Chirp
Encyclopedia
A chirp is a signal in which the frequency
increases ('up-chirp') or decreases ('down-chirp') with time. In some sources, the term chirp is used interchangeably with sweep signal. It is commonly used in sonar
and radar
, but has other applications, such as in spread spectrum
communications. In spread spectrum usage, SAW
devices such as RACs are often used to generate and demodulate the chirped signals. In optics
, ultrashort
laser
pulses also exhibit chirp, which, in optical transmission systems interacts with the dispersion
properties of the materials, increasing or decreasing total pulse dispersion as the signal propagates.
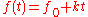
where f0 is the starting frequency (at time t = 0), and k is the rate of frequency increase or chirp rate. The corresponding time-domain function for a
sinusoidal linear chirp is:
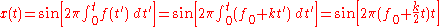
In the frequency domain, the instantaneous frequency described by the equation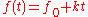 is accompanied by additional frequencies (harmonics) which exist as a fundamental consequence of Frequency Modulation
is accompanied by additional frequencies (harmonics) which exist as a fundamental consequence of Frequency Modulation
. These harmonics are quantifiably described through the use of Bessel Functions. However with the aid of Frequency vs. Time profile Spectrogram
one can readily see that the linear chirp has spectral components at harmonics of the fundamental chirp.
relationship over time. In other words, if two points in the waveform are chosen, t1 and t2, and the time interval between them t2 − t1 is kept constant, the frequency ratio f(t2)/f(t1) will also be constant.
In an exponential chirp, the frequency of the signal varies exponentially
as a function of time:
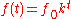
where f0 is the starting frequency (at t = 0), and k is the rate of exponential increase
in frequency.
Unlike the linear chirp, which has a constant chirp rate, an exponential chirp has an exponentially increasing chirp rate.
The corresponding time-domain function for a sinusoidal exponential chirp is:
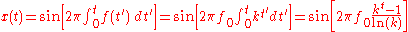
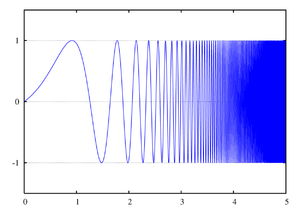
As was the case for the Linear Chirp, the instantaneous frequency of the Exponential Chirp consists of the fundamental frequency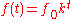 accompanied by additional harmonics.
accompanied by additional harmonics.
Although somewhat harder to generate, a geometric chirp does not suffer from reduction in correlation
gain if the echo is Doppler
-shifted by a moving target. This is because the Doppler shift actually scales the frequencies of a wave by a multiplier (shown below as the constant c).

From the equations above, it can be seen that this actually changes the rate of frequency increase of a linear chirp (kt multiplied by a constant) so that the correlation of the original function with the reflected function is low.
Because of the geometric relationship, the Doppler shifted geometric chirp will effectively start at a different frequency (f0 multiplied by a constant), but follow the same pattern of exponential frequency increase, so the end of the original wave, for instance, will still overlap perfectly with the beginning of the reflected wave, and the magnitude of the correlation will be high for that section of the wave.
, and a linearly or exponentially ramping control voltage
. It can also be generated digital
ly by a DSP
and DAC, using a Direct digital synthesizer (DDS) and by varying the step in the numerically controlled oscillator.
in 1954 with significant later work performed by Winkler in 1962. This type of modulation employs sinusoidal waveforms whose instantaneous frequency increases or decreases linearly over time. These waveforms are commonly referred to as linear chirps or simply chirps.
Hence the rate at which their frequency changes is called the chirp rate. In binary chirp modulation, binary data is transmitted by mapping the bits into chirps of opposite chirp rates. For instance, over one bit period "1" is assigned a chirp with positive rate a and "0" a chirp with negative rate −a. Chirps have been heavily used in radar applications and as a result advanced sources for transmission and matched filters for reception of linear chirps are available.
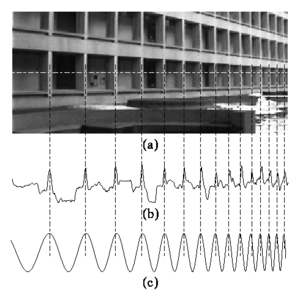
 , having the three parameters a (scale), b (translation), and c (chirpiness). The projective chirp is ideally suited to image processing
, having the three parameters a (scale), b (translation), and c (chirpiness). The projective chirp is ideally suited to image processing
, and forms the basis for the projective chirplet transform
.
from the desired frequency, due to poor stability in the RF
Oscillator is known as chirp, and in the RST code
is given an appended letter 'C'.
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
increases ('up-chirp') or decreases ('down-chirp') with time. In some sources, the term chirp is used interchangeably with sweep signal. It is commonly used in sonar
Sonar
Sonar is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, communicate with or detect other vessels...
and radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
, but has other applications, such as in spread spectrum
Spread spectrum
Spread-spectrum techniques are methods by which a signal generated in a particular bandwidth is deliberately spread in the frequency domain, resulting in a signal with a wider bandwidth...
communications. In spread spectrum usage, SAW
Surface acoustic wave
]A surface acoustic wave is an acoustic wave traveling along the surface of a material exhibiting elasticity, with an amplitude that typically decays exponentially with depth into the substrate.-Discovery:...
devices such as RACs are often used to generate and demodulate the chirped signals. In optics
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, ultrashort
Ultrashort pulse
In optics, an ultrashort pulse of light is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a femtosecond . Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by mode-locked oscillators...
laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
pulses also exhibit chirp, which, in optical transmission systems interacts with the dispersion
Dispersion (optics)
In optics, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency, or alternatively when the group velocity depends on the frequency.Media having such a property are termed dispersive media...
properties of the materials, increasing or decreasing total pulse dispersion as the signal propagates.
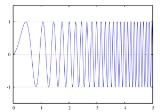
Linear chirp
In a linear chirp, the instantaneous frequency f(t ) varies linearly with time: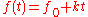
where f0 is the starting frequency (at time t = 0), and k is the rate of frequency increase or chirp rate. The corresponding time-domain function for a
sinusoidal linear chirp is:
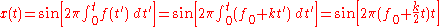
In the frequency domain, the instantaneous frequency described by the equation
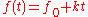 is accompanied by additional frequencies (harmonics) which exist as a fundamental consequence of Frequency Modulation
is accompanied by additional frequencies (harmonics) which exist as a fundamental consequence of Frequency ModulationFrequency modulation
In telecommunications and signal processing, frequency modulation conveys information over a carrier wave by varying its instantaneous frequency. This contrasts with amplitude modulation, in which the amplitude of the carrier is varied while its frequency remains constant...
. These harmonics are quantifiably described through the use of Bessel Functions. However with the aid of Frequency vs. Time profile Spectrogram
Spectrogram
A spectrogram is a time-varying spectral representation that shows how the spectral density of a signal varies with time. Also known as spectral waterfalls, sonograms, voiceprints, or voicegrams, spectrograms are used to identify phonetic sounds, to analyse the cries of animals; they were also...
one can readily see that the linear chirp has spectral components at harmonics of the fundamental chirp.
Exponential chirp
In a geometric chirp, also called an exponential chirp, the frequency of the signal varies with a geometricGeometric progression
In mathematics, a geometric progression, also known as a geometric sequence, is a sequence of numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous one by a fixed non-zero number called the common ratio. For example, the sequence 2, 6, 18, 54, ... is a geometric progression...
relationship over time. In other words, if two points in the waveform are chosen, t1 and t2, and the time interval between them t2 − t1 is kept constant, the frequency ratio f(t2)/f(t1) will also be constant.
In an exponential chirp, the frequency of the signal varies exponentially
Exponential function
In mathematics, the exponential function is the function ex, where e is the number such that the function ex is its own derivative. The exponential function is used to model a relationship in which a constant change in the independent variable gives the same proportional change In mathematics,...
as a function of time:
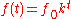
where f0 is the starting frequency (at t = 0), and k is the rate of exponential increase
Exponential growth
Exponential growth occurs when the growth rate of a mathematical function is proportional to the function's current value...
in frequency.
Unlike the linear chirp, which has a constant chirp rate, an exponential chirp has an exponentially increasing chirp rate.
The corresponding time-domain function for a sinusoidal exponential chirp is:
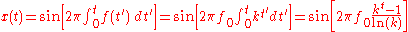

As was the case for the Linear Chirp, the instantaneous frequency of the Exponential Chirp consists of the fundamental frequency
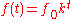 accompanied by additional harmonics.
accompanied by additional harmonics.Although somewhat harder to generate, a geometric chirp does not suffer from reduction in correlation
Correlation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
gain if the echo is Doppler
Doppler effect
The Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...
-shifted by a moving target. This is because the Doppler shift actually scales the frequencies of a wave by a multiplier (shown below as the constant c).

From the equations above, it can be seen that this actually changes the rate of frequency increase of a linear chirp (kt multiplied by a constant) so that the correlation of the original function with the reflected function is low.
Because of the geometric relationship, the Doppler shifted geometric chirp will effectively start at a different frequency (f0 multiplied by a constant), but follow the same pattern of exponential frequency increase, so the end of the original wave, for instance, will still overlap perfectly with the beginning of the reflected wave, and the magnitude of the correlation will be high for that section of the wave.
Generation of a chirp signal
A chirp signal can be generated with analog circuitry via a VCOVoltage-controlled oscillator
A voltage-controlled oscillator or VCO is an electronic oscillator designed to be controlled in oscillation frequency by a voltage input. The frequency of oscillation is varied by the applied DC voltage, while modulating signals may also be fed into the VCO to cause frequency modulation or phase...
, and a linearly or exponentially ramping control voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
. It can also be generated digital
Digital
A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information...
ly by a DSP
Digital signal processor
A digital signal processor is a specialized microprocessor with an architecture optimized for the fast operational needs of digital signal processing.-Typical characteristics:...
and DAC, using a Direct digital synthesizer (DDS) and by varying the step in the numerically controlled oscillator.
Chirp modulation
Chirp modulation, or linear frequency modulation for digital communication was patented by Sidney DarlingtonSidney Darlington
Sidney Darlington was an electrical engineer and inventor of a transistor configuration in 1953, the Darlington pair...
in 1954 with significant later work performed by Winkler in 1962. This type of modulation employs sinusoidal waveforms whose instantaneous frequency increases or decreases linearly over time. These waveforms are commonly referred to as linear chirps or simply chirps.
Hence the rate at which their frequency changes is called the chirp rate. In binary chirp modulation, binary data is transmitted by mapping the bits into chirps of opposite chirp rates. For instance, over one bit period "1" is assigned a chirp with positive rate a and "0" a chirp with negative rate −a. Chirps have been heavily used in radar applications and as a result advanced sources for transmission and matched filters for reception of linear chirps are available.

Chirplet transform
Another kind of chirp is the projective chirp, of the form , having the three parameters a (scale), b (translation), and c (chirpiness). The projective chirp is ideally suited to image processing
, having the three parameters a (scale), b (translation), and c (chirpiness). The projective chirp is ideally suited to image processingImage processing
In electrical engineering and computer science, image processing is any form of signal processing for which the input is an image, such as a photograph or video frame; the output of image processing may be either an image or, a set of characteristics or parameters related to the image...
, and forms the basis for the projective chirplet transform
Chirplet transform
In signal processing, the chirplet transform is an inner product of an input signal with a family of analysis primitives called chirplets.-Similarity to other transforms:...
.
Key chirp
A change in frequency of Morse codeMorse code
Morse code is a method of transmitting textual information as a series of on-off tones, lights, or clicks that can be directly understood by a skilled listener or observer without special equipment...
from the desired frequency, due to poor stability in the RF
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
Oscillator is known as chirp, and in the RST code
RST code
The RST code is used by amateur radio operators, shortwave listeners, and other radio hobbyists to exchange information about the quality of a radio signal being received. The code is a three digit number, with one digit each for conveying an assessment of the signal's readability, strength, and...
is given an appended letter 'C'.
See also
- Chirplet transformChirplet transformIn signal processing, the chirplet transform is an inner product of an input signal with a family of analysis primitives called chirplets.-Similarity to other transforms:...
- A signal representation based on a family of localized chirp functions, each member of which can usually be expressed as parameterized transformations of each other. - Pulse compressionPulse compressionPulse compression is a signal processing technique mainly used in radar, sonar and echography to increase the range resolution as well as the signal to noise ratio...
- A signal processing technique designed to maximize the sensitivity and resolution of radar systems by modifying transmitted pulses to improve their auto-correlation properties. One way of accomplishing this is to chirp the RADAR signal (also known as Chirp Radar). - Chirp Spread SpectrumChirp spread spectrumIn digital communications, Chirp spread spectrum is a spread spectrum technique that uses wideband linear frequency modulated chirp pulses to encode information. A chirp is a sinusoidal signal whose frequency increases or decreases over a certain amount of time...
- A part of the wireless telecommunications standard IEEE 802.15.4a CSS (see Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS) PHY Presentation for IEEE P802.15.4a). - Continuous-wave radarContinuous-wave radarContinuous-wave radar is a type of radar system where a known stable frequency continuous wave radio energy is transmitted and then received from any reflecting objects.Continuous wave radar uses Doppler, which renders the radar immune to interference from large stationary objects and slow moving...
- SHARADSHARADSHARAD is a subsurface sounding radar embarked on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter probe. It complements the MARSIS instrument on Mars Express, providing lower penetration capabilities but much finer resolution .SHARAD is developed under the responsibility of the Italian Space Agency SHARAD (Mars...
- Chirped pulse amplificationChirped pulse amplificationChirped pulse amplification is a technique for amplifying an ultrashort laser pulse up to the petawatt level with the laser pulse being stretched out temporally and spectrally prior to amplification...
- Chirped mirrorChirped mirrorA chirped mirror is a dielectric mirror with chirped spaces—spaces of varying depth designed to reflect varying wavelengths of lights—between the dielectric layers ....
- Dispersion (optics)Dispersion (optics)In optics, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency, or alternatively when the group velocity depends on the frequency.Media having such a property are termed dispersive media...

