
General (United States)
Encyclopedia
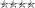
United States Army
The United States Army is the main branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. It is the largest and oldest established branch of the U.S. military, and is one of seven U.S. uniformed services...
, United States Air Force
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the American uniformed services. Initially part of the United States Army, the USAF was formed as a separate branch of the military on September 18, 1947 under the National Security Act of...
, and United States Marine Corps
United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps is a branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for providing power projection from the sea, using the mobility of the United States Navy to deliver combined-arms task forces rapidly. It is one of seven uniformed services of the United States...
, general is a four-star
4 star rank
Four-star rank is a term used to describe a very senior commander in many of the armed services holding a rank described by the NATO OF-9 code. The term is also used by some armed forces which are not NATO members...
general officer rank, with the pay grade of O-10. General ranks above lieutenant general
Lieutenant General (United States)
In the United States Army, the United States Air Force and the United States Marine Corps, lieutenant general is a three-star general officer rank, with the pay grade of O-9. Lieutenant general ranks above major general and below general...
and below General of the Army
General of the Army (United States)
General of the Army is a five-star general officer and is the second highest possible rank in the United States Army. A special rank of General of the Armies, which ranks above General of the Army, does exist but has only been conferred twice in the history of the Army...
or General of the Air Force
General of the Air Force (United States)
General of the Air Force is a five-star general officer rank and is the highest possible rank in the United States Air Force. General of the Air Force ranks immediately above a general and is equivalent to General of the Army in the United States Army and Fleet Admiral in the United States Navy;...
; the Marine Corps does not have an established grade above general. General is equivalent to the rank of admiral
Admiral (United States)
In the United States Navy, the United States Coast Guard and the United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, admiral is a four-star flag officer rank, with the pay grade of O-10. Admiral ranks above vice admiral and below Fleet Admiral in the Navy; the Coast Guard and the Public Health...
in the other uniformed services
Uniformed services of the United States
The United States has seven federal uniformed services that commission officers as defined by Title 10, and subsequently structured and organized by Title 10, Title 14, Title 33 and Title 42 of the United States Code.-Uniformed services:...
. Since the grades of General of the Army and General of the Air Force are reserved for war-time use only, and since the Marine Corps has no five-star equivalent, the grade of general is currently considered to be the highest appointment an officer can achieve in these three services.
Statutory limits
U.S. Code of law explicitly limits the total number of four-star officers that may be on active duty at any given time. The total number of active duty general officers is capped at 230 for the Army, 208 for the Air Force, 60 for the Marine Corps. For the Army, Navy, and Air Force, no more than about 25% of the service's active duty general or flag officers may have more than two stars, and statute sets the total number of four-star generals allowed in each service. This is set at 7 four-star Army generals, 9 four-star Air Force generals and 3 four-star Marine generals.Several of these slots are reserved by statute. For the Army and the Air Force, the Chief
Chief of Staff of the United States Army
The Chief of Staff of the Army is a statutory office held by a four-star general in the United States Army, and is the most senior uniformed officer assigned to serve in the Department of the Army, and as such is the principal military advisor and a deputy to the Secretary of the Army; and is in...
of Staff
Chief of Staff of the United States Air Force
The Chief of Staff of the Air Force is a statutory office held by a four-star general in the United States Air Force, and is the most senior uniformed officer assigned to serve in the Department of the Air Force, and as such is the principal military advisor and a deputy to the Secretary of the...
and the Vice Chief
Vice Chief of Staff of the United States Army
The Vice Chief of Staff of the United States Army is the principal advisor and assistant to the Army Chief of Staff, the second-highest ranking officer in the US Army. He handles the day to day administration of the Army bureaucracy, freeing the Chief of Staff to attend to the interservice...
of Staff
Vice Chief of Staff of the United States Air Force
The Vice Chief of Staff of the United States Air Force is the second highest ranking military officer in the United States Air Force. In the event that the Chief of Staff of the Air Force is absent or is unable to perform his duties, the VCSAF assumes the duties and responsibilities of the CSAF...
for both services are all four-star generals; for the Marine Corps, the Commandant
Commandant of the Marine Corps
The Commandant of the Marine Corps is normally the highest ranking officer in the United States Marine Corps and is a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff...
and the Assistant Commandant
Assistant Commandant of the Marine Corps
The Assistant Commandant of the Marine Corps is the second highest ranking officer in the United States Marine Corps, and serves as a deputy for the Commandant of the Marine Corps...
are both four-star generals. In addition, for the National Guard, the Chief of the National Guard Bureau
Chief of the National Guard Bureau
The Chief of the National Guard Bureau is the head of the National Guard Bureau, which is a joint activity of the Department of Defense , and is the highest ranking officer in the National Guard and the National Guard of the United States ; the latter of which is a joint reserve component of the...
is a four-star general under active duty in the Army or Air Force.
There are several exceptions to these limits allowing more than allotted within the statute. A four-star officer serving as Chairman
Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is by law the highest ranking military officer in the United States Armed Forces, and is the principal military adviser to the President of the United States, the National Security Council, the Homeland Security Council and the Secretary of Defense...
or Vice Chairman
Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is by law the second highest ranking military officer in the United States Armed Forces ranking just below the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff...
of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Joint Chiefs of Staff is a body of senior uniformed leaders in the United States Department of Defense who advise the Secretary of Defense, the Homeland Security Council, the National Security Council and the President on military matters...
does not count against his service's general or flag officer cap. An officer serving as Chief of the National Guard Bureau
Chief of the National Guard Bureau
The Chief of the National Guard Bureau is the head of the National Guard Bureau, which is a joint activity of the Department of Defense , and is the highest ranking officer in the National Guard and the National Guard of the United States ; the latter of which is a joint reserve component of the...
does not count against his service's general officer cap. An officer serving in one of several joint positions does not count against his service's four-star limit, but he does count against his service's limit on officers with more than two stars; these positions include the commander of a unified combatant command
Unified Combatant Command
A Unified Combatant Command is a United States Department of Defense command that is composed of forces from at least two Military Departments and has a broad and continuing mission. These commands are established to provide effective command and control of U.S. military forces, regardless of...
, the commander of United States Forces Korea
United States Forces Korea
United States Forces Korea refers to the ground, air and naval divisions of the United States armed forces stationed in South Korea....
, and the deputy commander of United States European Command
United States European Command
The United States European Command is one of ten Unified Combatant Commands of the United States military, headquartered in Stuttgart, Germany. Its area of focus covers and 51 countries and territories, including Europe, Russia, Iceland, Greenland, and Israel...
but only if the commander of that command is also the Supreme Allied Commander
Supreme Allied Commander
Supreme Allied Commander is the title held by the most senior commander within certain multinational military alliances. It originated as a term used by the Western Allies during World War II, and is currently used only within NATO. Dwight Eisenhower served as Supreme Commander Allied Expeditionary...
, Europe. Officers serving in certain intelligence positions are not counted against either limit, including the Director of the Central Intelligence Agency
Director of the Central Intelligence Agency
Director of the Central Intelligence Agency serves as the head of the Central Intelligence Agency, which is part of the United States Intelligence Community. The Director reports to the Director of National Intelligence . The Director is assisted by the Deputy Director of the Central...
. The President may also add four-star slots to one service if they are offset by removing an equivalent number from other services. Finally, all statutory limits may be waived at the President's discretion during time of war or national emergency.
Appointment and tour length
Four-star grades go hand-in-hand with the positions of office to which they are linked, so these ranks are temporary. Officers may only achieve four-star grade if they are appointed to positions of office that require the officer to hold such a rank. Their rank expires with the expiration of their term of office, which is usually set by statute. Generals are nominated for appointment by the PresidentPresident of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
from any eligible officers holding the rank of brigadier general or above, who also meet the requirements for the position, under the advice and/or suggestion of their respective department secretary, service secretary, and if applicable the Joint Chiefs of Staff. For some specific positions, statute allows the President to waive those requirements for a nominee whom he deems would serve national interests. The nominee must be confirmed via majority vote by the Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
before the appointee can take office and thus assume the rank. The standard tour length for most four-star positions is three years, bundled as a two-year term plus a one-year extension, with the following exceptions:
- Service chiefs of staff serve for four years in one four-year term.
- Service vice chiefs of staff serve for a nominal four years, but are commonly reassigned after one or two years. The Assistant Commandant of the Marine Corps serves for two years.
- The Chief of the National Guard Bureau serves a nominal four years.
Extensions of the standard tour length can be approved, within statutory limits, by their respective service secretaries, the Secretary of Defense, the President, and/or Congress but these are rare, as they block other officers from being promoted. Some statutory limits under the U.S. Code can be waived in times of national emergency or war. Four-star ranks may also be given by act of Congress but this is extremely rare.
Retirement
Other than voluntary retirement, statute sets a number of mandates for retirement. A four-star general must retire after 40 years of service unless he or she is reappointed to serve longer. Otherwise all general officers must retire the month after their 64th birthday. However, the Secretary of Defense can defer a four-star officer's retirement until the officer's 66th birthday and the President can defer it until the officer's 68th birthday.General officers typically retire well in advance of the statutory age and service limits, so as not to impede the career paths of more junior officers. Since only a finite number of four-star slots are available to each service, typically one officer must leave office before another can be promoted. Maintaining a four-star rank is a game of musical chairs; once an officer vacates a position bearing that rank, he or she has no more than 60 days to be appointed or reappointed to a position of equal or greater importance before he or she must involuntarily retire. Historically, officers leaving four-star positions were allowed to revert to their permanent two-star ranks to mark time in lesser jobs until statutory retirement, but now such officers are expected to retire immediately to avoid obstructing the promotion flow.
To retire at four-star grade, an officer must accumulate at least three years of satisfactory active duty service in that grade, as certified by the Secretary of Defense. The Secretary of Defense may reduce this requirement to two years, but only if the officer is not being investigated for misconduct. Officers who do not meet the service-in-grade requirement revert to the next highest grade in which they served satisfactorily for at least six months. It is extraordinarily rare for a four-star officer not to be retired in grade.
Four-star officers typically step down from their posts up to 60 days in advance of their official retirement dates. Officers retire on the first day of the month, so once a retirement month has been selected, the relief and retirement ceremonies are scheduled by counting backwards from that date by the number of days of accumulated leave remaining to the retiring officer. During this period, termed transition leave or terminal leave, the officer is considered to be awaiting retirement but still on active duty.
See also
- List of active duty United States four-star officers
- List of United States Army four-star generals
- List of United States Marine Corps four-star generals
- List of United States Air Force four-star generals
- List of United States military leaders by rank
- United States Army officer rank insigniaUnited States Army officer rank insigniaUnited States Army officer rank insignia in use today.-History:The structure of U.S. ranks has its roots in British military traditions. At the start of the American Revolutionary War, uniforms, let alone insignia, were barely affordable and recognition of ranks in the field was problematic...
- United States Marine Corps officer rank insignia
- United States Air Force officer rank insigniaUnited States Air Force officer rank insignia-Current insignia:This chart displays the United States Air Force officer rank insignia. The ranks are divided into three sections: company grade, field grade, and general officers. Company grade officers are those officers of grades O-1 to O-3. Field grade officers are those of grades O-4 to O-6...
- Staff (military)

