
Femtosecond pulse shaping
Encyclopedia
In optics
, femtosecond pulse shaping is a technique that modifies the temporal profile of an ultrashort pulse
from a laser. Pulse shaping can be used to shorten/elongate the duration of optical pulse, or to generate more complex pulses.
 Generation of sequences of ultrashort optical pulses is key in realizing ultra high speed optical networks, Optical Code Division Multiple Access (OCDMA) systems, chemical and biological reaction triggering and monitoring etc. Based on the requirement, pulse shapers may be designed to stretch, compress or produce a train of pulses from a single input pulse. The ability to produce trains of pulses with femtosecond or picosecond separation implies transmission of optical information at very high speeds.
Generation of sequences of ultrashort optical pulses is key in realizing ultra high speed optical networks, Optical Code Division Multiple Access (OCDMA) systems, chemical and biological reaction triggering and monitoring etc. Based on the requirement, pulse shapers may be designed to stretch, compress or produce a train of pulses from a single input pulse. The ability to produce trains of pulses with femtosecond or picosecond separation implies transmission of optical information at very high speeds.
a) Direct space-to-time pulse shaping (DST-PS)
b) Fourier transform pulse shaping (FT-PS)
In DST-PS, for any required output temporal sequence of pulses, the modulating function is exactly the same. If the modulating function of the system is defined by binaries 1101, then the output sequence of optical pulses is again 1101 (1s mean pulse is present and 0s mean pulse is absent).
In FT-PS, for a specific output pulse sequence, the modulating function is simply its Fourier Transform.
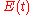 can be modified with an appropriate filter
can be modified with an appropriate filter
acting in the frequency domain. Mathematically, the pulse is Fourier transform
ed, filtered, and back-transformed to yield a new pulse: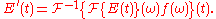
It is possible to design an optical setup with an arbitrary filter function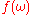 which can be complex-valued, as long as
which can be complex-valued, as long as 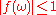 . Figure 1 shows how a bandwidth-limited pulse could be transformed into a chirp
. Figure 1 shows how a bandwidth-limited pulse could be transformed into a chirp
ed pulse (with a filter only acting on the phase
) or into a more complex pulse (with the filter acting on both phase and amplitude
).
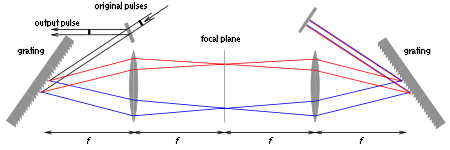 Typically, a pulse shaper is based on the design of a pulse stretcher
Typically, a pulse shaper is based on the design of a pulse stretcher
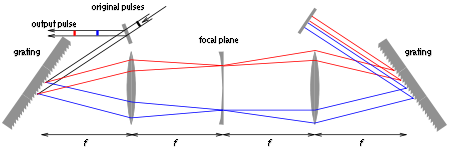
, but in a 4f configuration such that the stretcher actually neither stretches nor compresses incoming pulses. This is shown in Figure 2. A diffraction grating
directs different frequency (wavelength) components into different directions and each frequency component is focused
at a particular spot in the focal plane. A second grating and a mirror are used to recombine the different frequency components. The two lenses
have a focal length
f, and the distance from the center of the first grating to the center of the second grating is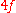 .
.
In the focal plane, undesired frequency components can easily be blocked, which would correspond to a real-valued filter function without any effect on the phase.
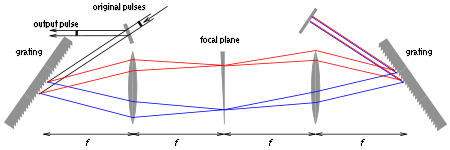 To make the filter act on the phase of the frequency components, a slab of transparent material with a varying thickness could be used to introduce an extra frequency-dependent delay, as shown in Figure 3. Although one might think that an extra delay is introduced for longer wavelengths (shown in red), the actual effect is that the pulse as a whole will have a shorter travel distance, mainly because the light has a shorter travel distance to the rightmost grating. This is in agreement with the fact that a Fourier filter
To make the filter act on the phase of the frequency components, a slab of transparent material with a varying thickness could be used to introduce an extra frequency-dependent delay, as shown in Figure 3. Although one might think that an extra delay is introduced for longer wavelengths (shown in red), the actual effect is that the pulse as a whole will have a shorter travel distance, mainly because the light has a shorter travel distance to the rightmost grating. This is in agreement with the fact that a Fourier filter 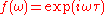 ('linear phase shift') is equivalent to a time-shift
('linear phase shift') is equivalent to a time-shift  .
.
 For a more interesting effect on the pulse shape, a quadratic or higher-order phase shift is needed, as shown in Figures 4 and 5.
For a more interesting effect on the pulse shape, a quadratic or higher-order phase shift is needed, as shown in Figures 4 and 5.
technology, it is possible to create a filter that can have an arbitrary computer-controlled phase and amplitude spectrum. Multiphoton Intrapulse Interference Phase Scan (MIIPS) is a technique based on the computer-controlled phase scan of Spatial light modulator
. Through the phase scan to an ultrashort pulse, MIIPS can not only characterize but also manipulate the ultrashort pulse to get the needed pulse shape at target spot (such as Transform-Limited pulse
for optimized peak power, and other specific pulse shapes). This technique features with full calibration and control of the ultrashort pulse, with no moving parts, and simple optical setup.
s, which corresponds to just a few tenths of a millimeter of transversal displacement, which is only a minor concern.
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, femtosecond pulse shaping is a technique that modifies the temporal profile of an ultrashort pulse
Ultrashort pulse
In optics, an ultrashort pulse of light is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a femtosecond . Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by mode-locked oscillators...
from a laser. Pulse shaping can be used to shorten/elongate the duration of optical pulse, or to generate more complex pulses.
Introduction

Techniques
A pulse shaper may be visualized as a modulator. The input pulse is multiplied with a modulating function to get a desired output pulse. The modulating function in pulse shapers may be in time domain or a frequency domain (obtained by Fourier Transform of time profile of pulse). This gives rise to two well known femtosecond pulse shaping techniques:a) Direct space-to-time pulse shaping (DST-PS)
b) Fourier transform pulse shaping (FT-PS)
Direct space-to-time pulse shaping
In DST-PS, the output sequence of pulses is directly proportional to the modulating function of the system. Let us assume that occurrence of an optical pulse as 1 and absence of pulse as 0. Then, information can be transmitted by presence or absence of optical pulses which will correspond to a specific sequence of 1s and 0s.In DST-PS, for any required output temporal sequence of pulses, the modulating function is exactly the same. If the modulating function of the system is defined by binaries 1101, then the output sequence of optical pulses is again 1101 (1s mean pulse is present and 0s mean pulse is absent).
Fourier transform pulse shaping
In contrast to DST-PS, the FT-PS uses a modulating function which is a Fourier Transform of the required sequence. This implies that for a specific temporal sequence of pulses, the modulating function is its Fourier Transform and acts in frequency domain. The reason for using this technique is because in optics a lens performs a Fourier Transform of the input light. A typical FT-PS will consist of an input laser, a lens which will perform Fourier Transform (conversion of time data to frequency data), a modulating function (which may be a phase or intensity modulation), a second lens which will perform another Fourier Transform (converting frequency data back to time data).In FT-PS, for a specific output pulse sequence, the modulating function is simply its Fourier Transform.
Details of FT-PS
An ultrashort pulse with a well-defined electrical field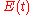 can be modified with an appropriate filter
can be modified with an appropriate filterFilter (signal processing)
In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes from a signal some unwanted component or feature. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal...
acting in the frequency domain. Mathematically, the pulse is Fourier transform
Fourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
ed, filtered, and back-transformed to yield a new pulse:
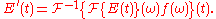
It is possible to design an optical setup with an arbitrary filter function
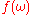 which can be complex-valued, as long as
which can be complex-valued, as long as 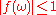 . Figure 1 shows how a bandwidth-limited pulse could be transformed into a chirp
. Figure 1 shows how a bandwidth-limited pulse could be transformed into a chirpChirp
A chirp is a signal in which the frequency increases or decreases with time. In some sources, the term chirp is used interchangeably with sweep signal. It is commonly used in sonar and radar, but has other applications, such as in spread spectrum communications...
ed pulse (with a filter only acting on the phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
) or into a more complex pulse (with the filter acting on both phase and amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
).
Basic principles

Chirped pulse amplification
Chirped pulse amplification is a technique for amplifying an ultrashort laser pulse up to the petawatt level with the laser pulse being stretched out temporally and spectrally prior to amplification...
, but in a 4f configuration such that the stretcher actually neither stretches nor compresses incoming pulses. This is shown in Figure 2. A diffraction grating
Diffraction grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure, which splits and diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions. The directions of these beams depend on the spacing of the grating and the wavelength of the light so that the grating acts as...
directs different frequency (wavelength) components into different directions and each frequency component is focused
Focus (optics)
In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is the point where light rays originating from a point on the object converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by...
at a particular spot in the focal plane. A second grating and a mirror are used to recombine the different frequency components. The two lenses
Lens (optics)
A lens is an optical device with perfect or approximate axial symmetry which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element...
have a focal length
Focal length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light. For an optical system in air, it is the distance over which initially collimated rays are brought to a focus...
f, and the distance from the center of the first grating to the center of the second grating is
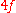 .
.In the focal plane, undesired frequency components can easily be blocked, which would correspond to a real-valued filter function without any effect on the phase.

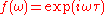 ('linear phase shift') is equivalent to a time-shift
('linear phase shift') is equivalent to a time-shift  .
.

Active filters
The examples above are with static filters. With liquid crystalLiquid crystal display
A liquid crystal display is a flat panel display, electronic visual display, or video display that uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals . LCs do not emit light directly....
technology, it is possible to create a filter that can have an arbitrary computer-controlled phase and amplitude spectrum. Multiphoton Intrapulse Interference Phase Scan (MIIPS) is a technique based on the computer-controlled phase scan of Spatial light modulator
Spatial light modulator
A spatial light modulator is an object that imposes some form of spatially-varying modulation on a beam of light. A simple example is an overhead projector transparency. Usually when the phrase SLM is used, it means that the transparency can be controlled by a computer. In the 1980s, large SLMs...
. Through the phase scan to an ultrashort pulse, MIIPS can not only characterize but also manipulate the ultrashort pulse to get the needed pulse shape at target spot (such as Transform-Limited pulse
Bandwidth-limited pulse
A bandwidth-limited pulse is a pulse of a wave that has the minimum possible duration for a given spectral bandwidth. Optical pulses of this type can be generated by mode-locked lasers...
for optimized peak power, and other specific pulse shapes). This technique features with full calibration and control of the ultrashort pulse, with no moving parts, and simple optical setup.
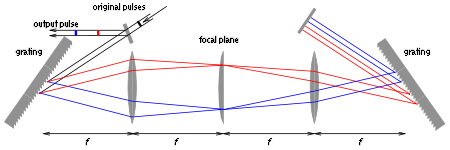
Single versus double-pass design
In the configuration shown above, the light hits each of the two gratings twice. In many applications, the back-reflecting mirror on the right is omitted, which makes the design simpler. The main disadvantage of such a single-pass design is that the different frequency components do not overlap in space, as can be seen in Figures 4 and 5. However, for many applications, it is only necessary to separate different frequencies in time by only a few picosecondPicosecond
A picosecond is 10−12 of a second. That is one trillionth, or one millionth of one millionth of a second, or 0.000 000 000 001 seconds. A picosecond is to one second as one second is to 31,700 years....
s, which corresponds to just a few tenths of a millimeter of transversal displacement, which is only a minor concern.
Related techniques
- MIIPS Multiphoton Intrapulse Interference Phase Scan, a method to characterize and manipulate the ultrashort pulse.

