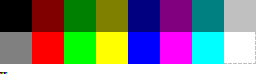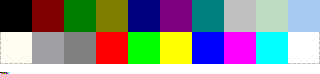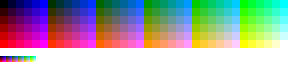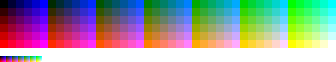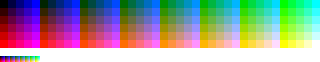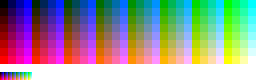List of software palettes
Encyclopedia
-
-
- For a full listing of computer's color palettes, see List of palettes
-
Computer systems that use a 4-bit or 8-bit pixel
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
depth
Color depth
In computer graphics, color depth or bit depth is the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. This concept is also known as bits per pixel , particularly when specified along with the number of bits used...
can display up to 16 or 256 colors simultaneously. Many personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s in the early 1990s displayed at most 256 different colors, freely selected by software (either by the user or by a program) from their wider hardware's RGB color palette.
Usual selections of colors in limited subsets (generally 16 or 256) of the full palette includes some RGB level arrangements commomly used with the 8-bit palettes as master palettes or universal palettes (i.e., palettes for multipurpose uses).
These are some representative software palettes, but any selection can be made in such type of systems.
For specific hardware color palettes, see the List of monochrome and RGB palettes, List of 8-bit computer hardware palettes, the List of 16-bit computer hardware palettes and the List of videogame consoles palettes articles.
Each palette is represented by an array of color patches. A one-pixel size version appears below each palette, to make it easy to compare palette sizes.
For each unique palette, an image color test chart and sample image (truecolor original follows) rendered with that palette (without dithering) are given. The test chart shows the full 8-bit, 256 levels of the red, green, and blue (RGB) primary colors and cyan, magenta, and yellow complementary colors, along with a full 8-bit, 256 levels grayscale. Gradients of RGB intermediate colors (orange, lime green, sea green, sky blue, violet and fuchsia), and a full hue
Hue
Hue is one of the main properties of a color, defined technically , as "the degree to which a stimulus can be describedas similar to or different from stimuli that are described as red, green, blue, and yellow,"...
spectrum are also present. Color charts are not gamma
Gamma correction
Gamma correction, gamma nonlinearity, gamma encoding, or often simply gamma, is the name of a nonlinear operation used to code and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems...
corrected.
 |
 |
These elements illustrate the color depth
Color depth
In computer graphics, color depth or bit depth is the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. This concept is also known as bits per pixel , particularly when specified along with the number of bits used...
and distribution of the colors of any given palette, and the sample image indicates how the color selection of such palettes could represent real-life images.
System specifics
These are selections of colors officially employed as system palettes in some popular operating systemOperating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
s for personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s that supports 8-bit displays.
Microsoft Windows default 16-color palette
 |
 |
Used by this platform as a roughly backward compatible palette for the CGA
Color Graphics Adapter
The Color Graphics Adapter , originally also called the Color/Graphics Adapter or IBM Color/Graphics Monitor Adapter, introduced in 1981, was IBM's first color graphics card, and the first color computer display standard for the IBM PC....
, EGA
Enhanced Graphics Adapter
The Enhanced Graphics Adapter is the IBM PC computer display standard specification which is between CGA and VGA in terms of color and space resolution. Introduced in October 1984 by IBM shortly after its new PC/AT, EGA produces a display of 16 simultaneous colors from a palette of 64 at a...
and VGA
Video Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector or the 640×480 resolution...
text modes, but with colors arranged in a different order. Also is the default palette for 16 color icons. Command Prompt
Command Prompt
Command Prompt is the Microsoft-supplied command-line interpreter on OS/2, Windows CE and on Windows NT-based operating systems...
uses the CGA
Color Graphics Adapter
The Color Graphics Adapter , originally also called the Color/Graphics Adapter or IBM Color/Graphics Monitor Adapter, introduced in 1981, was IBM's first color graphics card, and the first color computer display standard for the IBM PC....
color palette instead.
The corresponding indices into this palette are:
| 0 — black | 8 — gray |
| 1 — maroon | 9 — red |
| 2 — green | 10 — lime |
| 3 — olive | 11 — yellow |
| 4 — navy | 12 — blue |
| 5 — purple | 13 — fuchsia |
| 6 — teal | 14 — aqua |
| 7 — silver | 15 — white |
Microsoft Windows default 20-color palette
 |
 |
In 256-color mode, there are four additional standard Windows colors, twenty system reserved colors in total; thus the system leaves 236 palette indexes free for applications to use. The system color entries inside a 256-color palette table are the first ten plus the last ten. In any case, the additional system colors do not seem to add a sharp color richness: they are only some intermediate shades of grayish colors.
The complete 20-color Windows' system palette is:
| 0 — black | 246 — cream |
| 1 — dark red | 247 — medium grey |
| 2 — dark green | 248 — dark grey |
| 3 — dark yellow | 249 — red |
| 4 — dark blue | 250 — green |
| 5 — dark magenta | 251 — yellow |
| 6 — dark cyan | 252 — blue |
| 7 — light grey | 253 — magenta |
| 8 — money green | 254 — cyan |
| 9 — sky blue | 255 — white |
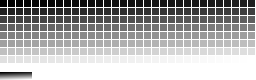
RISC OS default palette
 |
 |
Acorn
Acorn Computers
Acorn Computers Ltd. was a British computer company established in Cambridge, England, in 1978. The company produced a number of computers which were especially popular in the UK. These included the Acorn Electron, the BBC Micro, and the Acorn Archimedes...
RISC OS
RISC OS
RISC OS is a computer operating system originally developed by Acorn Computers Ltd in Cambridge, England for their range of desktop computers, based on their own ARM architecture. First released in 1987, under the name Arthur, the subsequent iteration was renamed as in 1988...
2.x and 3.x provided this 16-color palette :
| 0 — white | 8 — dark blue |
| 1 | 9 — yellow |
| 2 | 10 — green |
| 3 | 11 — red |
| 4 | 12 — beige |
| 5 | 13 — dark green |
| 6 | 14 — orange |
| 7 — black | 15 — light blue |
RGB arrangements
These are selections of colors based in evenly ordered RGB levels which provide complete RGB combinations, mainly used as master palettes to display any kind of image within the limitations of the 8-bit pixel depthColor depth
In computer graphics, color depth or bit depth is the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. This concept is also known as bits per pixel , particularly when specified along with the number of bits used...
.
6 level RGB
 |
 |
Having six levels for every primary, with 63 = 216 combinations. The index can be addressed by (36×R)+(6×G)+B, with all R, G and B values in a range from 0 to 5. Intended as homogeneous RGB cube, it gives six true grays. Also there is room for another sorts of 40 colors, so this disposition wastes many places in the 8-bit palette.
Systems that use this software palette are:
- Web palette
- Microsoft WindowsMicrosoft WindowsMicrosoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
256 color default palette (this also contain fixed system colors and other intemediate levels of gray, so RGB simple direct addressing is not possible). - Apple Macintosh 256 color default palette, it also contains four gradients of ten shades each for gray, red, green and blue.
6-7-6 levels RGB
 |
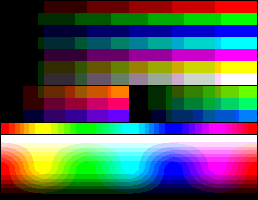 |
This palette is constructed with six levels for red and blue primaries and seven levels for the green primary, giving 6×7×6 = 252 combinations. The index can be addressed by (42×R)+(6×G)+B, with R and B values in a range from 0 to 5 and G in a range from 0 to 6. The same case as the former, but with an added level of green due to the greater sensibility of the normal human eye to this frequency.
It does not provide true grays, but remaining indexes can be filled with four intermediate grays. In any case, there is little room for any other color.
6-8-5 levels RGB
 |
 |
This palette is constructed with six levels for red, eight levels for green and five levels for the blue primaries, giving 6×8×5 = 240 combinations. The index can be addressed by (40×R)+(5×G)+B, with R ranging from 0 to 5, G from 0 to 7 and B from 0 to 4. Levels are chosen in function of sensibility of the normal human eye to every primary color.
Also, it does not provide true grays. Remaining indexes can be filled with sixteen intermediate grays or other fixed colors. In fact, this is the best balanced RGB master software palette, in a compromise between the RGB arrangement based in the human eye's sensibility and a sufficient remaining palette entries for another purposes.
8-8-4 levels RGB
 |
 |
The 8-8-4 level RGB use eight levels for each of the red and green color components (3+3 high order bits), and four levels (2 low order bits) for the blue component, due to the lesser sensitivity of the normal human eye to this primary color. This results in a 8×8×4 = 256-color palette as follows:
This RGB software palette occupies the full 8-bit range of possible palette entries, so there is no room for other fixed colors. Software using this palette must draw their user interface elements with the same colors used to show pictures. Also again, it does not provide true grays.
Grayscale palettes
 |
 |
Simple palette made doing every triplet RGB primaries having equal values as a continuous gradient from black to white through the full available palette entries. Here is the 8-bit, 256 levels palette:
Used to display pure grayscale
Grayscale
In photography and computing, a grayscale or greyscale digital image is an image in which the value of each pixel is a single sample, that is, it carries only intensity information...
TIFF or JPEG
JPEG
In computing, JPEG . The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality....
images, for example.
Color gradient palettes
Palettes made of a continuous color gradient from darkest to lightest arbitrary hues. The pixel data is treated as if it were grayscale, but the color table plays with RGB color combinations, not only gray. The relationship between the original luminance and the mapped one can vary, but the lighting scale is preserved along all the palette entries.One very common case of such palettes is the sepia tone palette, which gives an image an old fashioned and aged look (left). Another gradient example, based on blue hues, is presented here (right), but any hue or mixing of hues can be used. Many cell phones with built-in cameras have options to take colorized photos using this technique.
_palette_sample_image.png) |
_palette_sample_image.png) |
|
_palette.png) |
_palette.png) |
Adaptive palettes
 |
 |
Those whose whole number of available indexes are filled with RGB combinations selected from the statistical order of apparience (usually balanced) of a concrete full true color original image. There exists many algorithms to pick the colors through color quantization
Color quantization
In computer graphics, color quantization or color image quantization is a process that reduces the number of distinct colors used in an image, usually with the intention that the new image should be as visually similar as possible to the original image. Computer algorithms to perform color...
; one well known is the Heckbert's median-cut algorithm. Here is the 8-bit, 256 color palette used with the color test chart and the image sample above:
Adaptive palettes only work well with a unique image. Trying to display different images with adaptive palettes over an 8-bit display usually results in only one image with correct colors, because the images have different palettes and only one can be displayed at a time. Here is an example of what happens when an indexed color image is displayed with any color palette that is not its own adaptive palette:
False color palettes
 |
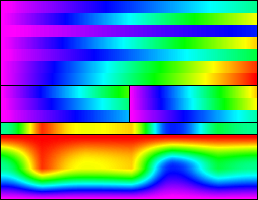 |
Arbitrary gradient color scales, usually 256 shades, with no relationship with real colors of a given image. They are employed to artificially colorize a grayscale image to reveal details and/or to map the pixel level values to amounts of some physical magnitude (potential
Potential
*In linguistics, the potential mood*The mathematical study of potentials is known as potential theory; it is the study of harmonic functions on manifolds...
, temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, altitude, etc.)
Note, in the example above, that new details can be seen as blue over magenta in the background's dark areas of the original photograph.
Here is the 8-bit, 256 color gradient palette used with the color test chart and the image sample above:
There exist many false color
False-color
A false-color image is an image that depicts a subject in colors that differ from those a full-color photograph would show.-True- and false-color:...
palettes, some of them standardized, used mainly in scientifical applications: astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
and radioastronomy, satellite land imaging
Remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon, without making physical contact with the object. In modern usage, the term generally refers to the use of aerial sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth by means of propagated signals Remote sensing...
, thermography
Thermography
Infrared thermography, thermal imaging, and thermal video are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermal imaging cameras detect radiation in the infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms...
, study of materials, tomography
Tomography
Tomography refers to imaging by sections or sectioning, through the use of any kind of penetrating wave. A device used in tomography is called a tomograph, while the image produced is a tomogram. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology, geophysics, oceanography, materials science,...
and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
in medicine, etc.
See also
- Palette (computing)Palette (computing)In computer graphics, a palette is either a given, finite set of colors for the management of digital images , or a small on-screen graphical element for choosing from a limited set of choices, not necessarily colors .Depending on the context In computer graphics, a palette is either a given,...
- Indexed colorIndexed colorIn computing, indexed color is a technique to manage digital images' colors in a limited fashion, in order to save computer memory and file storage, while speeding up display refresh and file transfers...
- Color Lookup TableCLUTA colour look-up table is a mechanism used to transform a range of input colours into another range of colours. It can be a hardware device built into an imaging system or a software function built into an image processing application...
- Color depthColor depthIn computer graphics, color depth or bit depth is the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. This concept is also known as bits per pixel , particularly when specified along with the number of bits used...
- Web colorsWeb colorsWeb colors are colors used in designing web pages, and the methods for describing and specifying those colors. Hexadecimal color codes begin with a hash ....
- X11 color namesX11 color namesIn computing, on the X Window System, X11 color names are represented in a simple text file, which maps certain strings to RGB color values. It is shipped with every X11 installation, hence the name, and is usually located in <X11root>/lib/X11/rgb.txt.It is not known who originally compiled...