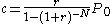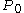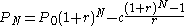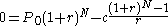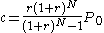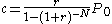Fixed rate mortgage
Encyclopedia
A fixed-rate mortgage is a mortgage loan
first developed by the Federal Housing Administration
(FHA) where the interest rate
on the note
remains the same through the term of the loan, as opposed to loans where the interest rate may adjust or "float." Other forms of mortgage loan include interest only mortgage, graduated payment mortgage
, variable rate (including adjustable rate mortgage
s and tracker mortgages) , negative amortization mortgage
, and balloon payment mortgage
. Please note that each of the loan types above except for a straight adjustable rate mortgage can have a period of the loan for which a fixed rate may apply. A Balloon Payment mortgage, for example, can have a fixed rate for the term of the loan followed by the ending balloon payment. Terminology may differ from country to country: loans for which the rate is fixed for less than the life of the loan may be called hybrid adjustable rate mortgages (in the United States).
This payment amount is independent of the additional costs on a home sometimes handled in escrow
, such as property taxes and property insurance. Consequently, payments made by the borrower may change over time with the changing escrow amount, but the payments handling the principal and interest on the loan will remain the same.
Fixed-rate mortgages are characterized by their interest rate
(including compounding frequency
, amount of loan, and term of the mortgage). With these three values, the calculation of the monthly payment can then be done.
Fixed-rate mortgages are often referred to as "plain vanilla" mortgage products for their ease of comprehension among borrowers, lacking many of the dangerous features that can come about vis-a-vis ARMs or floating-rate mortgages with fixed "teaser rate
s."
The fixed monthly payment for a fixed-rate mortgage is the amount paid by the borrower every month that ensures that the loan is paid off in full with interest at the end of its term.
. The most common terms are 15-year and 30-year mortgages, but shorter terms are available, and 40-year and 50-year mortgages are now available (common in areas with high priced housing, where even a 30-year term leaves the mortgage amount out of reach of the average family).
Outside the United States, fixed-rate mortgages are less popular, and in some countries, true fixed-rate mortgages are not available except for shorter-term loans. For example, in Canada the longest term for which a mortgage rate can be fixed is typically no more than ten years, while mortgage maturities are commonly 25 years.
, long-term fixed rate loans will tend to be at a higher interest rate than short-term loans. The relationship between interest rates for short and long-term loans is represented by the yield curve
, which generally slopes upward (longer terms are more expensive). The opposite circumstance is known as an inverted yield curve and occurs less often.
The fact that a fixed rate mortgage has a higher starting interest rate does not indicate that this is a worse form of borrowing compared to the adjustable rate mortgages. If interest rates rise, the ARM cost will be higher while the FRM will remain the same. In effect, the lender has agreed to take the interest rate risk
on a fixed-rate loan. Some studies have shown that the majority of borrowers with adjustable rate mortgages save money in the long term, but that some borrowers pay more. The price of potentially saving money, in other words, is balanced by the risk of potentially higher costs. In each case, a choice would need to be made based upon the loan term, the current interest rate, and the likelihood that the rate will increase or decrease during the life of the loan.
Some mortgages may offer a lower interest rate in exchange for the borrower accepting a prepayment penalty.
The fixed monthly payment for a fixed rate mortgage is the amount paid by the borrower every month that ensures that the loan is paid off in full with interest at the end of its term. This monthly payment depends upon the monthly interest rate
depends upon the monthly interest rate
 (expressed as a fraction
(expressed as a fraction
, not a percentage, i.e., divide the quoted yearly nominal percentage rate by 100 and by 12 to obtain the monthly interest rate), the number of monthly payments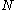 called the loan's term, and the amount borrowed
called the loan's term, and the amount borrowed 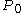 known as the loan's principal; rearranging the formula for the present value of an ordinary annuity we get the formula for
known as the loan's principal; rearranging the formula for the present value of an ordinary annuity we get the formula for  :
:
For example, for a home loan for $200,000 with a fixed yearly nominal interest rate of 6.5% for 30 years, the principal is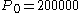 , the monthly interest rate is
, the monthly interest rate is 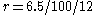 , the number of monthly payments is
, the number of monthly payments is 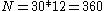 , the fixed monthly payment
, the fixed monthly payment 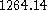 . This formula is provided using the financial function PMT in a spreadsheet
. This formula is provided using the financial function PMT in a spreadsheet
such as Excel
. In the example, the monthly payment is obtained by entering either of the these formulas:
This monthly payment formula is easy to derive, and the derivation illustrates how fixed-rate mortgage loans work. The amount owed on the loan at the end of every month equals the amount owed from the previous month, plus the interest on this amount, minus the fixed amount paid every month.
This derivation illustrates three key components of fixed-rate loans: (1) the fixed monthly payment depends upon the amount borrowed, the interest rate, and the length of time over which the loan is repaid; (2) the amount owed every month equals the amount owed from the previous month plus interest on that amount, minus the fixed monthly payment; (3) the fixed monthly payment is chosen so that the loan is paid off in full with interest at the end of its term and no more money is owed.
Mortgage loan
A mortgage loan is a loan secured by real property through the use of a mortgage note which evidences the existence of the loan and the encumbrance of that realty through the granting of a mortgage which secures the loan...
first developed by the Federal Housing Administration
Federal Housing Administration
The Federal Housing Administration is a United States government agency created as part of the National Housing Act of 1934. It insured loans made by banks and other private lenders for home building and home buying...
(FHA) where the interest rate
Interest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by a borrower for the use of money that they borrow from a lender. For example, a small company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for their business, and in return the lender receives interest at a predetermined interest rate for...
on the note
Promissory note
A promissory note is a negotiable instrument, wherein one party makes an unconditional promise in writing to pay a determinate sum of money to the other , either at a fixed or determinable future time or on demand of the payee, under specific terms.Referred to as a note payable in accounting, or...
remains the same through the term of the loan, as opposed to loans where the interest rate may adjust or "float." Other forms of mortgage loan include interest only mortgage, graduated payment mortgage
Graduated payment mortgage loan
A graduated payment mortgage loan, often referred to as GPM, is a mortgage with low initial monthly payments which gradually increase over a specified time frame. These plans are mostly geared towards young men and women who cannot afford large payments now, but can realistically expect to do...
, variable rate (including adjustable rate mortgage
Adjustable rate mortgage
A variable-rate mortgage, adjustable-rate mortgage , or tracker mortgage is a mortgage loan with the interest rate on the note periodically adjusted based on an index which reflects the cost to the lender of borrowing on the credit markets. The loan may be offered at the lender's standard variable...
s and tracker mortgages) , negative amortization mortgage
Negative amortization
In finance, negative amortization, also known as NegAm, deferred interest or graduated payment mortgage, occurs whenever the loan payment for any period is less than the interest charged over that period so that the outstanding balance of the loan increases...
, and balloon payment mortgage
Balloon payment mortgage
A balloon payment mortgage is a mortgage which does not fully amortize over the term of the note, thus leaving a balance due at maturity. The final payment is called a balloon payment because of its large size. Balloon payment mortgages are more common in commercial real estate than in...
. Please note that each of the loan types above except for a straight adjustable rate mortgage can have a period of the loan for which a fixed rate may apply. A Balloon Payment mortgage, for example, can have a fixed rate for the term of the loan followed by the ending balloon payment. Terminology may differ from country to country: loans for which the rate is fixed for less than the life of the loan may be called hybrid adjustable rate mortgages (in the United States).
This payment amount is independent of the additional costs on a home sometimes handled in escrow
Escrow
An escrow is:* an arrangement made under contractual provisions between transacting parties, whereby an independent trusted third party receives and disburses money and/or documents for the transacting parties, with the timing of such disbursement by the third party dependent on the fulfillment of...
, such as property taxes and property insurance. Consequently, payments made by the borrower may change over time with the changing escrow amount, but the payments handling the principal and interest on the loan will remain the same.
Fixed-rate mortgages are characterized by their interest rate
Interest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by a borrower for the use of money that they borrow from a lender. For example, a small company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for their business, and in return the lender receives interest at a predetermined interest rate for...
(including compounding frequency
Compound interest
Compound interest arises when interest is added to the principal, so that from that moment on, the interest that has been added also itself earns interest. This addition of interest to the principal is called compounding...
, amount of loan, and term of the mortgage). With these three values, the calculation of the monthly payment can then be done.
Fixed-rate mortgages are often referred to as "plain vanilla" mortgage products for their ease of comprehension among borrowers, lacking many of the dangerous features that can come about vis-a-vis ARMs or floating-rate mortgages with fixed "teaser rate
Teaser rate
A teaser rate is a low, adjustable introductory interest rate advertised for a loan, credit card, or deposit account in order to attract potential customers to obtain the service. The teaser rates are normally too good to be true for the long term, and are far below the common realistic rate for...
s."
Overview
Unlike adjustable rate mortgages, fixed-rate mortgages are not tied to an index. Instead, the interest rate is set (or "fixed") in advance to an advertised rate, usually in increments of 1/4 or 1/8 percent.The fixed monthly payment for a fixed-rate mortgage is the amount paid by the borrower every month that ensures that the loan is paid off in full with interest at the end of its term.
Popularity
Fixed-rate mortgages are the most classic form of loan for home and product purchasing in the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. The most common terms are 15-year and 30-year mortgages, but shorter terms are available, and 40-year and 50-year mortgages are now available (common in areas with high priced housing, where even a 30-year term leaves the mortgage amount out of reach of the average family).
Outside the United States, fixed-rate mortgages are less popular, and in some countries, true fixed-rate mortgages are not available except for shorter-term loans. For example, in Canada the longest term for which a mortgage rate can be fixed is typically no more than ten years, while mortgage maturities are commonly 25 years.
Pricing
Fixed rate mortgages are usually more expensive than adjustable rate mortgages. Due to the inherent interest rate riskInterest rate risk
Interest rate risk is the risk borne by an interest-bearing asset, such as a loan or a bond, due to variability of interest rates. In general, as rates rise, the price of a fixed rate bond will fall, and vice versa...
, long-term fixed rate loans will tend to be at a higher interest rate than short-term loans. The relationship between interest rates for short and long-term loans is represented by the yield curve
Yield curve
In finance, the yield curve is the relation between the interest rate and the time to maturity, known as the "term", of the debt for a given borrower in a given currency. For example, the U.S. dollar interest rates paid on U.S...
, which generally slopes upward (longer terms are more expensive). The opposite circumstance is known as an inverted yield curve and occurs less often.
The fact that a fixed rate mortgage has a higher starting interest rate does not indicate that this is a worse form of borrowing compared to the adjustable rate mortgages. If interest rates rise, the ARM cost will be higher while the FRM will remain the same. In effect, the lender has agreed to take the interest rate risk
Interest rate risk
Interest rate risk is the risk borne by an interest-bearing asset, such as a loan or a bond, due to variability of interest rates. In general, as rates rise, the price of a fixed rate bond will fall, and vice versa...
on a fixed-rate loan. Some studies have shown that the majority of borrowers with adjustable rate mortgages save money in the long term, but that some borrowers pay more. The price of potentially saving money, in other words, is balanced by the risk of potentially higher costs. In each case, a choice would need to be made based upon the loan term, the current interest rate, and the likelihood that the rate will increase or decrease during the life of the loan.
Prepayment
In the United States, fixed-rate mortgages, like other types of mortgage, may offer the ability to prepay principal (or capital) early without penalty. Early payments of part of the principal will reduce the total cost of the loan (total interest paid), and will shorten the amount of time needed to pay off the loan. Early payoff of the entire loan amount through refinancing is sometimes done when interest rates drop significantly.Some mortgages may offer a lower interest rate in exchange for the borrower accepting a prepayment penalty.
Monthly payment formula
- Note: Fixed-rate mortgage interest may be compounded differently in other countries, such as in Canada, where it is compounded every 6 months.
The fixed monthly payment for a fixed rate mortgage is the amount paid by the borrower every month that ensures that the loan is paid off in full with interest at the end of its term. This monthly payment
 depends upon the monthly interest rate
depends upon the monthly interest rateInterest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by a borrower for the use of money that they borrow from a lender. For example, a small company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for their business, and in return the lender receives interest at a predetermined interest rate for...
 (expressed as a fraction
(expressed as a fractionFraction
In common usage a fraction is any part of a unit.Fraction may also mean:*Fraction , one of more equal parts of something, eg...
, not a percentage, i.e., divide the quoted yearly nominal percentage rate by 100 and by 12 to obtain the monthly interest rate), the number of monthly payments
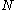 called the loan's term, and the amount borrowed
called the loan's term, and the amount borrowed 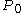 known as the loan's principal; rearranging the formula for the present value of an ordinary annuity we get the formula for
known as the loan's principal; rearranging the formula for the present value of an ordinary annuity we get the formula for  :
:
For example, for a home loan for $200,000 with a fixed yearly nominal interest rate of 6.5% for 30 years, the principal is
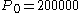 , the monthly interest rate is
, the monthly interest rate is 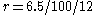 , the number of monthly payments is
, the number of monthly payments is 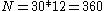 , the fixed monthly payment
, the fixed monthly payment 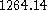 . This formula is provided using the financial function PMT in a spreadsheet
. This formula is provided using the financial function PMT in a spreadsheetSpreadsheet
A spreadsheet is a computer application that simulates a paper accounting worksheet. It displays multiple cells usually in a two-dimensional matrix or grid consisting of rows and columns. Each cell contains alphanumeric text, numeric values or formulas...
such as Excel
Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel is a proprietary commercial spreadsheet application written and distributed by Microsoft for Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X. It features calculation, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for Applications...
. In the example, the monthly payment is obtained by entering either of the these formulas:
-
- =PMT(6.5/100/12,30*12,200000)
- =((6.5/100/12)/(1-(1+6.5/100/12)^(-30*12)))*200000
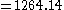
This monthly payment formula is easy to derive, and the derivation illustrates how fixed-rate mortgage loans work. The amount owed on the loan at the end of every month equals the amount owed from the previous month, plus the interest on this amount, minus the fixed amount paid every month.
-
- Amount owed at month 0:
- Amount owed at month 1:
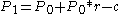 ( principal + interest – payment)
( principal + interest – payment)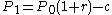 (equation 1)
(equation 1)
- Amount owed at month 2:
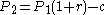
- Using equation 1 for
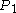
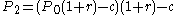
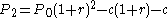 (equation 2)
(equation 2)
- Amount owed at month 3:
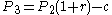
- Using equation 2 for
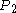
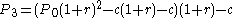
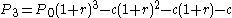
- Amount owed at month N:
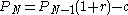
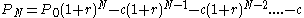
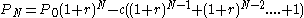
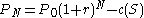 (equation 3)
(equation 3)- Where
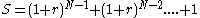 (equation 4) (see geometric progressionGeometric progressionIn mathematics, a geometric progression, also known as a geometric sequence, is a sequence of numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous one by a fixed non-zero number called the common ratio. For example, the sequence 2, 6, 18, 54, ... is a geometric progression...
(equation 4) (see geometric progressionGeometric progressionIn mathematics, a geometric progression, also known as a geometric sequence, is a sequence of numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous one by a fixed non-zero number called the common ratio. For example, the sequence 2, 6, 18, 54, ... is a geometric progression...
) 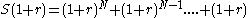 (equation 5)
(equation 5)
- With the exception of two terms the
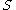 and
and 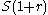 series are the same so when you subtract all but two terms cancel:
series are the same so when you subtract all but two terms cancel:
- Using equation 4 and 5
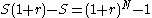
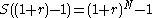
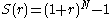
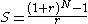 (equation 6)
(equation 6)
- Putting equation 6 back into 3:
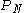 will be zero because we have paid the loan off.
will be zero because we have paid the loan off.
- We want to know

- Divide top and bottom with
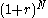
- Amount owed at month 0:
This derivation illustrates three key components of fixed-rate loans: (1) the fixed monthly payment depends upon the amount borrowed, the interest rate, and the length of time over which the loan is repaid; (2) the amount owed every month equals the amount owed from the previous month plus interest on that amount, minus the fixed monthly payment; (3) the fixed monthly payment is chosen so that the loan is paid off in full with interest at the end of its term and no more money is owed.