
Isotropic radiator
Encyclopedia
An isotropic radiator is a theoretical point source
of electromagnetic or sound waves which radiates the same intensity of radiation in all directions. It has no preferred direction of radiation. It radiates uniformly in all directions over a sphere centred on the source. Isotropic radiators are used as reference radiators with which other sources are compared.
Whether a radiator is isotropic is independent of whether it obeys Lambert's law. As radiators, a spherical black body is both, a flat black body is Lambertian but not isotropic, a flat chrome sheet is neither, and by symmetry the Sun is isotropic, but not Lambertian on account of limb darkening
.
is another example of an isotropic radiator - the Cosmic Microwave Background.
s in all directions. It has a directivity
of 0 dBi (dB relative to isotropic),
In reality, a coherent
isotropic radiator cannot exist, as the isotropic radiator, with a radiation pattern
(as expressed in spherical coordinates) of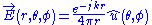
would violate the Helmholtz Wave Equation
, as derived from Maxwell's Equations
.
Although the Sun
and other star
s radiate equally in all directions, their radiation pattern does not violate Maxwell's equations, because radiation from a star is incoherent
. Sound waves can also expand uniformly in all directions, but sound waves are longitudinal waves and not transverse waves.
Even though an isotropic radiator cannot exist in practice, antenna directivity is usually compared to the directivity of an isotropic radiator, because the gain (which is closely related to directivity) relative to an isotropic radiator is useful in the Friis transmission equation
. The smallest directivity a radiator can have relative to an isotropic radiator, is a Hertzian Dipole, which has 1.76 dBi.
, which asserts that a continuous
vector field
tangent
to the surface of the sphere, must fall to zero at at least one point on the sphere. This means that there is some direction for which the electric field must be zero, and hence, non-uniform.
applications, an isotropic receiver (also called isotropic antenna), is a field measurement instrument which allows to obtain the total field independently of the tri-axial orthogonal arrangement chosen for orientation of the device itself.
In practice a quasi-ideal isotropic receiver is obtained with three orthogonal sensing devices
with a radiation diagram of the omnidirectional type , like that of short dipole and small loop antennas.
, like that of short dipole and small loop antennas.
The parameter used to define accuracy in the measurements is called isotropic deviation.
Point source
A point source is a localised, relatively small source of something.Point source may also refer to:*Point source , a localised source of pollution**Point source water pollution, water pollution with a localized source...
of electromagnetic or sound waves which radiates the same intensity of radiation in all directions. It has no preferred direction of radiation. It radiates uniformly in all directions over a sphere centred on the source. Isotropic radiators are used as reference radiators with which other sources are compared.
Whether a radiator is isotropic is independent of whether it obeys Lambert's law. As radiators, a spherical black body is both, a flat black body is Lambertian but not isotropic, a flat chrome sheet is neither, and by symmetry the Sun is isotropic, but not Lambertian on account of limb darkening
Limb darkening
Limb darkening refers to the diminishing of intensity in the image of a star as one moves from the center of the image to the edge or "limb" of the image...
.
Physics
A point radiation or sound source. At a distance, the sun is an isotropic radiator of electromagnetic radiation. The Big BangBig Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
is another example of an isotropic radiator - the Cosmic Microwave Background.
Antenna Theory
In antenna theory, an isotropic antenna is a hypothetical antenna radiating the same intensity of radio waveRadio Wave
Radio Wave may refer to:*Radio frequency*Radio Wave 96.5, a radio station in Blackpool, UK...
s in all directions. It has a directivity
Directivity
In electromagnetics, directivity is a figure of merit for an antenna. It measures the power density the antenna radiates in the direction of its strongest emission, versus the power density radiated by an ideal isotropic radiator radiating the same total power.An antenna's directivity is a...
of 0 dBi (dB relative to isotropic),
In reality, a coherent
Coherence (physics)
In physics, coherence is a property of waves that enables stationary interference. More generally, coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of a wave....
isotropic radiator cannot exist, as the isotropic radiator, with a radiation pattern
Radiation pattern
In the field of antenna design the term radiation pattern most commonly refers to the directional dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source ....
(as expressed in spherical coordinates) of
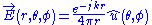
would violate the Helmholtz Wave Equation
Helmholtz equation
The Helmholtz equation, named for Hermann von Helmholtz, is the elliptic partial differential equation\nabla^2 A + k^2 A = 0where ∇2 is the Laplacian, k is the wavenumber, and A is the amplitude.-Motivation and uses:...
, as derived from Maxwell's Equations
Maxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations are a set of partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electrodynamics, classical optics, and electric circuits. These fields in turn underlie modern electrical and communications technologies.Maxwell's equations...
.
Although the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
and other star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s radiate equally in all directions, their radiation pattern does not violate Maxwell's equations, because radiation from a star is incoherent
Coherence (physics)
In physics, coherence is a property of waves that enables stationary interference. More generally, coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of a wave....
. Sound waves can also expand uniformly in all directions, but sound waves are longitudinal waves and not transverse waves.
Even though an isotropic radiator cannot exist in practice, antenna directivity is usually compared to the directivity of an isotropic radiator, because the gain (which is closely related to directivity) relative to an isotropic radiator is useful in the Friis transmission equation
Friis transmission equation
The Friis transmission equation is used in telecommunications engineering, and gives the power received by one antenna under idealized conditions given another antenna some distance away transmitting a known amount of power. The formula was derived in 1945 by Danish-American radio engineer Harald T...
. The smallest directivity a radiator can have relative to an isotropic radiator, is a Hertzian Dipole, which has 1.76 dBi.
Hairy ball theorem
Another way to explain why an isotropic radiator cannot exist is by using the hairy ball theoremHairy ball theorem
The hairy ball theorem of algebraic topology states that there is no nonvanishing continuous tangent vector field on an even-dimensional n-sphere. An ordinary sphere is a 2-sphere, so that this theorem will hold for an ordinary sphere...
, which asserts that a continuous
Continuous function
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function for which, intuitively, "small" changes in the input result in "small" changes in the output. Otherwise, a function is said to be "discontinuous". A continuous function with a continuous inverse function is called "bicontinuous".Continuity of...
vector field
Vector field
In vector calculus, a vector field is an assignmentof a vector to each point in a subset of Euclidean space. A vector field in the plane for instance can be visualized as an arrow, with a given magnitude and direction, attached to each point in the plane...
tangent
Tangent
In geometry, the tangent line to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. More precisely, a straight line is said to be a tangent of a curve at a point on the curve if the line passes through the point on the curve and has slope where f...
to the surface of the sphere, must fall to zero at at least one point on the sphere. This means that there is some direction for which the electric field must be zero, and hence, non-uniform.
Isotropic receiver
In EMF measurementsEMF measurements
EMF measurements are measurements of ambient electromagnetic fields that are taken with particular sensors or probes, such as EMF meters. These probes can be generally considered as antennas although with different characteristics...
applications, an isotropic receiver (also called isotropic antenna), is a field measurement instrument which allows to obtain the total field independently of the tri-axial orthogonal arrangement chosen for orientation of the device itself.
In practice a quasi-ideal isotropic receiver is obtained with three orthogonal sensing devices
with a radiation diagram of the omnidirectional type
 , like that of short dipole and small loop antennas.
, like that of short dipole and small loop antennas.The parameter used to define accuracy in the measurements is called isotropic deviation.
Optics
A point source of light. The sun approximates an isotropic radiator of light. Certain munitions such as flares and chaff have isotropic radiator properties.Sound
An isotropic radiator is a theoretical perfect speaker exhibiting equal sound volume in all directions.External links
- Isotropic Radiators, Matzner and McDonald, arXiv Antennas
- Antennas D.Jefferies
- isotropic radiator AMS Glossary
- U.S. Patent 4,130,023 - Method and apparatus for testing and evaluating loudspeaker performance
- Non Lethal Concepts - Implications for Air Force Intelligence Published Aerospace Power Journal, Winter 1994
- Glossary
- Cosmic Microwave Background - Introduction

