ class The NZR WJ class was a class of one steam locomotive built by Baldwin Locomotive Works for service on New Zealand's private Wellington and Manawatu Railway . She acquired the WJ classification when the publicly owned New Zealand Railways Department purchased the WMR and its locomotive fleet in... |
1 | 1904 | 1928 | 2-8-4T | Originally from Wellington & Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | ||
| WS NZR Wab class The WAB class locomotives were steam locomotives designed, built and used by New Zealand Railways Department. Their wheel arrangement is described by the Whyte notation 4-6-4T. The locomotives were designed by NZR chief draughtsman S.H. Jenkinson as tank versions of the AB class 4-6-2 Pacific... |
14 | 1917 | 1936 | 4-6-4T | All rebuilt as WAB class | ||
| WW | 51 | 1913 | 1969 | 4-6-4T | 14 rebuilt from WG class | ||
| X NZR X class The NZR X class was a pioneering class of eighteen 4-8-2 steam locomotives designed by A. L. Beattie that operated on the national rail network of New Zealand... |
18 | 1909 | 1957 | 4-8-2 4-8-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... |
The world's first 4-8-2 Mountain 4-8-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... locomotive |
||
| Y | 3 | 1923 | 1958 | 0-6-0T |
Steam locomotive notes:
- Two other types of locomotives built in the 1870s were included in the A class. All three had a wheel arrangementWheel arrangementIn rail transport, a wheel arrangement is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed beneath a locomotive.. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and connections, with the adopted notations varying by country...
of 0-4-00-4-0Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-4-0 represents one of the simplest possible types, that with two axles and four coupled wheels, all of which are driven...
T, but were technically and aesthetically quite different. The other A types are often known as the Shanks A and the Mills A, after their respective builders. - A completely different type of locomotive was nominally classified as being the solitary member of the S class in 1877 (the main S class was not introduced until 1880), but it was typically known as Robina.

