
Generalized entropy index
Encyclopedia
The generalized entropy index is a general formula for measuring redundancy in data. The redundancy can be viewed as inequality, lack of diversity, non-randomness, compressibility, or segregation in the data. The primary use is for income inequality
. It is equal to the definition of redundancy in information theory
that is based on Shannon entropy when α = 1 which is also called the Theil index
(TT) in income inequality research. Completely "diverse" data has no redundancy so that GE=0, so that it increases in the opposite direction of a Diversity index
. It increases with order rather than disorder, so it is a negated measure of entropy.
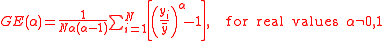

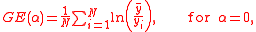
where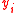 is the income for individual i that is part of N and α is the weight given to distances between incomes at different parts of the income distribution. Sometimes a different notation is used where α = β + 1.
is the income for individual i that is part of N and α is the weight given to distances between incomes at different parts of the income distribution. Sometimes a different notation is used where α = β + 1.
For lower values of α close to 0, GE is more sensitive to changes in the lower incomes and vice versa for values closer to 1. Theil's TT is α = 1 and Theil's TL (also called mean log deviation) is α = 0. When α = 2 the value is half the square of the coefficient of variation
: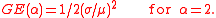
The generalized entropy index is a transformation of the Atkinson index
where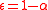 . The transformation is A=1-e^(-GE), so that the Atkinson index is a probability instead of entropy.
. The transformation is A=1-e^(-GE), so that the Atkinson index is a probability instead of entropy.
When the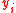 of
of  is replaced with
is replaced with 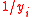 (for example, income/person becomes persons/income) then
(for example, income/person becomes persons/income) then  is equivalent to
is equivalent to  .
.
Economic inequality
Economic inequality comprises all disparities in the distribution of economic assets and income. The term typically refers to inequality among individuals and groups within a society, but can also refer to inequality among countries. The issue of economic inequality is related to the ideas of...
. It is equal to the definition of redundancy in information theory
Redundancy (information theory)
Redundancy in information theory is the number of bits used to transmit a message minus the number of bits of actual information in the message. Informally, it is the amount of wasted "space" used to transmit certain data...
that is based on Shannon entropy when α = 1 which is also called the Theil index
Theil index
The Theil index is a statistic used to measure economic inequality. It has also been used to measure the lack of racial diversity. The basic Theil index TT is the same as redundancy in information theory which is the maximum possible entropy of the data minus the observed entropy. It is a special...
(TT) in income inequality research. Completely "diverse" data has no redundancy so that GE=0, so that it increases in the opposite direction of a Diversity index
Diversity index
A diversity index is a statistic which is intended to measure the local members of a set consisting of various types of objects. Diversity indices can be used in many fields of study to assess the diversity of any population in which each member belongs to a unique group, type or species...
. It increases with order rather than disorder, so it is a negated measure of entropy.
Formula
The formula is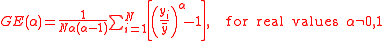

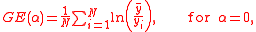
where
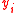 is the income for individual i that is part of N and α is the weight given to distances between incomes at different parts of the income distribution. Sometimes a different notation is used where α = β + 1.
is the income for individual i that is part of N and α is the weight given to distances between incomes at different parts of the income distribution. Sometimes a different notation is used where α = β + 1.For lower values of α close to 0, GE is more sensitive to changes in the lower incomes and vice versa for values closer to 1. Theil's TT is α = 1 and Theil's TL (also called mean log deviation) is α = 0. When α = 2 the value is half the square of the coefficient of variation
Coefficient of variation
In probability theory and statistics, the coefficient of variation is a normalized measure of dispersion of a probability distribution. It is also known as unitized risk or the variation coefficient. The absolute value of the CV is sometimes known as relative standard deviation , which is...
:
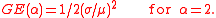
The generalized entropy index is a transformation of the Atkinson index
Atkinson index
The Atkinson index is a measure of income inequality developed by British economist Anthony Barnes Atkinson...
where
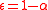 . The transformation is A=1-e^(-GE), so that the Atkinson index is a probability instead of entropy.
. The transformation is A=1-e^(-GE), so that the Atkinson index is a probability instead of entropy.When the
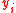 of
of  is replaced with
is replaced with 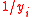 (for example, income/person becomes persons/income) then
(for example, income/person becomes persons/income) then  is equivalent to
is equivalent to  .
.See also
- Theil indexTheil indexThe Theil index is a statistic used to measure economic inequality. It has also been used to measure the lack of racial diversity. The basic Theil index TT is the same as redundancy in information theory which is the maximum possible entropy of the data minus the observed entropy. It is a special...
- Atkinson indexAtkinson indexThe Atkinson index is a measure of income inequality developed by British economist Anthony Barnes Atkinson...
- Lorenz curveLorenz curveIn economics, the Lorenz curve is a graphical representation of the cumulative distribution function of the empirical probability distribution of wealth; it is a graph showing the proportion of the distribution assumed by the bottom y% of the values...
- Gini coefficientGini coefficientThe Gini coefficient is a measure of statistical dispersion developed by the Italian statistician and sociologist Corrado Gini and published in his 1912 paper "Variability and Mutability" ....
- Hoover index
- Robin Hood indexRobin Hood indexThe Hoover index is a measure of income inequality. It is equal to the portion of the total community income that would have to be redistributed for there to be perfect equality....
- Suits indexSuits indexThe Suits index of a public policy is a measure of collective progressivity, named for economist Daniel B. Suits. Similar to the Gini coefficient, the Suits index is calculated by comparing the area under the Lorenz curve to the area under a proportional line...
- Income inequality metricsIncome inequality metricsThe concept of inequality is distinct from that of poverty and fairness. Income inequality metrics or income distribution metrics are used by social scientists to measure the distribution of income, and economic inequality among the participants in a particular economy, such as that of a specific...
- Rényi entropyRényi entropyIn information theory, the Rényi entropy, a generalisation of Shannon entropy, is one of a family of functionals for quantifying the diversity, uncertainty or randomness of a system...

