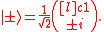Light spin angular momentum
Encyclopedia
The spin angular momentum of light (SAM) is the component of angular momentum
of a light beam that can be associated with its circular
or elliptical polarization
.
when its electric and magnetic field
s rotate continuously around the beam axis during the propagation. The circular polarization
is left (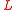 ) or right (
) or right ( ) depending on the field rotation direction (but be careful that both conventions are used in science, depending on the subfield).
) depending on the field rotation direction (but be careful that both conventions are used in science, depending on the subfield).
When a light beam is circularly polarized, each of its photon
s carries a spin angular momentum of , where
, where 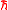 is the reduced Planck constant and the
is the reduced Planck constant and the 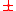 sign is positive for Left and negative for Right circular polarizations (this is adopting the convention most commonly used in optics
sign is positive for Left and negative for Right circular polarizations (this is adopting the convention most commonly used in optics
). This SAM is directed along the beam axis (parallel if positive, antiparallel if negative).
The above figure shows the instantaneous structure of the electric field of left (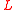 ) and right (
) and right ( ) circularly polarized light in space. The green arrows indicate the propagation direction.
) circularly polarized light in space. The green arrows indicate the propagation direction.
The mathematical expressions reported under the figures give the three electric field components of circularly polarized plane wave propagating in the -direction, in complex
-direction, in complex
notation.
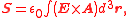
where and
and  are the electric field
are the electric field
and vector potential
, respectively,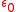 is the vacuum permittivity and we are using SI units.
is the vacuum permittivity and we are using SI units.
Monochromatic wave case:
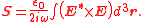
In particular, this expression shows that the SAM is nonzero when the light polarization is elliptical or circular, while it vanishes if the light polarization is linear. In the quantum theory
of the electromagnetic field, the SAM is a quantum observable, described by a corresponding operator.
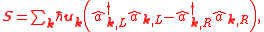
where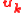 is the unit vector in the propagation direction,
is the unit vector in the propagation direction, 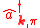 and
and 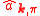 are the creation and annihilation operators for photon in the mode $\mathbf{k}$ and polarization state
are the creation and annihilation operators for photon in the mode $\mathbf{k}$ and polarization state  , respectively.
, respectively.
In this case, for a single photon the SAM can only have two values (eigenvalues of the SAM operator):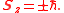
The corresponding eigenfunctions describing photons with well defined values of SAM are described as circularly polarized waves:
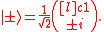
Angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
of a light beam that can be associated with its circular
Circular
Circular is a basic geometric shape such as a Circle.Circular may also refer to:-Documents:*Circular note, a document request by a bank to its foreign correspondents to pay a specified sum of money to a named person...
or elliptical polarization
Polarization
Polarization is a property of certain types of waves that describes the orientation of their oscillations. Electromagnetic waves, such as light, and gravitational waves exhibit polarization; acoustic waves in a gas or liquid do not have polarization because the direction of vibration and...
.
Introduction
An electromagnetic wave is said to have circular polarizationCircular polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization in which the electric field of the passing wave does not change strength but only changes direction in a rotary type manner....
when its electric and magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
s rotate continuously around the beam axis during the propagation. The circular polarization
Circular polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization in which the electric field of the passing wave does not change strength but only changes direction in a rotary type manner....
is left (
 ) or right (
) or right ( ) depending on the field rotation direction (but be careful that both conventions are used in science, depending on the subfield).
) depending on the field rotation direction (but be careful that both conventions are used in science, depending on the subfield).When a light beam is circularly polarized, each of its photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
s carries a spin angular momentum of
 , where
, where 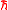 is the reduced Planck constant and the
is the reduced Planck constant and the  sign is positive for Left and negative for Right circular polarizations (this is adopting the convention most commonly used in optics
sign is positive for Left and negative for Right circular polarizations (this is adopting the convention most commonly used in opticsOptics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
). This SAM is directed along the beam axis (parallel if positive, antiparallel if negative).
The above figure shows the instantaneous structure of the electric field of left (
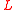 ) and right (
) and right ( ) circularly polarized light in space. The green arrows indicate the propagation direction.
) circularly polarized light in space. The green arrows indicate the propagation direction. The mathematical expressions reported under the figures give the three electric field components of circularly polarized plane wave propagating in the
 -direction, in complex
-direction, in complexComplex
A complex is a whole that comprehends a number of intricate parts, especially one with interconnected or mutually related parts; for example, a complex of buildings.Complex may refer to:-Biology:...
notation.
Mathematical expressions for the spin angular momentum of light
In the following the main formula used for the spin angular momentum of light are given: General expression (paraxial limit only) :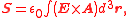
where
 and
and  are the electric field
are the electric fieldElectric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
and vector potential
Vector potential
In vector calculus, a vector potential is a vector field whose curl is a given vector field. This is analogous to a scalar potential, which is a scalar field whose negative gradient is a given vector field....
, respectively,
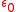 is the vacuum permittivity and we are using SI units.
is the vacuum permittivity and we are using SI units.Monochromatic wave case:
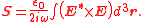
In particular, this expression shows that the SAM is nonzero when the light polarization is elliptical or circular, while it vanishes if the light polarization is linear. In the quantum theory
Quantum theory
Quantum theory may mean:In science:*Quantum mechanics: a subset of quantum physics explaining the physical behaviours at atomic and sub-atomic levels*Old quantum theory under the Bohr model...
of the electromagnetic field, the SAM is a quantum observable, described by a corresponding operator.
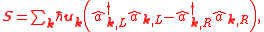
where
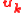 is the unit vector in the propagation direction,
is the unit vector in the propagation direction, 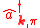 and
and 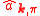 are the creation and annihilation operators for photon in the mode $\mathbf{k}$ and polarization state
are the creation and annihilation operators for photon in the mode $\mathbf{k}$ and polarization state  , respectively.
, respectively.In this case, for a single photon the SAM can only have two values (eigenvalues of the SAM operator):
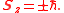
The corresponding eigenfunctions describing photons with well defined values of SAM are described as circularly polarized waves: