
Equiareal
Encyclopedia
In differential geometry, an equiareal map is a smooth map from one surface
to another that preserves the area
of figures. If M and N are two surface
s in the Euclidean space
R3, then an equi-areal map ƒ can be characterized by any of the following equivalent conditions:
An example of an equiareal map, due to Archimedes of Syracuse, is the projection from the unit sphere to the unit cylinder outward from their common axis. An explicit formula is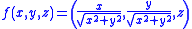
for (x,y,z) a point on the unit sphere.
In the context of geographic maps, a map projection
is called equiareal, or more commonly equi-area, if areas are preserved up to a constant factor; embedding the target map, usually considered a subset of R2, in the obvious way in R3, the requirement above then is weakened to:
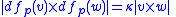
for some κ > 0 not depending on and
and 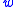 .
.
For examples of such projections, see Equal-area map projections. Linear equi-areal maps are 2 × 2 real matrices making up the group SL(2,R) of special linear transformations.
Surface
In mathematics, specifically in topology, a surface is a two-dimensional topological manifold. The most familiar examples are those that arise as the boundaries of solid objects in ordinary three-dimensional Euclidean space R3 — for example, the surface of a ball...
to another that preserves the area
Area
Area is a quantity that expresses the extent of a two-dimensional surface or shape in the plane. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat...
of figures. If M and N are two surface
Surface
In mathematics, specifically in topology, a surface is a two-dimensional topological manifold. The most familiar examples are those that arise as the boundaries of solid objects in ordinary three-dimensional Euclidean space R3 — for example, the surface of a ball...
s in the Euclidean space
Euclidean space
In mathematics, Euclidean space is the Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, as well as the generalizations of these notions to higher dimensions...
R3, then an equi-areal map ƒ can be characterized by any of the following equivalent conditions:
- The surface areaSurface areaSurface area is the measure of how much exposed area a solid object has, expressed in square units. Mathematical description of the surface area is considerably more involved than the definition of arc length of a curve. For polyhedra the surface area is the sum of the areas of its faces...
of ƒ(U) is equal to the area of U for every open setOpen setThe concept of an open set is fundamental to many areas of mathematics, especially point-set topology and metric topology. Intuitively speaking, a set U is open if any point x in U can be "moved" a small amount in any direction and still be in the set U...
U on M. - The pullback of the area elementVolume elementIn mathematics, a volume element provides a means for integrating a function with respect to volume in various coordinate systems such as spherical coordinates and cylindrical coordinates...
μN on N is equal to μM, the area element on M. - At each point p of M, and tangent vectorTangent vectorA tangent vector is a vector that is tangent to a curve or surface at a given point.Tangent vectors are described in the differential geometry of curves in the context of curves in Rn. More generally, tangent vectors are elements of a tangent space of a differentiable manifold....
s v and w to M at p,
-
- where × denotes the Euclidean cross productCross productIn mathematics, the cross product, vector product, or Gibbs vector product is a binary operation on two vectors in three-dimensional space. It results in a vector which is perpendicular to both of the vectors being multiplied and normal to the plane containing them...
of vectors and dƒ denotes the pushforward along ƒ.
An example of an equiareal map, due to Archimedes of Syracuse, is the projection from the unit sphere to the unit cylinder outward from their common axis. An explicit formula is
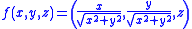
for (x,y,z) a point on the unit sphere.
In the context of geographic maps, a map projection
Map projection
A map projection is any method of representing the surface of a sphere or other three-dimensional body on a plane. Map projections are necessary for creating maps. All map projections distort the surface in some fashion...
is called equiareal, or more commonly equi-area, if areas are preserved up to a constant factor; embedding the target map, usually considered a subset of R2, in the obvious way in R3, the requirement above then is weakened to:
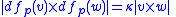
for some κ > 0 not depending on
 and
and  .
.For examples of such projections, see Equal-area map projections. Linear equi-areal maps are 2 × 2 real matrices making up the group SL(2,R) of special linear transformations.


