Ionic partition diagram
Encyclopedia
Similar to Pourbaix's diagram
for the speciation of redox
species as a function of the redox potential and the pH
, ionic partition diagrams indicate in which an acid or a base are predominantly present in a biphasic
system as a function of the Galvani potential
difference
between the two phases and the pH of the aqueous solution
Ionic partition diagram of an hydrophilic acid AH in a biphasic water/organic solvent system.
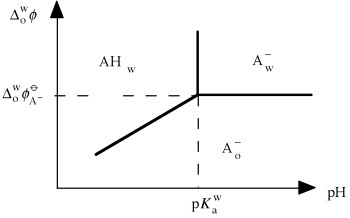
At a high aqueous pH, the acid is in the anionic form and can exist in both phases according to the Galvani potential difference. The Nernst equation
for the distribution of the anion, ignoring the activity coefficient
s is written.
Thus, the separation limit between the anionic form in water and the organic solvent is a horizontal straight line. As in Pourbaix diagrams, the separation limit between the acid and
basic forms in water is a vertical line given by .
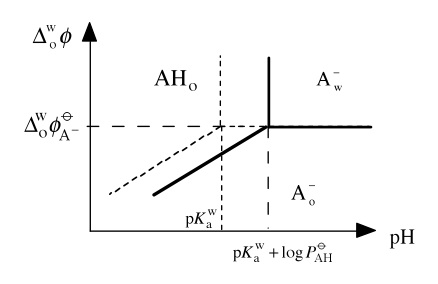
The line separating the neutral acid in water and the anion Ao– in the organic phase is given by considering the aqueous acidity constant to give
As in the Pourbaix diagrams, we obtain a delimiting line that depends
on the pH as shown below.
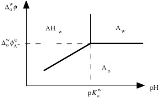
Pourbaix diagram
In chemistry, a Pourbaix diagram, also known as a potential/pH diagram, maps out possible stable phases of an aqueous electrochemical system. Predominant ion boundaries are represented by lines. As such a Pourbaix diagram can be read much like a standard phase diagram with a different set of axes...
for the speciation of redox
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
species as a function of the redox potential and the pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
, ionic partition diagrams indicate in which an acid or a base are predominantly present in a biphasic
Biphasic
A biphasic system is one which has two phases.* In the physical sciences, a liquid water and steam system would represent a biphasic system. See phase ....
system as a function of the Galvani potential
Galvani potential
Galvani potential in electrochemistry, is the electric potential difference between two points in the bulk of two phases...
difference
between the two phases and the pH of the aqueous solution
Ionic partition diagram of an hydrophilic acid AH in a biphasic water/organic solvent system.

At a high aqueous pH, the acid is in the anionic form and can exist in both phases according to the Galvani potential difference. The Nernst equation
Nernst equation
In electrochemistry, the Nernst equation is an equation that can be used to determine the equilibrium reduction potential of a half-cell in an electrochemical cell. It can also be used to determine the total voltage for a full electrochemical cell...
for the distribution of the anion, ignoring the activity coefficient
Activity coefficient
An activity coefficient is a factor used in thermodynamics to account for deviations from ideal behaviour in a mixture of chemical substances. In an ideal mixture, the interactions between each pair of chemical species are the same and, as a result, properties of the mixtures can be expressed...
s is written.
Thus, the separation limit between the anionic form in water and the organic solvent is a horizontal straight line. As in Pourbaix diagrams, the separation limit between the acid and
basic forms in water is a vertical line given by .
The line separating the neutral acid in water and the anion Ao– in the organic phase is given by considering the aqueous acidity constant to give
As in the Pourbaix diagrams, we obtain a delimiting line that depends
on the pH as shown below.


