
Existentially closed model
Encyclopedia
In model theory
, a branch of mathematical logic
, the notion of an existentially closed model (or existentially complete model) of a theory
generalizes the notions of algebraically closed field
s (for the theory of field
s), real closed field
s (for the theory of ordered fields), existentially closed group
s (for the class of groups), and dense linear orders without endpoints (for the class of linear orders).
N is said to be existentially closed in (or existentially complete in)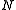 if for every quantifier-free formula φ(x,y1,…,yn) and all elements b1,…,bn of M such that φ(x,b1,…,bn) is realized in N, then φ(x,b1,…,bn) is also realized in M. In other words: If there is an element a in N such that φ(a,b1,…,bn) holds in N, then such an element also exists in M.
if for every quantifier-free formula φ(x,y1,…,yn) and all elements b1,…,bn of M such that φ(x,b1,…,bn) is realized in N, then φ(x,b1,…,bn) is also realized in M. In other words: If there is an element a in N such that φ(a,b1,…,bn) holds in N, then such an element also exists in M.
A model M of a theory T is called existentially closed in T if it is existentially closed in every superstructure N which is itself a model of T. More generally, a structure M is called existentially closed in a class K of structures (in which it is contained as a member) if M is existentially closed in every superstructure N which is itself a member of K.
The existential closure in K of a member M of K, when it exists, is, up to isomorphism, the least existentially closed superstructure of M. More precisely, it is any extensionally closed superstructure M∗ of M such that for every existentially closed superstructure N of M, M∗ is isomorphic to a substructure of N via an isomorphism that is the identity on M.
of fields, i.e. +,× are binary relation symbols and 0,1 are constant symbols. Let K be the class of structures of signature σ which are fields.
If A is a subfield of B, then A is existentially closed in B if and only if every system of polynomial
s over A which has a solution in B also has a solution in A. It follows that the existentially closed members of K are exactly the algebraically closed fields.
Similarly in the class of ordered field
s, the existentially closed structures are the real closed field
s. In the class of totally ordered structures
, the existentially closed structures are those that are dense
without endpoints, while the existential closure of any countable (including empty) total order is, up to isomorphism, the countable dense total order without endpoints, namely the order type
of the rationals.
Model theory
In mathematics, model theory is the study of mathematical structures using tools from mathematical logic....
, a branch of mathematical logic
Mathematical logic
Mathematical logic is a subfield of mathematics with close connections to foundations of mathematics, theoretical computer science and philosophical logic. The field includes both the mathematical study of logic and the applications of formal logic to other areas of mathematics...
, the notion of an existentially closed model (or existentially complete model) of a theory
Theory (mathematical logic)
In mathematical logic, a theory is a set of sentences in a formal language. Usually a deductive system is understood from context. An element \phi\in T of a theory T is then called an axiom of the theory, and any sentence that follows from the axioms is called a theorem of the theory. Every axiom...
generalizes the notions of algebraically closed field
Algebraically closed field
In mathematics, a field F is said to be algebraically closed if every polynomial with one variable of degree at least 1, with coefficients in F, has a root in F.-Examples:...
s (for the theory of field
Field (mathematics)
In abstract algebra, a field is a commutative ring whose nonzero elements form a group under multiplication. As such it is an algebraic structure with notions of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, satisfying certain axioms...
s), real closed field
Real closed field
In mathematics, a real closed field is a field F that has the same first-order properties as the field of real numbers. Some examples are the field of real numbers, the field of real algebraic numbers, and the field of hyperreal numbers.-Definitions:...
s (for the theory of ordered fields), existentially closed group
Divisible group
In mathematics, especially in the field of group theory, a divisible group is an abelian group in which every element can, in some sense, be divided by positive integers, or more accurately, every element is an nth multiple for each positive integer n...
s (for the class of groups), and dense linear orders without endpoints (for the class of linear orders).
Definition
A substructure M of a structureStructure (mathematical logic)
In universal algebra and in model theory, a structure consists of a set along with a collection of finitary operations and relations which are defined on it....
N is said to be existentially closed in (or existentially complete in)
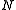 if for every quantifier-free formula φ(x,y1,…,yn) and all elements b1,…,bn of M such that φ(x,b1,…,bn) is realized in N, then φ(x,b1,…,bn) is also realized in M. In other words: If there is an element a in N such that φ(a,b1,…,bn) holds in N, then such an element also exists in M.
if for every quantifier-free formula φ(x,y1,…,yn) and all elements b1,…,bn of M such that φ(x,b1,…,bn) is realized in N, then φ(x,b1,…,bn) is also realized in M. In other words: If there is an element a in N such that φ(a,b1,…,bn) holds in N, then such an element also exists in M.A model M of a theory T is called existentially closed in T if it is existentially closed in every superstructure N which is itself a model of T. More generally, a structure M is called existentially closed in a class K of structures (in which it is contained as a member) if M is existentially closed in every superstructure N which is itself a member of K.
The existential closure in K of a member M of K, when it exists, is, up to isomorphism, the least existentially closed superstructure of M. More precisely, it is any extensionally closed superstructure M∗ of M such that for every existentially closed superstructure N of M, M∗ is isomorphic to a substructure of N via an isomorphism that is the identity on M.
Examples
Let σ = (+,×,0,1) be the signatureSignature (logic)
In logic, especially mathematical logic, a signature lists and describes the non-logical symbols of a formal language. In universal algebra, a signature lists the operations that characterize an algebraic structure. In model theory, signatures are used for both purposes.Signatures play the same...
of fields, i.e. +,× are binary relation symbols and 0,1 are constant symbols. Let K be the class of structures of signature σ which are fields.
If A is a subfield of B, then A is existentially closed in B if and only if every system of polynomial
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
s over A which has a solution in B also has a solution in A. It follows that the existentially closed members of K are exactly the algebraically closed fields.
Similarly in the class of ordered field
Ordered field
In mathematics, an ordered field is a field together with a total ordering of its elements that is compatible with the field operations. Historically, the axiomatization of an ordered field was abstracted gradually from the real numbers, by mathematicians including David Hilbert, Otto Hölder and...
s, the existentially closed structures are the real closed field
Real closed field
In mathematics, a real closed field is a field F that has the same first-order properties as the field of real numbers. Some examples are the field of real numbers, the field of real algebraic numbers, and the field of hyperreal numbers.-Definitions:...
s. In the class of totally ordered structures
Total order
In set theory, a total order, linear order, simple order, or ordering is a binary relation on some set X. The relation is transitive, antisymmetric, and total...
, the existentially closed structures are those that are dense
Dense order
In mathematics, a partial order ≤ on a set X is said to be dense if, for all x and y in X for which x In mathematics, a partial order ≤ on a set X is said to be dense if, for all x and y in X for which x...
without endpoints, while the existential closure of any countable (including empty) total order is, up to isomorphism, the countable dense total order without endpoints, namely the order type
Order type
In mathematics, especially in set theory, two ordered sets X,Y are said to have the same order type just when they are order isomorphic, that is, when there exists a bijection f: X → Y such that both f and its inverse are monotone...
of the rationals.

