
Geography of French Guiana
Encyclopedia
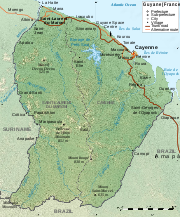
French Guiana
French Guiana is an overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department located on the northern Atlantic coast of South America. It has borders with two nations, Brazil to the east and south, and Suriname to the west...
is an overseas region of France, located on the northern coast of South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
between Suriname
Suriname
Suriname , officially the Republic of Suriname , is a country in northern South America. It borders French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, Brazil to the south, and on the north by the Atlantic Ocean. Suriname was a former colony of the British and of the Dutch, and was previously known as...
and Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
.
Location
Northern South AmericaSouth America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
and part of Caribbean South America
Caribbean South America
Caribbean South America is a region of South America consisting of the nations that border the Caribbean Sea, namely:*Colombia*Venezuela...
, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
, between Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
and Suriname
Suriname
Suriname , officially the Republic of Suriname , is a country in northern South America. It borders French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, Brazil to the south, and on the north by the Atlantic Ocean. Suriname was a former colony of the British and of the Dutch, and was previously known as...
Land boundaries
total: 1,183 kmborder countries: Brazil 673 km, Suriname 510 km (disputed)
Coastline: 378 km
Maritime claims
exclusive economic zone: 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
Elevation extremes
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Bellevue de l'Inini
Bellevue de l'Inini
Bellevue de l'Inini is the highest point of French Guiana, an overseas department of France, with an altitude of 851 metres ....
851 m
other mountains: Montaigne d'Argent, on the edge of Oiapoque river
regions: 432 m
Natural resources
bauxiteBauxite
Bauxite is an aluminium ore and is the main source of aluminium. This form of rock consists mostly of the minerals gibbsite Al3, boehmite γ-AlO, and diaspore α-AlO, in a mixture with the two iron oxides goethite and hematite, the clay mineral kaolinite, and small amounts of anatase TiO2...
, timber
Timber
Timber may refer to:* Timber, a term common in the United Kingdom and Australia for wood materials * Timber, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the U.S...
, gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
(widely scattered), cinnabar
Cinnabar
Cinnabar or cinnabarite , is the common ore of mercury.-Word origin:The name comes from κινναβαρι , a Greek word most likely applied by Theophrastus to several distinct substances...
, kaolin, fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
, shrimp
Shrimp
Shrimp are swimming, decapod crustaceans classified in the infraorder Caridea, found widely around the world in both fresh and salt water. Adult shrimp are filter feeding benthic animals living close to the bottom. They can live in schools and can swim rapidly backwards. Shrimp are an important...
Land use
arable land: 0%permanent crops: 0%
permanent pastures: 0%
forests and woodland: 0%
other: 10% (1996 est.)
irrigated land: 20 km² (1993 est.)
natural hazards: high frequency of heavy showers and severe thunderstorms; flooding
environment - current issues: NA
geography - note: mostly an unsettled wilderness

