
Lanosterol
Encyclopedia
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid
, which is the compound from which all steroid
s are derived.
.
Terpene
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds, produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers, though also by some insects such as termites or swallowtail butterflies, which emit terpenes from their osmeterium. They are often strong smelling and thus may have had a protective...
, which is the compound from which all steroid
Steroid
A steroid is a type of organic compound that contains a characteristic arrangement of four cycloalkane rings that are joined to each other. Examples of steroids include the dietary fat cholesterol, the sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, and the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone.The core...
s are derived.
Role in creation of steroids
Elaboration of lanosterol under enzyme catalysis leads to the core structure of steroids. 14-Demethylation of lanosterol by CYP51 eventually yields cholesterolCholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
.

Biosynthesis
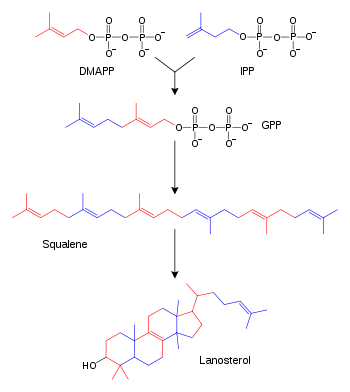
| Description | Illustration | Enzyme >- | Two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate Farnesyl pyrophosphate Farnesyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes, terpenoids, and sterols... condense with reduction by NADPH to form squalene Squalene Squalene is a natural organic compound originally obtained for commercial purposes primarily from shark liver oil, though plant sources are used as well, including amaranth seed, rice bran, wheat germ, and olives. All plants and animals produce squalene, including humans... |
 |
>- | 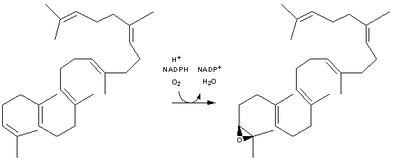 |
squalene monooxygenase Squalene monooxygenase Squalene monooxygenase is an enzyme that uses NADPH and molecular oxygen to oxidize squalene to 2,3-oxidosqualene . Squalene epoxidase catalyzes the first oxygenation step in sterol biosynthesis and is thought to be one of the rate-limiting enzymes in this pathway... >- | 2,3-Oxidosqualene is converted to a protosterol cation and finally to lanosterol |
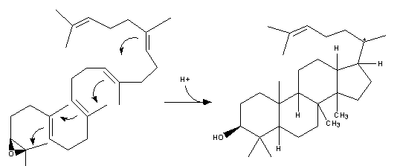 |
lanosterol synthase Lanosterol synthase Lanosterol synthase is an oxidosqualene cyclase enzyme that converts -2,3-oxidosqualene to a protosterol cation and finally to lanosterol. Lanosterol is a key four-ringed intermediate in cholesterol biosynthesis... >- | (step 2) |
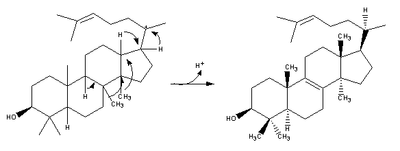 |
(step 2) |

