
External sorting
Encyclopedia
External sorting is a term for a class of sorting
algorithm
s that can handle massive amounts of data
. External sorting is required when the data being sorted do not fit into the main memory of a computing device (usually RAM
) and instead they must reside in the slower external memory (usually a hard drive). External sorting typically uses a sort-merge strategy. In the sorting phase, chunks of data small enough to fit in main memory are read, sorted, and written out to a temporary file. In the merge phase, the sorted subfiles are combined into a single larger file.
algorithm, which sorts chunks that each fit in RAM, then merges the sorted chunks together. For example, for sorting 900 megabyte
s of data using only 100 megabytes of RAM:
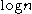 merge passes total. The reason for this is that every merge pass requires reading and writing every value in the array from and to disk once. Disk access is usually slow, and so reads and writes should be avoided as much as possible.
merge passes total. The reason for this is that every merge pass requires reading and writing every value in the array from and to disk once. Disk access is usually slow, and so reads and writes should be avoided as much as possible.
However, there is a trade-off with using fewer merge passes. As the number of chunks increases, the amount of data we can read from each chunk at a time during the merge process decreases. For sorting, say, 50 GB in 100 MB of RAM, using a single merge pass isn't efficient: the disk seeks required to fill the input buffers with data from each of the 500 chunks (we read 100MB / 501 ~ 200KB from each chunk at one time) take up most of the sort time. Using two merge passes solves the problem. Then the sorting process might look like this:
Like in-memory sorts, efficient external sorts require O
(n log n) time: exponential increases in data size require linear increases in the number of passes. If one makes liberal use of the gigabytes of RAM provided by modern computers, the logarithmic factor grows very slowly: under reasonable assumptions, one could sort at least 500 GB of data using 1 GB of main memory before a third pass became advantageous, and could sort many times that before a fourth pass became useful.
. There is a duality
, or fundamental similarity, between merge- and distribution-based algorithms that can aid in thinking about sorting and other external memory algorithms. There are in-place algorithm
s for external sort, which require no more disk space than the original data.
Sorting
Sorting is any process of arranging items in some sequence and/or in different sets, and accordingly, it has two common, yet distinct meanings:# ordering: arranging items of the same kind, class, nature, etc...
algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
s that can handle massive amounts of data
Data
The term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
. External sorting is required when the data being sorted do not fit into the main memory of a computing device (usually RAM
Ram
-Animals:*Ram, an uncastrated male sheep*Ram cichlid, a species of freshwater fish endemic to Colombia and Venezuela-Military:*Battering ram*Ramming, a military tactic in which one vehicle runs into another...
) and instead they must reside in the slower external memory (usually a hard drive). External sorting typically uses a sort-merge strategy. In the sorting phase, chunks of data small enough to fit in main memory are read, sorted, and written out to a temporary file. In the merge phase, the sorted subfiles are combined into a single larger file.
External merge sort
One example of external sorting is the external merge sortMerge sort
Merge sort is an O comparison-based sorting algorithm. Most implementations produce a stable sort, meaning that the implementation preserves the input order of equal elements in the sorted output. It is a divide and conquer algorithm...
algorithm, which sorts chunks that each fit in RAM, then merges the sorted chunks together. For example, for sorting 900 megabyte
Megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage or transmission with two different values depending on context: bytes generally for computer memory; and one million bytes generally for computer storage. The IEEE Standards Board has decided that "Mega will mean 1 000...
s of data using only 100 megabytes of RAM:
- Read 100 MB of the data in main memory and sort by some conventional method, like quicksort.
- Write the sorted data to disk.
- Repeat steps 1 and 2 until all of the data is in sorted 100 MB chunks (there are 900MB / 100MB = 9 chunks), which now need to be merged into one single output file.
- Read the first 10 MB (= 100MB / (9 chunks + 1)) of each sorted chunk into input buffers in main memory and allocate the remaining 10 MB for an output buffer. (In practice, it might provide better performance to make the output buffer larger and the input buffers slightly smaller.)
- Perform a 9-way mergeMerge algorithmMerge algorithms are a family of algorithms that run sequentially over multiple sorted lists, typically producing more sorted lists as output. This is well-suited for machines with tape drives...
and store the result in the output buffer. If the output buffer is full, write it to the final sorted file, and empty it. If any of the 9 input buffers gets empty, fill it with the next 10 MB of its associated 100 MB sorted chunk until no more data from the chunk is available. This is the key step that makes external merge sort work externally -- because the merge algorithm only makes one pass sequentially through each of the chunks, each chunk does not have to be loaded completely; rather, sequential parts of the chunk can be loaded as needed.
Additional passes
That example shows a two-pass sort: a sort pass followed by a merge pass. Note that we had one merge pass that merged all the chunks at once, rather than in regular merge sort, where we merge two chunks at each step, and take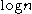 merge passes total. The reason for this is that every merge pass requires reading and writing every value in the array from and to disk once. Disk access is usually slow, and so reads and writes should be avoided as much as possible.
merge passes total. The reason for this is that every merge pass requires reading and writing every value in the array from and to disk once. Disk access is usually slow, and so reads and writes should be avoided as much as possible.However, there is a trade-off with using fewer merge passes. As the number of chunks increases, the amount of data we can read from each chunk at a time during the merge process decreases. For sorting, say, 50 GB in 100 MB of RAM, using a single merge pass isn't efficient: the disk seeks required to fill the input buffers with data from each of the 500 chunks (we read 100MB / 501 ~ 200KB from each chunk at one time) take up most of the sort time. Using two merge passes solves the problem. Then the sorting process might look like this:
- Run the initial chunk-sorting pass as before.
- Run a first merge pass combining 25 chunks at a time, resulting in 20 larger sorted chunks.
- Run a second merge pass to merge the 20 larger sorted chunks.
Like in-memory sorts, efficient external sorts require O
Big O notation
In mathematics, big O notation is used to describe the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity, usually in terms of simpler functions. It is a member of a larger family of notations that is called Landau notation, Bachmann-Landau notation, or...
(n log n) time: exponential increases in data size require linear increases in the number of passes. If one makes liberal use of the gigabytes of RAM provided by modern computers, the logarithmic factor grows very slowly: under reasonable assumptions, one could sort at least 500 GB of data using 1 GB of main memory before a third pass became advantageous, and could sort many times that before a fourth pass became useful.
Tuning performance
The Sort Benchmark, created by computer scientist Jim Gray, compares external sorting algorithms implemented using finely tuned hardware and software. Winning implementations use several techniques:- Using parallelism
- Multiple disk drives can be used in parallel in order to improve sequential read and write speed. This can be a very cost-efficient improvement: a recent Sort Benchmark winner in the cost-centric Penny Sort category uses six hard drives in an otherwise midrange machine.
- Sorting software can use multiple threadsThread (computer science)In computer science, a thread of execution is the smallest unit of processing that can be scheduled by an operating system. The implementation of threads and processes differs from one operating system to another, but in most cases, a thread is contained inside a process...
, to speed up the process on modern multicore computers. - Software can use asynchronous I/OAsynchronous I/OAsynchronous I/O, or non-blocking I/O, is a form of input/output processing that permits other processing to continue before the transmission has finished....
so that one run of data can be sorted or merged while other runs are being read from or written to disk. - Multiple machines connected by fast network links can each sort part of a huge dataset in parallel.
- Increasing hardware speed
- Using more RAM for sorting can reduce the number of disk seeks and avoid the need for more passes.
- Fast external memory, like 15K RPM disks or solid-state drives, can speed sorts (but adds substantial costs proportional to the data size).
- Many different factors can affect hardware's maximum sorting speed: CPU speed and number of cores, RAM access latency, input/output bandwidth, disk read/write speed, disk seek time, and others.
- Cost-efficiency as well as absolute speed can be critical, especially in cluster environments where lower node costs allow purchasing more nodes.
- Increasing software speed
- Some Sort Benchmark entrants use a variation on radix sortRadix sortIn computer science, radix sort is a non-comparative integer sorting algorithm that sorts data with integer keys by grouping keys by the individual digits which share the same significant position and value...
for the first phase of sorting: they separate data into one of many "bins" based on the beginning of its value. Sort Benchmark data is random and especially well-suited to this optimization. - Compacting the input, intermediate files, and output can reduce time spent on I/O, but is not allowed in the Sort Benchmark.
- Because the Sort Benchmark sorts long (100-byte) records using short (10-byte) keys, sorting software sometimes rearranges the keys separately from the values to reduce memory I/O volume.
- Some Sort Benchmark entrants use a variation on radix sort
Other algorithms
External merge sort is not the only external sorting algorithm; there are also distribution sorts, which work by partitioning the unsorted values into smaller "buckets" that can be sorted in main memory. Like merge sort, external distribution sort also has a main-memory sibling; see bucket sortBucket sort
Bucket sort, or bin sort, is a sorting algorithm that works by partitioning an array into a number of buckets. Each bucket is then sorted individually, either using a different sorting algorithm, or by recursively applying the bucket sorting algorithm. It is a distribution sort, and is a cousin of...
. There is a duality
Duality (mathematics)
In mathematics, a duality, generally speaking, translates concepts, theorems or mathematical structures into other concepts, theorems or structures, in a one-to-one fashion, often by means of an involution operation: if the dual of A is B, then the dual of B is A. As involutions sometimes have...
, or fundamental similarity, between merge- and distribution-based algorithms that can aid in thinking about sorting and other external memory algorithms. There are in-place algorithm
In-place algorithm
In computer science, an in-place algorithm is an algorithm which transforms input using a data structure with a small, constant amount of extra storage space. The input is usually overwritten by the output as the algorithm executes...
s for external sort, which require no more disk space than the original data.

