
Deamidation
Encyclopedia
Amide
In chemistry, an amide is an organic compound that contains the functional group consisting of a carbonyl group linked to a nitrogen atom . The term refers both to a class of compounds and a functional group within those compounds. The term amide also refers to deprotonated form of ammonia or an...
functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
is removed from an organic compound
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
. In biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
, the reaction is important in the degradation of protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s because it damages the amide-containing side chain
Side chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called "main chain" or backbone. The placeholder R is often used as a generic placeholder for alkyl group side chains in chemical structure diagrams. To indicate other non-carbon...
s of the amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s asparagine
Asparagine
Asparagine is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids on Earth. It has carboxamide as the side-chain's functional group. It is not an essential amino acid...
and glutamine
Glutamine
Glutamine is one of the 20 amino acids encoded by the standard genetic code. It is not recognized as an essential amino acid but may become conditionally essential in certain situations, including intensive athletic training or certain gastrointestinal disorders...
.
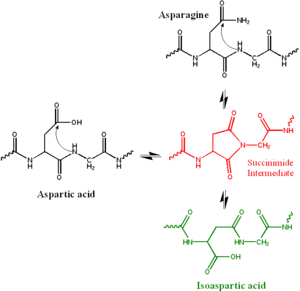
In the biochemical deamidation reaction, the side chain of an asparagine attacks the following peptide group (in black at top right of Figure), forming a symmetric succinimide
Succinimide
Succinimide is a cyclic imide with the formula C4H5NO2. It is used in a variety of organic syntheses, as well as in some industrial silver plating processes.-Succinimides:...
intermediate (in red). The symmetry of the intermediate results in two products of its hydrolysis, either aspartate (in black at left) or in isoaspartate
Isoaspartate
The isoaspartate group is a functional group in biochemistry. Its formation is a chemical reaction in which the side chain of an asparagine or aspartic acid residue attacks the following peptide group , forming a symmetric succinimide intermediate...
, which is a beta amino acid (in green at bottom right). This process is considered a deamidation because the amide in the asparagine side chain is replaced by a carboxylate group. However, a similar reaction can occur in aspartate side chains, yielding a partial conversion to isoaspartate.
Kinetics of deamidation
Deamidation reactions have been conjectured to be one of the factors that limit the useful lifetime of proteins.Deamidation proceeds much more quickly if the susceptible amino acid is followed by a small, flexible residue such as glycine
Glycine
Glycine is an organic compound with the formula NH2CH2COOH. Having a hydrogen substituent as its 'side chain', glycine is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG cf. the genetic code.Glycine is a colourless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid...
whose low steric hindrance leaves the peptide
Peptide bond
This article is about the peptide link found within biological molecules, such as proteins. A similar article for synthetic molecules is being created...
group open for attack. Deamidation reactions also proceed much more quickly at elevated pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
(>10) and temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
.
See also
- Peptide bondPeptide bondThis article is about the peptide link found within biological molecules, such as proteins. A similar article for synthetic molecules is being created...
- Post-translational modification

