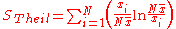
Theil index
Encyclopedia
The Theil index is a statistic used to measure economic inequality
. It has also been used to measure the lack of racial diversity. The basic Theil index TT is the same as redundancy in information theory
which is the maximum possible entropy of the data minus the observed entropy. It is a special case of the generalized entropy index
. It can be viewed as a measure of redundancy, lack of diversity, isolation, segregation, inequality, non-randomness, and compressibility. It was proposed by econometrician
Henri Theil
, a successor of Jan Tinbergen
at the Erasmus University Rotterdam.
Economic inequality
Economic inequality comprises all disparities in the distribution of economic assets and income. The term typically refers to inequality among individuals and groups within a society, but can also refer to inequality among countries. The issue of economic inequality is related to the ideas of...
. It has also been used to measure the lack of racial diversity. The basic Theil index TT is the same as redundancy in information theory
Redundancy (information theory)
Redundancy in information theory is the number of bits used to transmit a message minus the number of bits of actual information in the message. Informally, it is the amount of wasted "space" used to transmit certain data...
which is the maximum possible entropy of the data minus the observed entropy. It is a special case of the generalized entropy index
Generalized entropy index
The generalized entropy index is a general formula for measuring redundancy in data. The redundancy can be viewed as inequality, lack of diversity, non-randomness, compressibility, or segregation in the data. The primary use is for income inequality...
. It can be viewed as a measure of redundancy, lack of diversity, isolation, segregation, inequality, non-randomness, and compressibility. It was proposed by econometrician
Econometrics
Econometrics has been defined as "the application of mathematics and statistical methods to economic data" and described as the branch of economics "that aims to give empirical content to economic relations." More precisely, it is "the quantitative analysis of actual economic phenomena based on...
Henri Theil
Henri Theil
Henri Theil was a Dutch econometrician.He graduated from the University of Amsterdam. He was the successor of Jan Tinbergen at the Erasmus University Rotterdam. Later he taught in Chicago and at the University of Florida. He is most famous for his invention of 2-stage least squares...
, a successor of Jan Tinbergen
Jan Tinbergen
Jan Tinbergen , was a Dutch economist. He was awarded the first Bank of Sweden Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel in 1969, which he shared with Ragnar Frisch for having developed and applied dynamic models for the analysis of economic processes...
at the Erasmus University Rotterdam.
Formulas
The basic Theil index, which has higher resolution for changes to higher incomes, is-
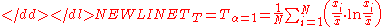
where is income/person. When
is income/person. When  is inverted to be people/income, or if changes in lower incomes are more important, a different formula is used that is derivable from
is inverted to be people/income, or if changes in lower incomes are more important, a different formula is used that is derivable from 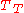 by
by
-
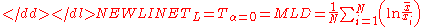
 is also known as the MLD (mean log deviation) because it gives the standard deviation of
is also known as the MLD (mean log deviation) because it gives the standard deviation of 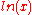 . Sometimes the average of
. Sometimes the average of  and
and 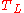 is used, which has the advantage of being "symmetric" like the Gini, Hoover, and Coulter indices. "Symmetric" means it gives the same result for x as it does for 1/x:
is used, which has the advantage of being "symmetric" like the Gini, Hoover, and Coulter indices. "Symmetric" means it gives the same result for x as it does for 1/x:
-
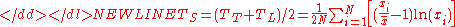
For these equations,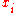 is the income of the
is the income of the  th person or subgroup,
th person or subgroup, 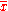 is the mean income of the persons or subgroups, and
is the mean income of the persons or subgroups, and  is the population or number of subgroups.
is the population or number of subgroups.
If everyone has the same income, the indices give 0 which, counter-intuitively, is when the population's income has maximum disorder. If one person has all the income, then TT gives the result , which is maximum order. Dividing TT by
, which is maximum order. Dividing TT by 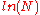 can normalize the equation to range from 0 to 1.
can normalize the equation to range from 0 to 1.
The indices measure an entropic "distance" the population is away from the "ideal" egalitarian state of everyone having the same income. The numerical result is in terms of negative entropy so that a higher number indicates more order that is further away from the "ideal" of maximum disorder. Formulating the index to represent negative entropy instead of entropy allows it to be a measure of inequality rather than equality.
If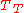 applies to the distribution of income in people, then
applies to the distribution of income in people, then 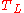 can be used to get the same numerical result for the distribution of people in income.
can be used to get the same numerical result for the distribution of people in income.
The two Theil indices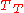 and
and 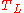 are special cases of the generalized entropy indexGeneralized entropy indexThe generalized entropy index is a general formula for measuring redundancy in data. The redundancy can be viewed as inequality, lack of diversity, non-randomness, compressibility, or segregation in the data. The primary use is for income inequality...
are special cases of the generalized entropy indexGeneralized entropy indexThe generalized entropy index is a general formula for measuring redundancy in data. The redundancy can be viewed as inequality, lack of diversity, non-randomness, compressibility, or segregation in the data. The primary use is for income inequality...
with and
and  . The Atkinson indexAtkinson indexThe Atkinson index is a measure of income inequality developed by British economist Anthony Barnes Atkinson...
. The Atkinson indexAtkinson indexThe Atkinson index is a measure of income inequality developed by British economist Anthony Barnes Atkinson...
with is a transformation of
is a transformation of 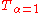 by A=1-e^-T. Likewise, the Atkinson index with
by A=1-e^-T. Likewise, the Atkinson index with  is a transformation of
is a transformation of  .
.
Derivation from Entropy
The Theil index is derived from Shannon's measure of information entropyInformation entropyIn information theory, entropy is a measure of the uncertainty associated with a random variable. In this context, the term usually refers to the Shannon entropy, which quantifies the expected value of the information contained in a message, usually in units such as bits...
(S), where entropy is a measure of randomness in a given set of information. In information theory, physics, and the Theil index, the general form of entropy is

where pi is the probability of finding member i from a random sample of the population. In physics, k is Boltzmann's constant. In information theory k=1 if it is in terms of bits and the log base is 2. Physics and the Theil index have chosen the natural logarithm as the logarithmic base. When pi is chosen to be income per person (xi), it needs to be normalized by dividing by the total population income, N*avg(x). This gives the observed entropy of a Theil population to be:
The Theil index is TT = Smax - STheil where the theoretical maximum entropy Smax is when all incomes are equal, i.e. each xi = average xi = a constant. This is substituted into STheil to give Smax = ln(N) for TT, a constant determined solely by the population. So the Theil index gives a value in terms of an entropy that measures how far STheil is away from the "ideal" Smax. The index is a "negative entropy" in the sense that it gets smaller as the disorder gets larger, so it is a measure of order rather than disorder.
When x is in units of population/species,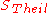 is a measure of biodiversity and is called the Shannon indexShannon indexThe Shannon index, sometimes referred to as the Shannon-Wiener Index or the Shannon-Weaver Index, is one of several diversity indices used to measure diversity in categorical data. It is simply the Information entropy of the distribution, treating species as symbols and their relative population...
is a measure of biodiversity and is called the Shannon indexShannon indexThe Shannon index, sometimes referred to as the Shannon-Wiener Index or the Shannon-Weaver Index, is one of several diversity indices used to measure diversity in categorical data. It is simply the Information entropy of the distribution, treating species as symbols and their relative population...
. If the Thiel index is used with x=population/species, it is a measure of inequality of population among a set of species, or "bio-isolation" as opposed to "wealth isolation".
The Theil index measures what is called redundancyRedundancy (information theory)Redundancy in information theory is the number of bits used to transmit a message minus the number of bits of actual information in the message. Informally, it is the amount of wasted "space" used to transmit certain data...
in information theory. It is the left over "information space" that was not utilized to convey information, which reduces the effectiveness of the price signalPrice signalA price signal is a message sent to consumers and producers in the form of a price charged for a commodity; this is seen as indicating a signal for producers to increase supplies and/or consumers to reduce demand.- Free price system :...
. The Theil index is a measure of the redundancy of income (or other measure of wealth) in some individuals. Redundancy in some individuals implies scarcity in others. A high Theil index indicates the total income is not distributed evenly among individuals in the same way an uncompressed text file does not have a similar number of byte locations assigned to the available unique byte characters.
Notation Information Theory Theil Index TT N number of unique characters number of individuals i a particular character a particular individual xi characteri count income of individuali N*avg(x) total characters in document total income in population TT unused information space unused potential in price mechanism data compression progressive tax
Application of the Theil index
Theil's measure can be converted by the operation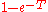 into one of the indexes of Anthony Barnes AtkinsonAnthony Barnes AtkinsonSir Anthony Barnes "Tony" Atkinson, FBA, is a British economist and has been a Senior Research Fellow of Nuffield College, Oxford since 2005.-Career:Atkinson served as Warden of Nuffield College from 1994 to 2005...
into one of the indexes of Anthony Barnes AtkinsonAnthony Barnes AtkinsonSir Anthony Barnes "Tony" Atkinson, FBA, is a British economist and has been a Senior Research Fellow of Nuffield College, Oxford since 2005.-Career:Atkinson served as Warden of Nuffield College from 1994 to 2005...
, where may or may not be used to introduce an inequality aversion factor into the formula, with
may or may not be used to introduce an inequality aversion factor into the formula, with  being the default. The result of the conversion also has been called normalized Theil index.
being the default. The result of the conversion also has been called normalized Theil index.
James E. Foster used such a measure to replace the Gini coefficient in Amartya SenAmartya SenAmartya Sen, CH is an Indian economist who was awarded the 1998 Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences for his contributions to welfare economics and social choice theory, and for his interest in the problems of society's poorest members...
's welfare function W=f(income,inequality). The income e.g. is the average income for individuals in a group of income earners. Thus, Foster's welfare function can be computed directly from the Theil index , if the conversion is included into the computation of the average per capita welfare functionSocial welfare functionIn economics, a social welfare function is a real-valued function that ranks conceivable social states from lowest to highest. Inputs of the function include any variables considered to affect the economic welfare of a society...
, if the conversion is included into the computation of the average per capita welfare functionSocial welfare functionIn economics, a social welfare function is a real-valued function that ranks conceivable social states from lowest to highest. Inputs of the function include any variables considered to affect the economic welfare of a society...
:
Using the "Theil-L" index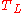 (see below) for
(see below) for  in that formula yields results similar to using the Atkinson indexAtkinson indexThe Atkinson index is a measure of income inequality developed by British economist Anthony Barnes Atkinson...
in that formula yields results similar to using the Atkinson indexAtkinson indexThe Atkinson index is a measure of income inequality developed by British economist Anthony Barnes Atkinson...
for computing the welfare function.
What does U mean ?
If U = 1 Then the "Naive" (NF1) Method is as good as the current Forecast Method
If U < 1 Then the Forecasting Method is better than the NF1 Method
If U > 1 Then the NF1 Method is better than the Forecasting Method. There is not need to waste time applying anymore Forecasting Techniques.
Decomposability
One of the advantages of the Theil index is that it is a weighted average of inequality within subgroups, plus inequality among those subgroups. For example, inequality within the United States is the average inequality within each state, weighted by state income, plus the inequality among states.
If for the Theil-T index the population is divided into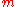 certain subgroups and
certain subgroups and  is the income share of group
is the income share of group 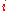 ,
, 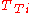 is the Theil-T index for that subgroup, and
is the Theil-T index for that subgroup, and 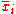 is the average income in group
is the average income in group  , then the Theil index is
, then the Theil index is
-
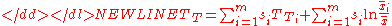
The formula for the Theil-L index is:-
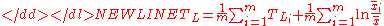
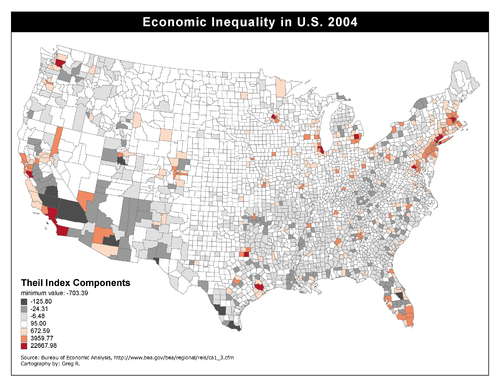
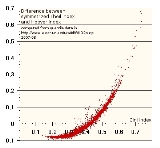
- Note: This image is not the Theil Index in each area of the United States, but of contributions to the US Theil Index by each area (the Theil Index is always positive, individual contributions to the Theil Index may be negative or positive).
The decomposition of the overall Theil index which identifies the share attributable to the between-region component becomes a helpful tool for the positive analysis of regional inequality as it suggests the relative importance of spatial dimension of inequality.
The decomposability is a property of the Theil index which the more popular Gini coefficientGini coefficientThe Gini coefficient is a measure of statistical dispersion developed by the Italian statistician and sociologist Corrado Gini and published in his 1912 paper "Variability and Mutability" ....
does not offer. The Gini coefficient is more intuitive to many people since it is based on the Lorenz curveLorenz curveIn economics, the Lorenz curve is a graphical representation of the cumulative distribution function of the empirical probability distribution of wealth; it is a graph showing the proportion of the distribution assumed by the bottom y% of the values...
. However, it is not easily decomposable like the Theil.
Applications
In addition to multitude of economic applications, the Theil index has been applied to assess performance of irrigationIrrigationIrrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
systems and distribution of software metrics.
See also
- Generalized entropy indexGeneralized entropy indexThe generalized entropy index is a general formula for measuring redundancy in data. The redundancy can be viewed as inequality, lack of diversity, non-randomness, compressibility, or segregation in the data. The primary use is for income inequality...
- Atkinson indexAtkinson indexThe Atkinson index is a measure of income inequality developed by British economist Anthony Barnes Atkinson...
- Gini coefficent
- Hoover index
- Income inequality metricsIncome inequality metricsThe concept of inequality is distinct from that of poverty and fairness. Income inequality metrics or income distribution metrics are used by social scientists to measure the distribution of income, and economic inequality among the participants in a particular economy, such as that of a specific...
- Suits indexSuits indexThe Suits index of a public policy is a measure of collective progressivity, named for economist Daniel B. Suits. Similar to the Gini coefficient, the Suits index is calculated by comparing the area under the Lorenz curve to the area under a proportional line...
- Wealth condensation
- Diversity indexDiversity indexA diversity index is a statistic which is intended to measure the local members of a set consisting of various types of objects. Diversity indices can be used in many fields of study to assess the diversity of any population in which each member belongs to a unique group, type or species...
External links
- Software:
- Free Online Calculator computes the Gini Coefficient, plots the Lorenz curve, and computes many other measures of concentration for any dataset
- Free Calculator: Online and downloadable scripts (PythonPython (programming language)Python is a general-purpose, high-level programming language whose design philosophy emphasizes code readability. Python claims to "[combine] remarkable power with very clear syntax", and its standard library is large and comprehensive...
and LuaLua programming languageLua is a lightweight multi-paradigm programming language designed as a scripting language with extensible semantics as a primary goal. Lua has a relatively simple C API compared to other scripting languages.- History :...
) for Atkinson, Gini, and Hoover inequalities - Users of the R data analysis software can install the "ineq" package which allows for computation of a variety of inequality indices including Gini, Atkinson, Theil.
- A MATLAB Inequality Package, including code for computing Gini, Atkinson, Theil indexes and for plotting the Lorenz Curve. Many examples are available.
-
-
-
-